ABSTRACT
Objectives: To identify the main reasons for performing point-of-care bladder ultrasonography (POCUS) by nurses and to compare the volume found on POCUS with the volume of urine drained by a relief bladder catheter (RBC) or delay bladder catheter (DBC).
Method: A cross-sectional study was conducted in intensive care, semi-intensive care, and medical-surgical units with patients over 18 years of age who had no spontaneous urination for more than six hours or for more than four hours after removal of the DBC.
Results: A total of 211 patients were included, with the main reasons for performing POCUS being absence of urination after surgical procedures (35.0%), removal of the DBC (35.1%), decreased level of consciousness (DLC) (13.7%), and DBC obstruction (0.9%). The correlation between POCUS volume and urine volume drained was considered very strong.
Conclusion: Situations such as postoperative, removal of DBC, DLC, and DBC obstruction lead to the performance of POCUS by nurses, with a very strong correlation between the volumes found in POCUS and those drained by RBC or DBC.
DESCRIPTORS
Nursing; Ultrasonography; Urinary Retention; Urinary Bladder; Advanced Practice Nursing

 Assessment of bladder volume by nurses using point-of-care ultrasound: a cross-sectional study
Assessment of bladder volume by nurses using point-of-care ultrasound: a cross-sectional study Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 POCUS: point of care ultrassonography, RBC cateter vesical de alívio, DBC: cateter vesical de demora, ml: mililitros.
POCUS: point of care ultrassonography, RBC cateter vesical de alívio, DBC: cateter vesical de demora, ml: mililitros.
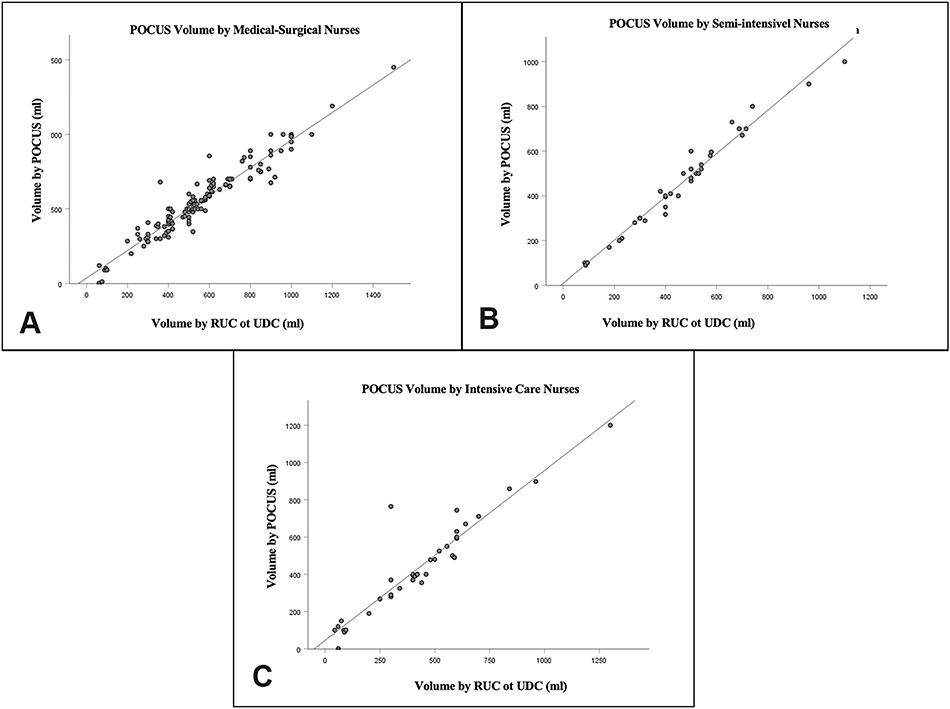 POCUS: point of care ultrasonography, RBC relief bladder catheter, DBC: Delay bladder catheter, ml: milliliters.
POCUS: point of care ultrasonography, RBC relief bladder catheter, DBC: Delay bladder catheter, ml: milliliters.