Abstract:
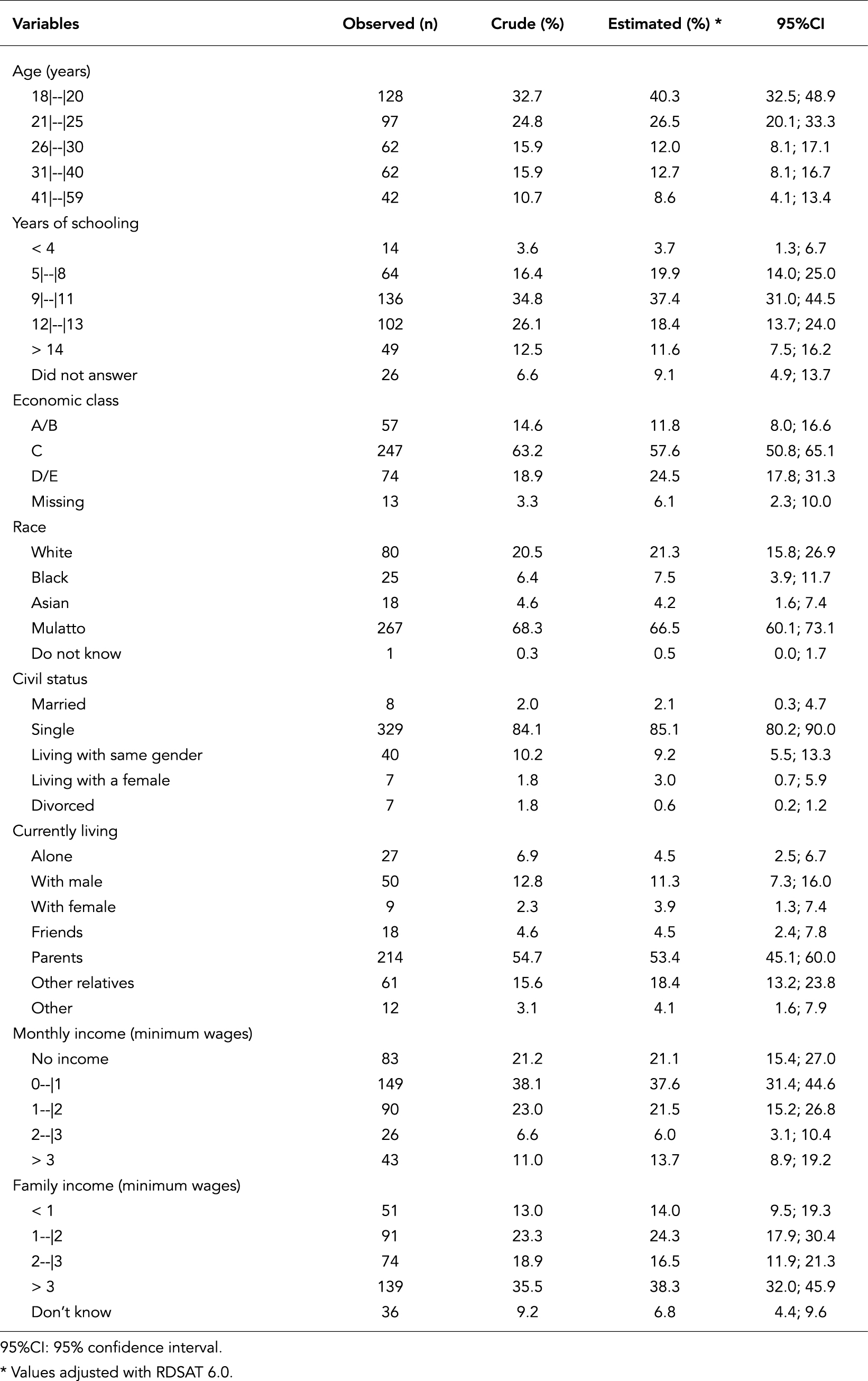
This study aimed to identify incentives and barriers to HIV testing in men who have sex with men (MSM). This was a cross-sectional study of MSM who had lived at least three months in greater metropolitan Fortaleza, Ceará State, Brazil, 2010. The study recruited 391 men ≥ 18 years of age who reported sexual relations with men in the previous six months, using Respondent Driven Sampling. Personal network and socio-demographic data were collected and HIV testing was offered, analyzed with RDSAT 6.0 and Stata 11.0. The majority were young (40.3%), had 5 to 11 years of schooling (57.3%), were single (85.1%), had low income (37.6%), and 58.1% had tested for HIV some time in life. Incentive to test: certainty of not being infected (34.1%) and the exposure to national campaign Fique Sabendo [Know your Status] (34%). Barriers: trust in partner(s) (21%) and fear of discrimination if tested positive (20.3%). Policies should be developed to ensure test confidentiality and communication campaigns focusing on information gaps and encouragement for testing.
Keywords:
HIV; Anonymous Testing; Male Homosexuality; Sexual Behavior

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail