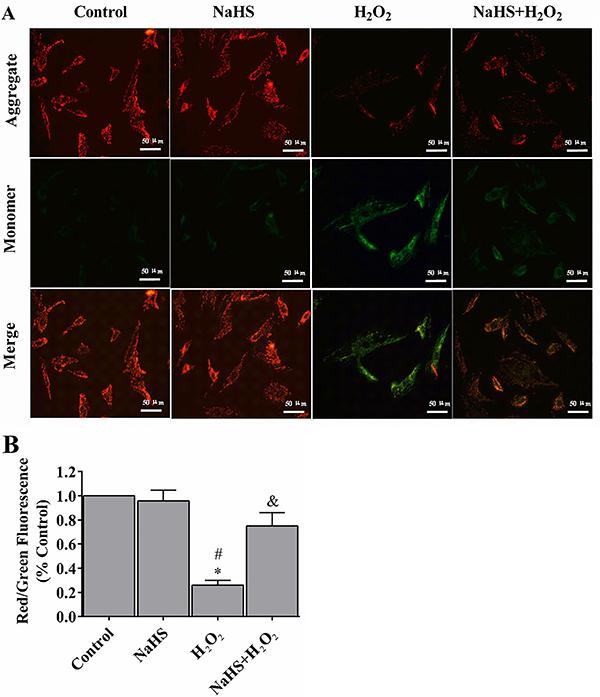
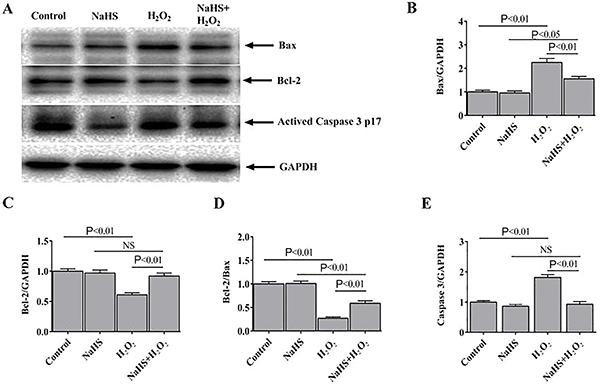
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemical species that may cause irreversible tissue damage, and play a critical role in cardiovascular diseases. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gasotransmitter that acts as a ROS scavenger with cardio-protective effects. In this study, we investigated the cytoprotective effect of H2S against H2O2-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts were treated with H2S (100 μM) 24 h before challenging with H2O2 (100 μM). Apoptosis was then assessed by annexin V and PI, and mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using a fluorescent probe, JC-1. Our results revealed that H2S improved cell viability, reduced the apoptotic rate, and preserved mitochondrial membrane potential. An increased Bcl-2 to Bax ratio was also seen in myocytes treated with H2S after H2O2-induced stress. Our findings indicated a therapeutic potential for H2S in preventing myocyte death following ischemia/reperfusion.
Reactive oxygen species; ROS; Hydrogen sulfide; H2O2-induced apoptosis; Cardiomyocytes