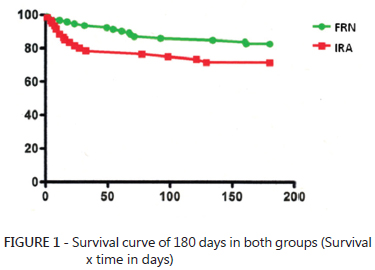
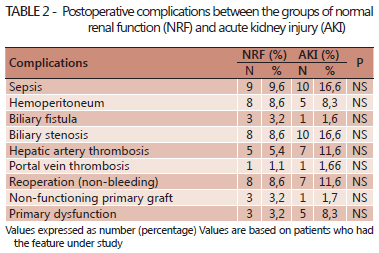
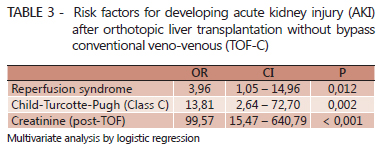
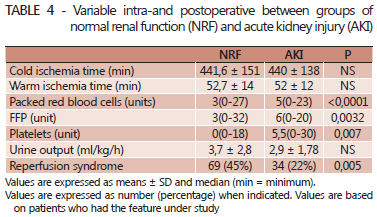
BACKGROUND: Acute kidney injury is one of the most common complications of orthotopic liver transplantation. The absence of universal criteria for definition of these conditions make comparisons difficult between studies. The conventional technique for transplantation is the total excision of the inferior vena cava during liver retro-native hepatectomy. Controversies about the effect of the conventional technique without venovenous bypass on renal function remain. AIM: To estimate the incidence and risk of acute kidney injury factors among recipients of orthotopic liver transplantation without conventional venovenous bypass. METHODS: Was studied 375 patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Variables were analyzed in preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative complications in 153 patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation without conventional venovenous bypass. The criterion for acute kidney injury was serum creatinine > 1.5 mg/dl or urinary debit <500 ml/24h within the first three days post-transplant. Univariate analysis and multivariate logistic regression were done. RESULTS: All transplants were performed with grafts from deceased donors. Sixty patients (39.2%) had acute kidney injury. Age, body mass index, Child-Turcotte-Pugh, urea, hypertension, and preoperative serum creatinine were higher in the acute kidney injury group. During the intraoperative period, the group acute kidney injury had more reperfusion syndrome, transfusion of red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma and platelets. Postoperatively, the duration of mechanical ventilation and postoperative creatinine levels were also variable, with significant differences for the group of acute kidney injury. After logistic regression, the reperfusion syndrome, the class C of the Child-Turcotte-Pugh and postoperative serum creatinine showed differences. CONCLUSION: Acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation without conventional venovenous bypass is a common disorder, but with good prognosis. Reperfusion syndrome, serum creatinine postoperatively and Child C are factors associated with acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation without conventional venovenous bypass.
Kidney failure; Acute renal; Failure, liver transplantation; Venovenous deviation