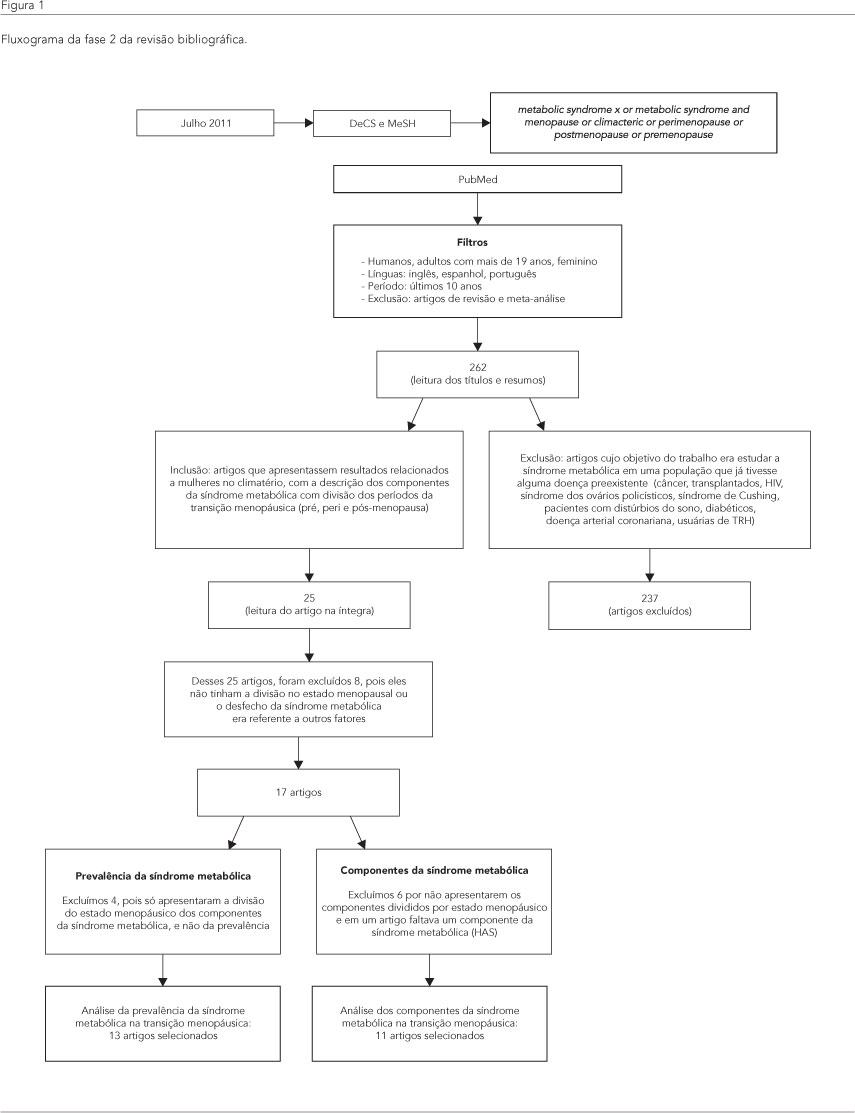
A síndrome metabólica é um transtorno complexo, caracterizado por um agrupamento de fatores de risco cardiovascular. Sugere-se que a fase da transição menopáusica possa ser um determinante importante no aumento da prevalência da síndrome metabólica. O presente estudo teve como objetivo verificar, por meio de uma revisão sistemática, a prevalência de síndrome metabólica e dos seus componentes na transição menopáusica. Três revisores fizeram a busca dos artigos na base de dados do PubMed. A qualidade dos artigos foi avaliada usando-se o Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE). Com base nos estudos analisados, a prevalência de síndrome metabólica aumenta na comparação do período da pré para a pós-menopausa, independentemente da população e do delineamento do estudo. Quanto aos componentes, a alteração foi mais expressiva nas medidas de circunferência da cintura e pressão arterial. Sugere-se que esses componentes sejam os que exercem maior influência na prevalência de síndrome metabólica.
Síndrome X Metabólica; Menopausa; Pós-menopausa; Perimenopausa; Pré-menopausa