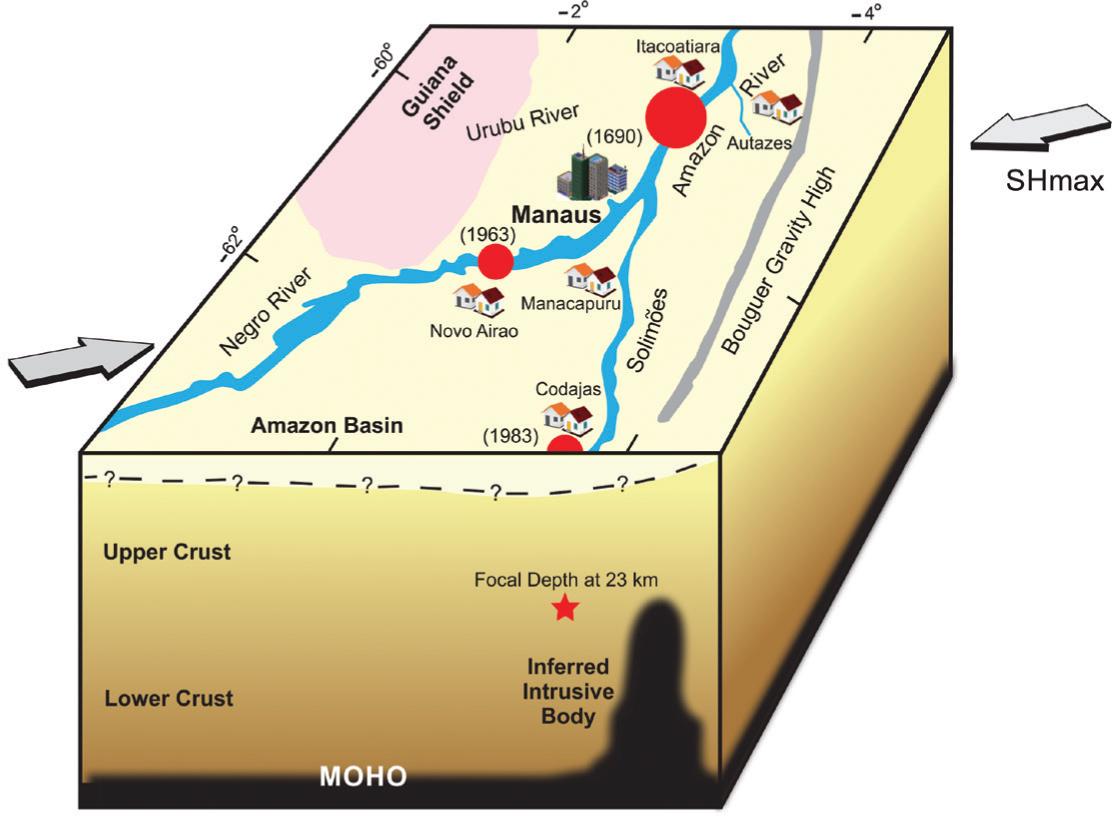
Combining historical accounts and seismological studies, three hundred years of dormant information emerged as a source of the largest known seismic event that rocked Brazil since the beginning of our colonization. The probable epicenter location of the 1690 tremor lies on the left bank of the Amazon River, about 45 km downstream from the modern day Manaus. A year later, while passing this area, a missionary met witnesses of the tremor and observed remarkable changes in the topography and vegetation along the margin of the river. By 1692 another priest confirmed this event and the occurrence of large waves in the river, which led to the flooding of the Native Indians' terrains. The tremor spread seismic waves throughout the forest and shook indigenous constructions as far as one thousand kilometers away. A calculation of the seismic parameters shows an estimated magnitude of 7, a maximum intensity of IX MM and a felt area of about 2 million km2. Due to the long recurrence period for this type of tremor, the discovery of one of these events is valuable for seismic global intraplate studies. As for Brazil, it unravels the myth that the country was never hit by severe earthquakes.
Amazon earthquake; historical tremor; intraplate seismicity; seismic intensity