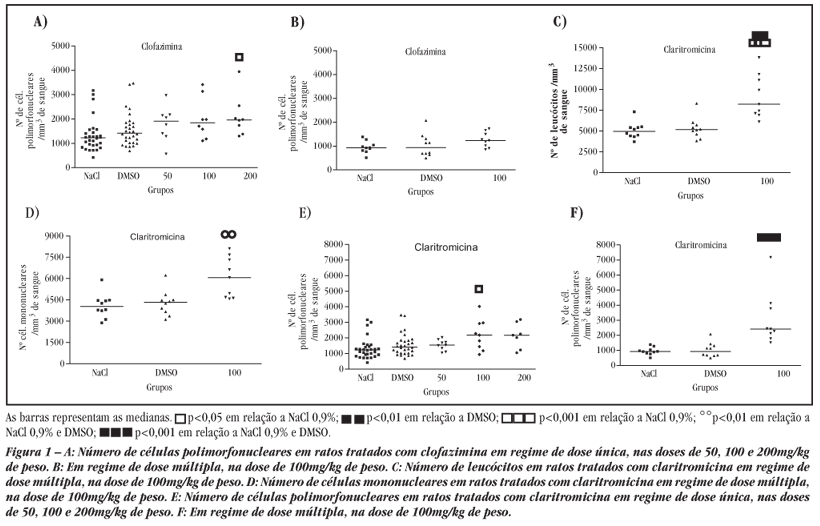
Clarithromycin and clofazimine have been used to treat leprosy, tuberculosis and infections caused by the Mycobacterium avium complex. Since there is a scarcity of data on the toxicity of therapeutic regimens that include these drugs, this study had the aim of determining the adverse effects of these therapies, through evaluation of hematological, hemostatic and biochemical parameters. The drugs were administered to male Wistar rats, as monotherapy, in regimens of single and multiple doses. Clarithromycin caused increases in the numbers of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Both of the drugs inverted the proportions between mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cells and increased the numbers of polymorphonuclear cells and degenerating cells. Clofazimine and clarithromycin prolonged the prothrombin time and clarithromycin also prolonged the activated partial thromboplastin time. Clarithromycin caused increases in total and direct bilirubin. Both of the drugs increased the plasma levels of gamma-glutamyltransferase. Therefore, clofazimine and clarithromycin induce hematological, hemostatic and hepatic changes.
Hematological changes; Clofazimine; Clarithromycin; Mycobacterium avium