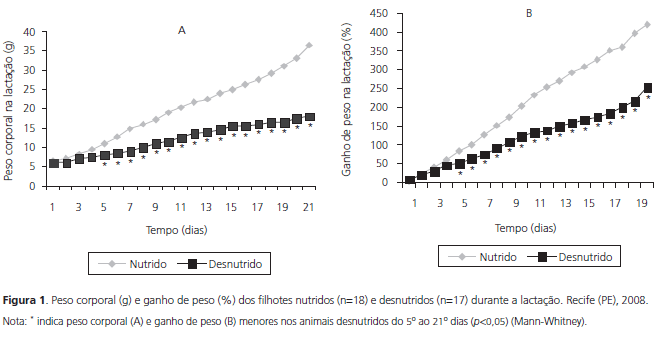
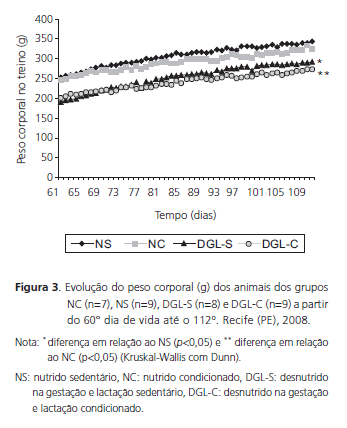
OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study was to assess the effects of moderate aerobic physical conditioning on the body weight and weight gain of rats whose mothers were fed a low protein diet during gestation and lactation. METHODS: Male Wistar rats were bred from dams fed a normal- (17% casein) or low-protein (8% casein) diet, constituting the initial nourished (n=18) and malnourished (n=17) groups. After weaning, they were fed the standard diet of the laboratory, with normal protein content (Labina®, Purina). At the age of 60 days, the animals were divided into four groups: inactive and well nourished (n=9), active and well nourished (n=7), inactive and malnourished from conception until weaning (n=8) and active and malnourished from conception until weaning (n=9). Moderate aerobic physical conditioning was done on a treadmill for 8 weeks, 5 days per week, 60 minutes per day. All animals were killed after this training period. Body weight (g) and weight gain (%) were analyzed. RESULTS: Lower body weights were seen in animals that were inactive and malnourished from conception until weaning (247.00: 134.00 - 335.00) and active and malnourished from conception until weaning (245.00: 166.00 - 324.50) when compared with the animals that were inactive and well nourished (303.75: 176.00 - 372.00) and active and well nourished (290.25: 190.00 - 372.00) (p<0.05). Weight gain was higher in the animals from the inactive and malnourished group (35.40: -6.20 - 77.10) in comparison with the inactive and well nourished group (24.30: -7.50 - 44.30) (p<0.05) and the active and malnourished group (20.50: 2.30 - 59.00) (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: Moderate aerobic physical conditioning had a beneficial effect on the animals that were malnourished during their mothers' gestation and lactation as it reduced their rapid weight gain.
Proteic malnutrition; Weight gain; Moderate aerobic physical conditioning; Pregnancy; Lactation