Abstract:
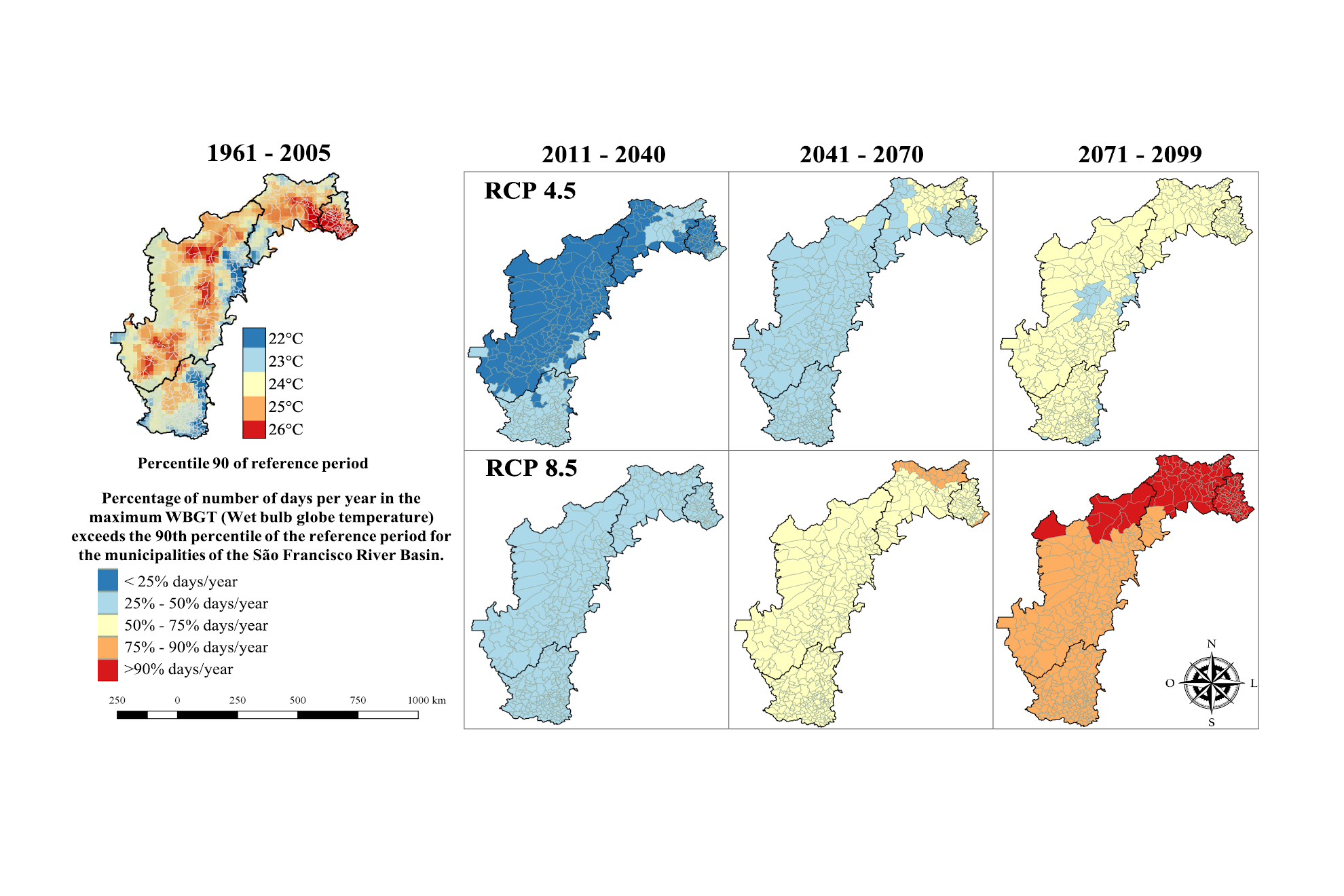
Objective: the aim of this study is to map thermal stress risks for human health at the São Francisco River Basin (SFRB) in the Semiarid region, for climatic scenarios RCP 4.5 and 8.5. Methods: The heat stress conditions were defined by the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) indicator and by the average number of annual days in which the WBGT values exceeded the 90th percentile of the reference period. The WBGT was estimated for the climate scenarios RCP 4.5 (intermediate) and 8.5 (pessimistic) for the period 2011-2090 comparing to the period of reference (1961-2005). Results: The projections show that for the pessimistic scenario practically all municipalities of the SFRB region can reach values of WBGT that indicate a high risk for heat stress in the period 2071-2099. For this same scenario and period, the municipalities of the Lower and Under-average regions may present values of WBGT above the 90th percentile of the reference period in more than 90% of the days/year. Conclusions: These results show that, if the emission of greenhouse gases continues in the present proportions, some municipalities of the SFRB region may present a high risk for heat stress affecting the work capacity and the practice of physical exercises.
Key words
Climate change; heat stress; health impacts; Wet Bulb Globe Temperature

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail