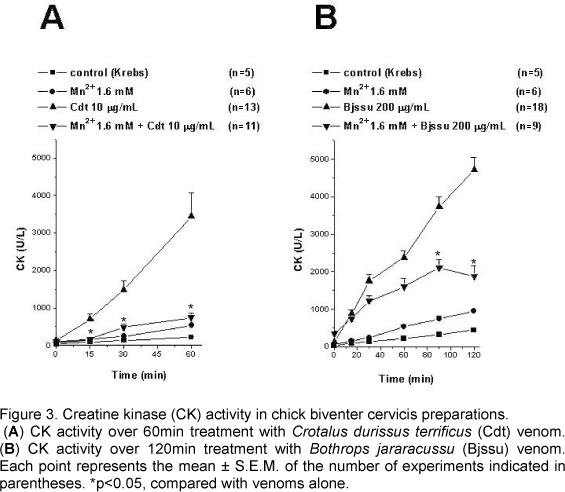
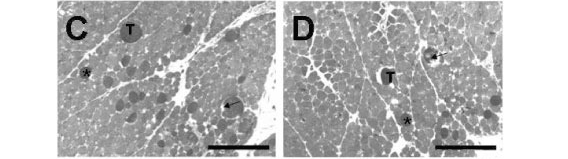
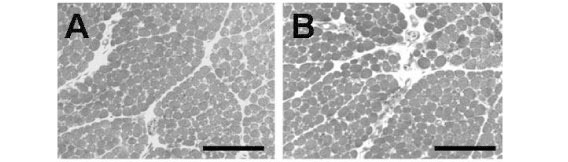
In the present study, manganese (Mn2+), a neuromuscular blocker with pre and postsynaptic actions, was used to verify the neurotoxicity and myotoxicity induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus (Cdt) and Bothrops jararacussu (Bjssu) venoms in biventer cervicis preparations (BCp). Preparations pretreated with 0.66 and 1.6mM Mn2+ did not affect Cdt venom-induced blockage nor change KCl-induced contracture but partially reduced ACh-induced contracture. However, both Mn2+ concentrations partially hindered Bjssu venom-induced blockage after washing the preparations with Krebs solution, and only 1.6mM Mn2+ preparations significantly recovered ACh-induced contracture. The effect of Cdt venom myotoxicity on contractile responses was different from that of Bjssu venom myotoxicity. Pretreatment with 1.6mM Mn2+ partially reduced muscle damage percentage and creatine kinase (CK) activity (U/l) induced by both venoms. In conclusion, Mn2+ interfered in ACh-induced contracture of the nicotinic receptor; did not prevent Cdt venom neurotoxicity but partially reduced its myotoxicity in vitro due to the stabilizing action of this venom on the sarcolemmal membrane; and partially attenuated myotoxicity and neuromuscular blockage induced by Bjssu venom. The Mn2+ dual action (pre and postsynaptic) is useful to study snake venoms since most of them present one or both of these actions; besides, Mn2+ allowed recovering coherent interpretation of experimental versus clinical results.
contracture; divalent cation; Mn2+; myotoxicity; neuromuscular blockage; neurotoxicity