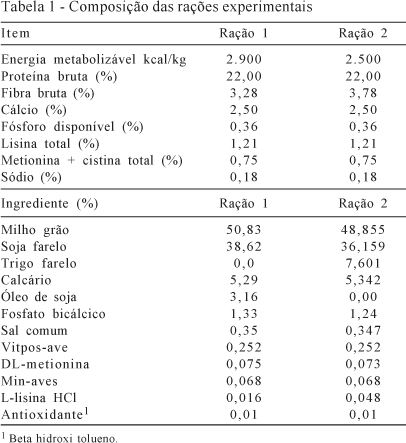
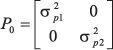Data of egg weight, albumen height, shell thickness, body weight and egg production at 90 days of laying from three lines of laying quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica), fed diets with 2,900 kcal or 2,500 kcal metabolizable energy, were used to check the existence of the genotype-environmental interaction. The MTGSAM software program was used, which allows Bayesian inference, using the Gibbs Sampling, applied to an animal model, to estimate the co-variance components, heritability and genetic correlation between both environments. The results of heritability and genetic correlations showed that there was a genotype-environment interaction only for albumen height and shell thickness. The traits egg weight and body weight are susceptible to genetic gains regardless of the diet energy level, while egg production has low potential for genetic gains if the selection is based on partial records.
albumen height; body weight; egg production; egg weight; heritability; shell thickness