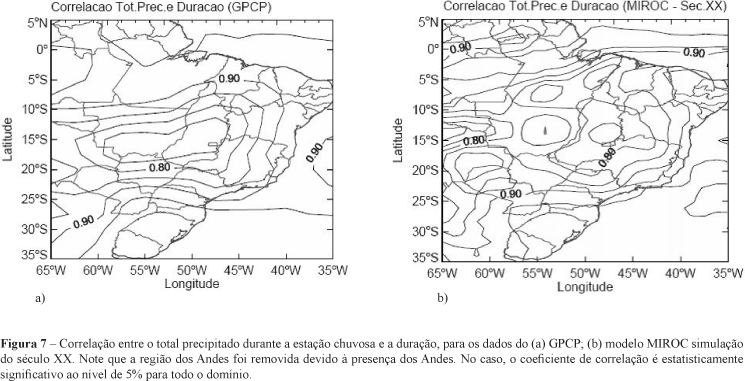
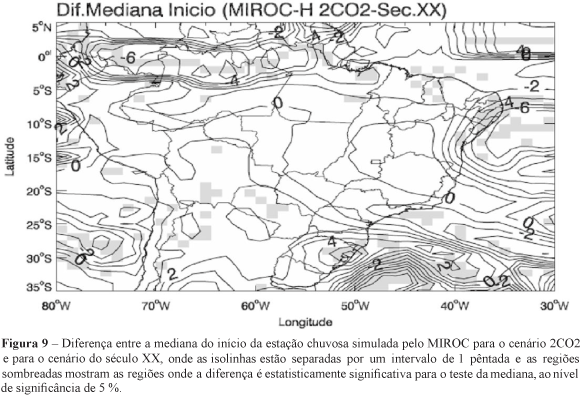
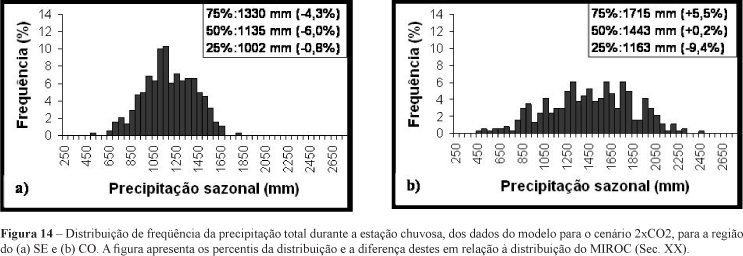
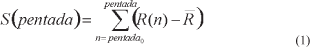This study investigates the temporal variability of the South America monsoon system (SAMS) over Brazil with focus on the Brazilian savanna. The onset, end, and total rainfall during the summer monsoon are investigated using precipitation pentad estimates from the Global Precipitation Climatology Project (1979-2004). Likewise, the variability of SAMS characteristics are investigated using the intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC) coupled global climate model for Interdisciplinary Research (MIROC) in the 20th century (1981-2000) and in a scenario with the double present concentration of CO2 (2xCO2) (2061-2080).. It is shown that the spatial variability of the onsets over central Brazil simulated by MIROC for the 20th century run corresponds very well to the observations. Moreover, there is indication of change in the tails of the seasonal precipitation distributions over the savanna for the scenario with 2xCO2, comparatively to the present climate. This suggests changes in the probability of extremes (dry or wet) events over that region in a scenario with 2xCO2, which indicates according to MIROC the large exposure of the region to possible consequences of climate changes resulting from increasing greenhouse gases.
Monsoon; Climate changes; Brazilian savanna; MIROC; 2xCO2; IPCC