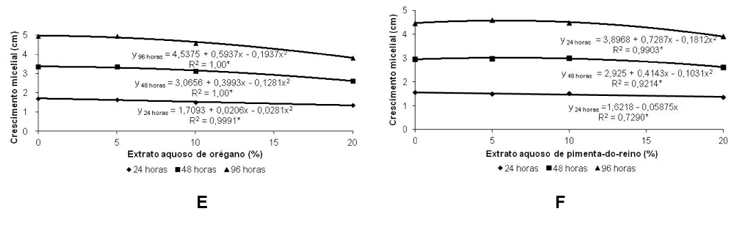
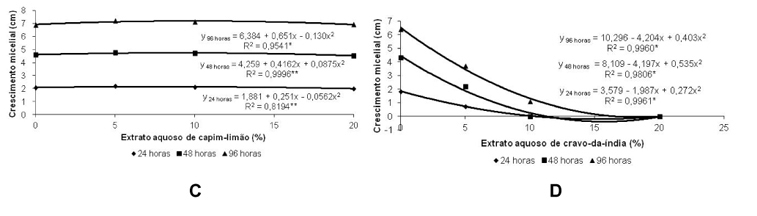
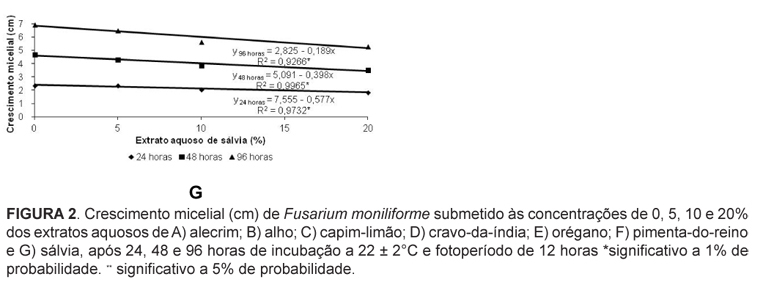
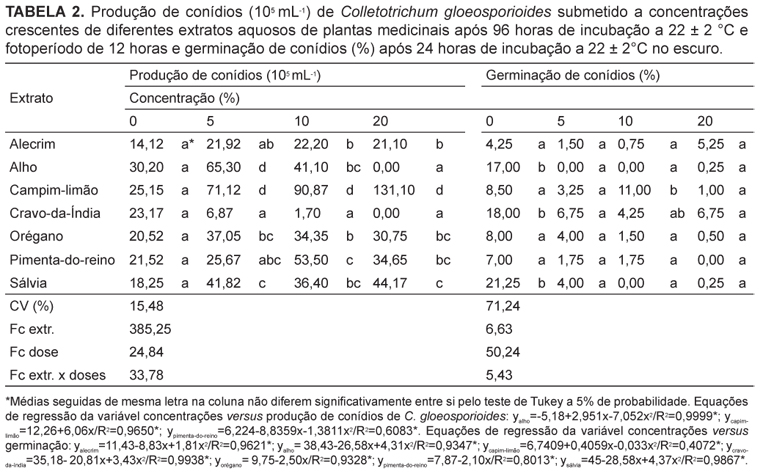
The objective of this study was to evaluate the influence of aqueous extracts of the medicinal plants rosemary, garlic, clove, sage, lemongrass, oregano and black pepper in the in vitro development of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Fusarium moniliforme. The extracts were obtained by infusing 60 g of each medicinal plant in 200 mL of boiling water. Each aqueous extract was fractionated in the concentrations of 0, 5, 10 and 20% (w:v) and incorporated into the PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium before sterilization by autoclaving. Later, an 8 mm diameter disc of each pathogen mycelium was transferred to the center of the Petri dishes. After 24, 48 and 96 hours of incubation in a growth chamber at 22 ± 2 ºC and a photoperiod of 12 hours, we evaluated the mycelial growth of F. moniliforme, and C. gloesporioides. In the last period of incubation, we quantified the production of conidia of each fungus. For the germination test, we added, into the wells of an ELISA test plates, a 40 µL aliquot of each extract at the concentrations of 0, 5, 10 and 20% and another aliquot of a suspension of conidia of each pathogen. After 24 hours at 22 ± 2 ºC in the dark, the germination of the fungi was stopped with the addition of 20 µL of lactophenol. Then, we evaluated the germination of conidia. The experiments followed a completely randomized 7 x 4 factorial design (medicinal plants x concentrations) with four replications. For both pathogens, the aqueous extract of garlic and clove showed a greater or total inhibition of the mycelial growth, when compared to the other extracts. For the C. gloeosporioides, the clove extract showed a lower number of conidia at all concentrations tested, and the garlic extract at 20% showed not conidial germination. The garlic extract was efficient to reduce the conidial number and germination of F. moniliforme at 20%. Extracts of rosemary, clove, oregano and black pepper, in the highest concentrations, had positive effect in reducing the production of spores of the same fungus.
alternative control; pathogenic fungi; organic agriculture