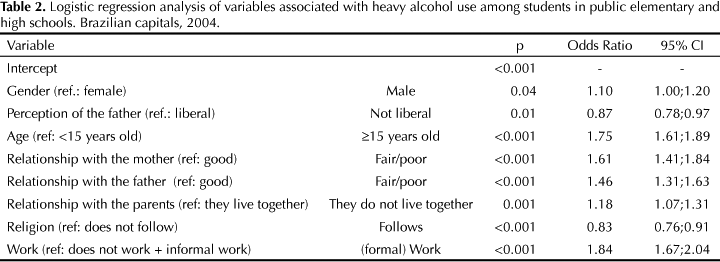
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the association between heavy use of alcohol among students and family, personal and social factors. METHODS: Cross-sectional study including public school students aged ten to 18 from 27 Brazilian capital cities in 2004. Data was collected using an anonymous, self-report questionnaire that was adapted from a World Health Organization instrument. A representative sample comprising 48,155 students was stratified by census tracts and clusters (schools). The associations between heavy alcohol use and the factors studied were analyzed using logistic regression at a 5% significance level. RESULTS: Of all students, 4,286 (8.9%) reported heavy alcohol use in the month prior to the interview. The logistic regression analysis showed an association between fair or poor relationship with the father (OR = 1.46) and the mother (OR = 1.61) and heavy use of alcohol. Following a religion (OR = 0.83) was inversely associated with heavy alcohol consumption. Sports practice and mother perceived as a "liberal" person had no significance in the model. However, a higher prevalence of heavy use of alcohol was seen among working students. CONCLUSIONS: Stronger family ties and religion may help preventing alcohol abuse among students.
Students; Alcohol Drinking; Family Characteristics; Socioeconomic Factors; Cross-Sectional Studies