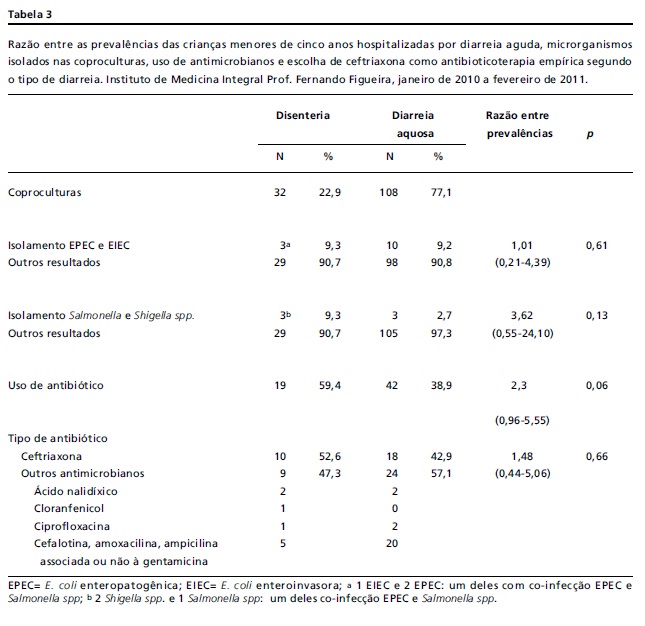
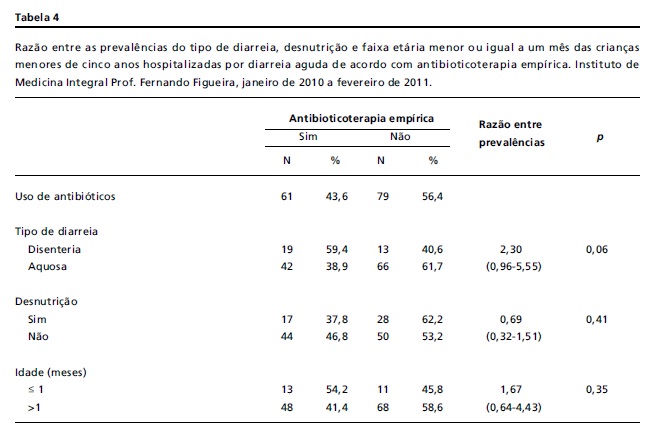
OBJECTIVES: to determine the frequency of diarrheic Escherichia coli and its sensitivity to antimicrobials in children aged under five years admitted to hospital for treatment of acute diarrhea. METHODS: a prospective cross-sectional study was carried out at the Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira, between January 2010 and February 2011. Children were excluded if they had been diagnosed as immunodeficient or were using antimicrobials. A single rectal swab was taken from each patient during the first 24 hours of hospitalization. The pathogens were identified in the coproculture and serotyping. Antibiograms were obtained using disc-diffusion. RESULTS: 140 children were recruited. Most were from low-income families in the Metropolitan Region of Recife. Ninety-nine micro-organisms were isolated: 9 (6.4%) enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and 4 (2.9%) enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) and 80 (57.1%) other E.coli that are neither EPEC nor EIEC, 3 (2.1%) Shigella spp and 3 (2.1%) Salmonella spp. The profile of sensitivity to antimicrobials showed high levels to resistance to ampicillin and sulfametho-xazol-trimetropime. CONCLUSIONS: the low frequency of EPEC found may be associated with basic sanitary conditions among the patients in the study. The local analysis of the profile of sensitivity of E. coli to antimicrobials corroborates the World Health Organization recommendation that these drugs be used prudently to ensure prevention of resistance in bacteria.
Diarrhea; infantile; Child; Escherichia coli; Drug resistance; bacterial