Abstract
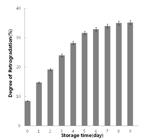
The aggregation of water molecules inside heat-gelatinized rice grain due to retrogradation of the grain was investigated by textural change and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis of cooked grains after storage at 11 °C in a sealed package. Relaxation tests using a disc-type tip showed an increase in hardness (strength) of the cooked grain as the degree of retrogradation increased with increasing storage time, measured by the α-amylase–iodine method. SEM analysis of the vacuum-dried cooked rice grain showed a gradual increase in crevices, which further developed into holes at the center of the granule with increasing storage time. The results suggest that the disruption of hydrogen bonds between water and starch molecules is the first step for the retrogradation of gelatinized rice grain stored in a hermetic environment to avoid drying, resulting in its increased hardness, followed by the aggregation of starch molecules with subsequent water extrusion.
Keywords:
rice grain; starch; gelatinization; retrogradation; texture; structure

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail


