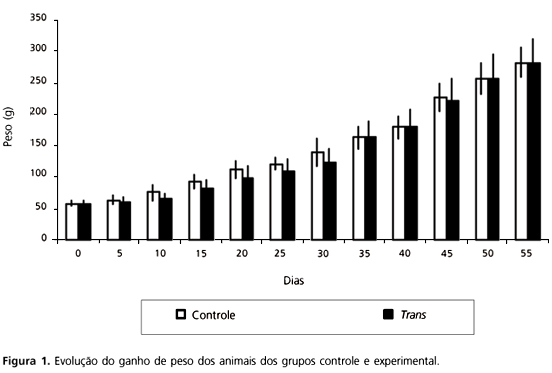
The lipid composition of the diet can influence the profile of fatty acids the tissues. The objective of this study was to evaluate the incorporation of trans fatty acids in the liver and in the heart of rats. Two groups with twelve weanling Wistar rats each were fed two different diets for eight weeks. One of the diets (experimental) was rich in trans fatty acids (33.0% of total lipids) and presented minimal amounts of linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids (8.0% and 0.7%, respectively, of total lipids), while the other (control) was nutritionally adequate. The profile of fatty acids of the diets and tissues was evaluated by gas chromatography. There was an incorporation of 14.0% of the trans fatty acids in the liver and 8.6% in the heart. There was no inhibitory effect of the trans fatty acids on the formation of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids in the liver. However, a significant decrease in the docosahexaenoic acid concentration was observed in the heart. It was probably a consequence of the deficiency of a-linolenic acid and of the incorporation of trans fatty acids.
trans fatty acids; hydrogenated vegetable fat; essential fatty acids; long-chain; polyunsaturated fatty acids; rats; diet