BACKGROUND
Biomphalaria glabrata is the major species used for the study of schistosomiasis-related parasite-host relationships, and understanding its gene regulation may aid in this endeavor. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) performs post-translational regulation in order to maintain cellular protein homeostasis and is related to several mechanisms, including immune responses.
OBJECTIVE
The aims of this work were to identify and characterise the putative genes and proteins involved in UPS using bioinformatic tools and also their expression on different tissues of B. glabrata.
METHODS
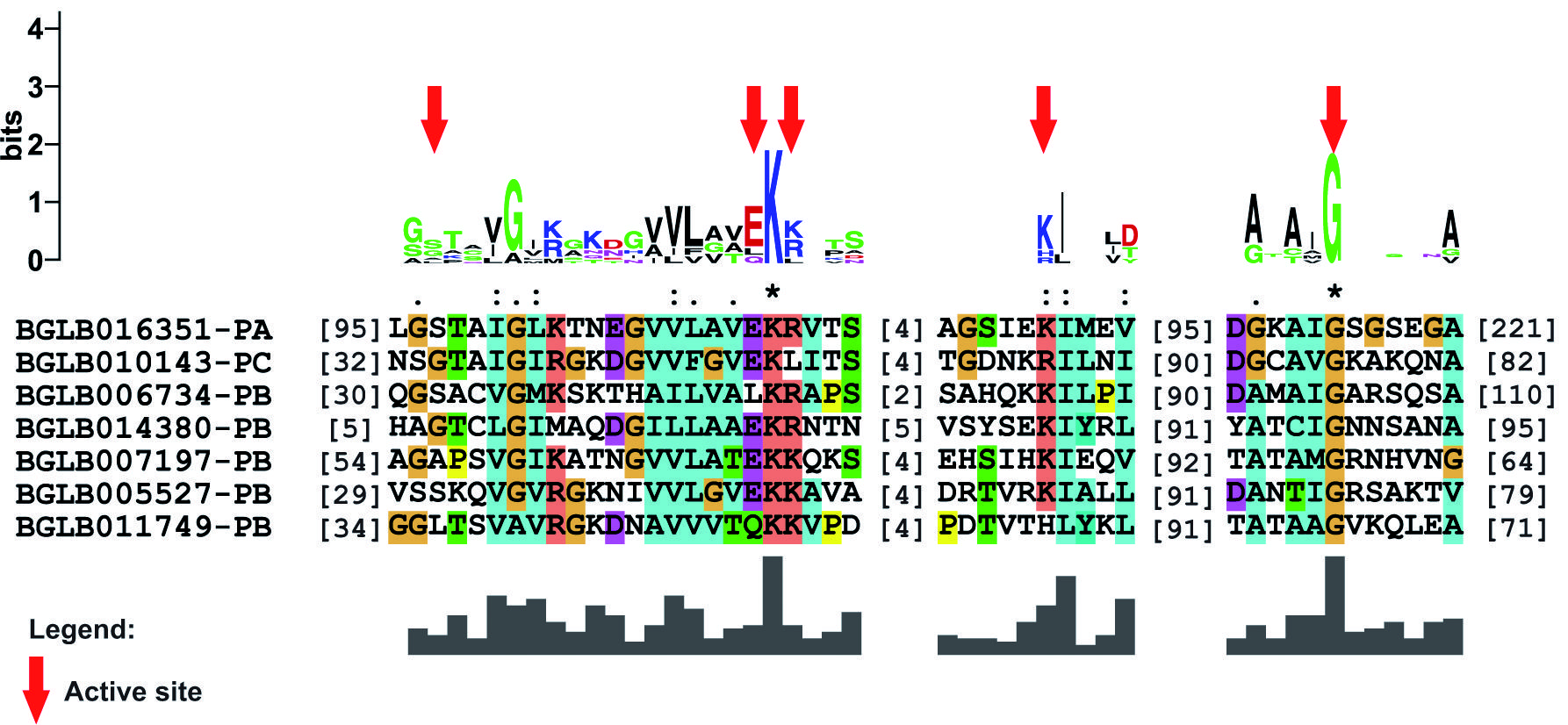
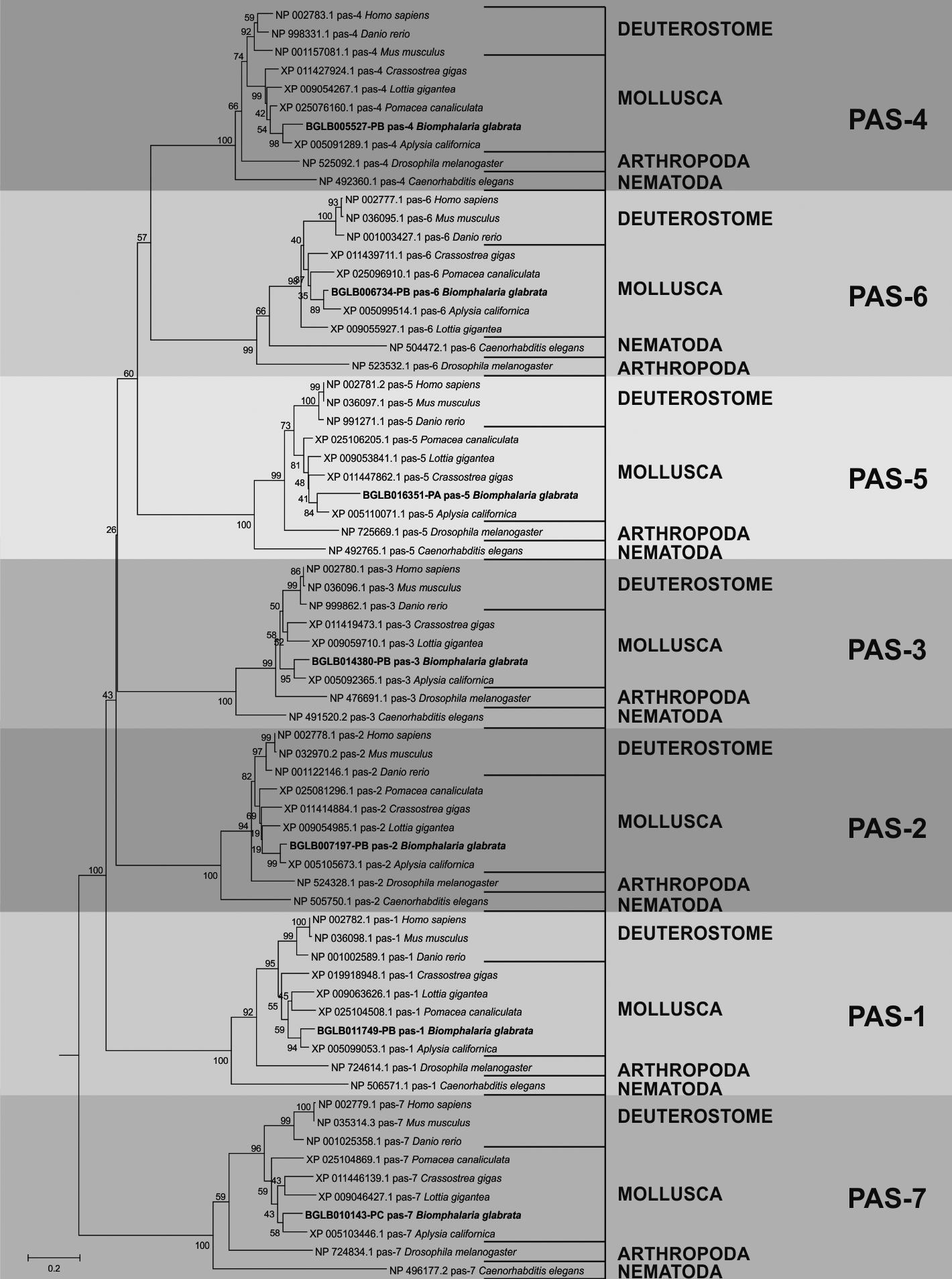
The putative genes and proteins of UPS in B. glabrata were predicted using BLASTp and as queries reference proteins from model organism. We characterised these putative proteins using PFAM and CDD software describing the conserved domains and active sites. The phylogenetic analysis was performed using ClustalX2 and MEGA5.2. Expression evaluation was performed from 12 snail tissues using RPKM.
FINDINGS
119 sequences involved in the UPS in B. glabrata were identified, which 86 have been related to the ubiquitination pathway and 33 to proteasome. In addition, the conserved domains found were associated with the ubiquitin family, UQ_con, HECT, U-box and proteasome. The main active sites were lysine and cysteine residues. Lysines are responsible and the starting point for the formation of polyubiquitin chains, while the cysteine residues of the enzymes are responsible for binding to ubiquitin. The phylogenetic analysis showed an organised distribution between the organisms and the clades of the sequences, corresponding to the tree of life of the animals, for all groups of sequences analysed. The ubiquitin sequence was the only one with a high expression profile found in all libraries, inferring its wide range of performance.
MAIN CONCLUSIONS
Our results show the presence, conservation and expression profile of the UPS in this mollusk, providing a basis and new knowledge for other studies involving this system. Due to the importance of the UPS and B. glabrata, this work may influence the search for new methodologies for the control of schistosomiasis.
Key words:
snail; UPS; signaling pathway; bioinformatics; schistosomiasis

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail