Abstract
Background
Current evidence suggests that upregulation of polyamines system plays a role both in cognitive deficit and synaptic loss observed in Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine the plasmatic concentration of polyamines in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD patients in comparison with healthy controls (HC).
Methods
Plasmatic polyamines were quantified using the AbsoluteIDQ® p180 and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS-MS).
Results
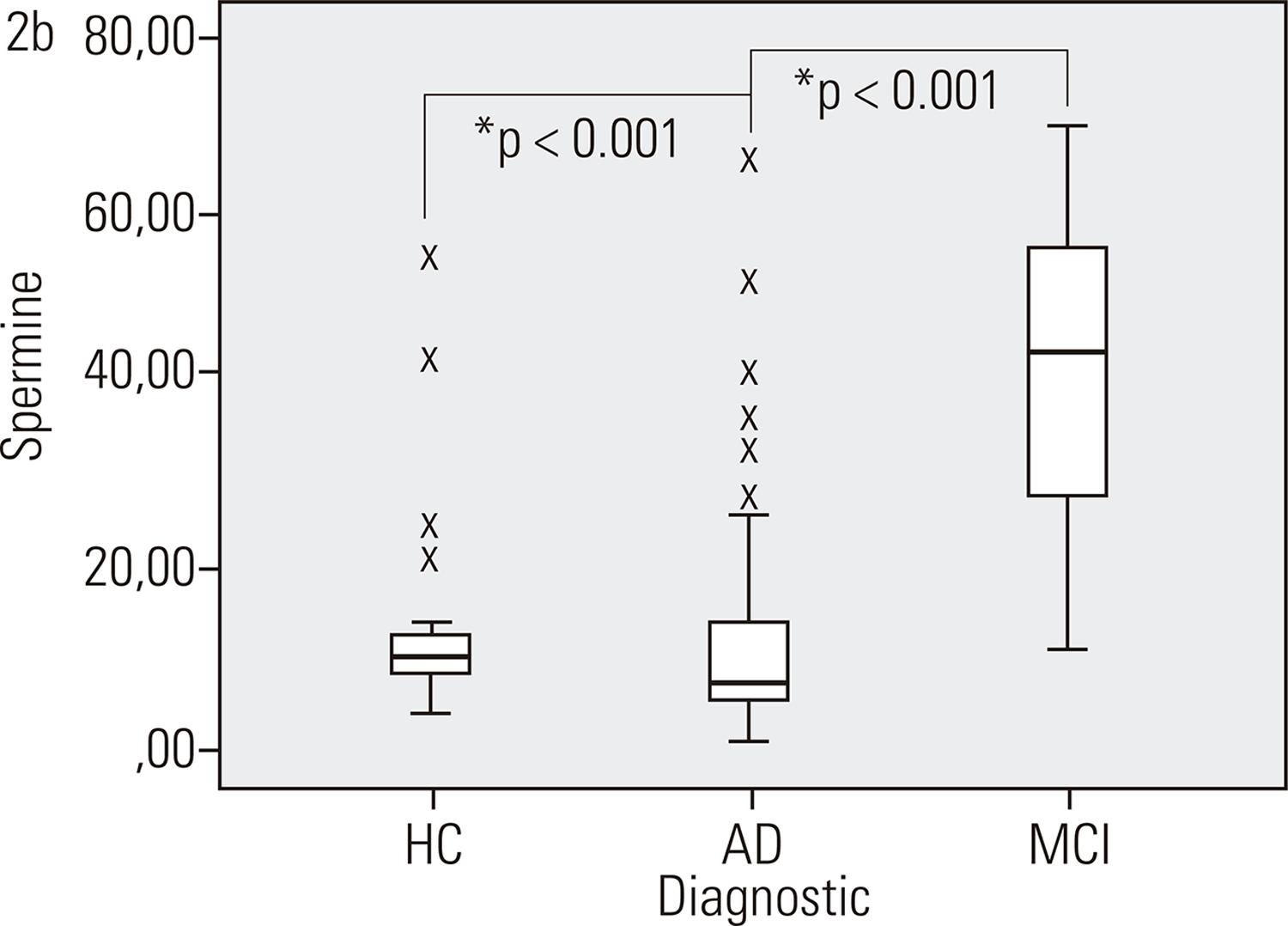
The study group comprised 34 AD patients, 20 MCI and 25 HC. All individuals were followed for 4 years. During this period 8 amnestic MCI patients (40% of the MCI sample at baseline) converted to AD. Spermidine level was lower in both patient groups (AD; MCI) compared to HC (p = 0.007). Plasma levels of spermine were higher in the MCI group (p < 0.001), but decreased in the sub-sample of MCI patients who converted to AD (p = 0.043). No statistically significant differences were found in ornithine and putrescine levels (p = 0.056 and p = 0.126, respectively).
Discussion
Our results suggest dynamic changes in the expression of polyamines in the MCI-AD continuum.
Biomarkers; Alzheimer’s disease; mild cognitive impairment; polyamines; plasma