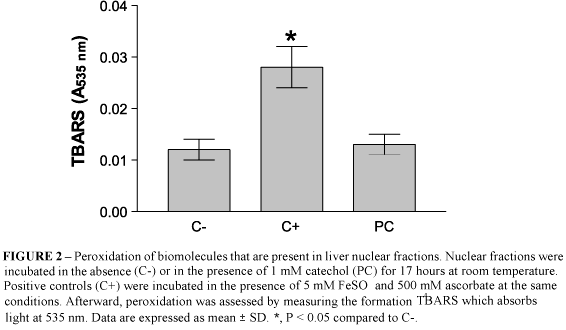
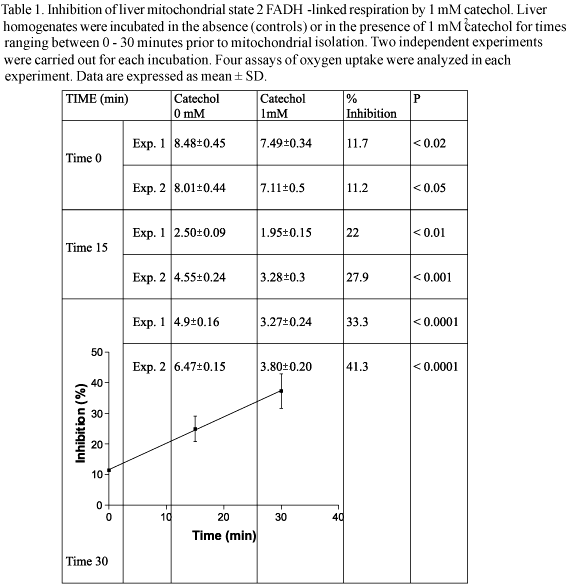
PURPOSE: The aim of this work was to investigate the hypothesis that catechol inhibits FADH2-linked basal respiration in mitochondria isolated from rat liver homogenates. Moreover, catechol ability to induce peroxidation of biomolecules in liver nuclear fractions was also studied. METHODS: Rat liver homogenates were incubated with 1mM 1,2-dihydroxybenzene (catechol) at pH 7.4 for up to 30 minutes. After that, mitochondrial fractions were isolated by differential centrifugation. Basal oxygen uptake was measured using a Clark-type electrode after the addition of 10 mM sodium succinate. Nuclear fractions were incubated in the presence of 1 mM catechol for 17 hours at room temperature and the peroxidation of biomolecules was investigated by the reaction with thiobarbituric acid, which was determined spectrophotometrically at 535 nm. RESULTS: Catechol induced a time-dependent partial inhibition of FADH2-linked basal mitochondrial respiration, however this substance was unable to induce a direct peroxidation of biomolecules in hepatic nuclear fractions. CONCLUSION: Catechol produced an inhibition of basal respiration associated to FADH2 in isolated liver mitochondria that could lead to cytotoxicity, ROS generation and cell death.
Catechol; Mitochondrial respiration; Peroxidation