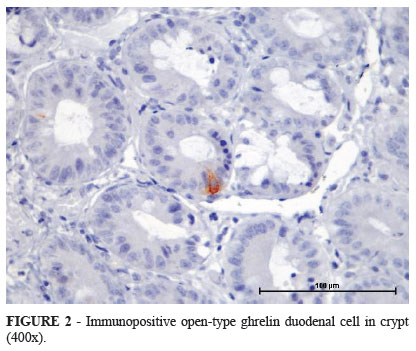
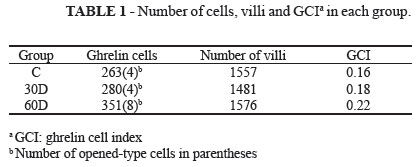
PURPOSE: Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) removes substantial part of the gastric mucosa, which produces ghrelin. This reduction is expected to force other organs, such as the duodenum, to compensate by increasing the number of ghrelin-producing cells. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether this response occurs. METHODS: Twelve adult male, Wistar rats underwent SG and were reoperated 30 or 60 days after the initial surgery. During the second surgery, a segment of the duodenum was resected to count ghrelin cells using immunohistochemistry. In six animals, SG was not performed, and the duodenal segment served as a control for ghrelin cell counts. The ghrelin cell index (GCI), which is the number of ghrelin cells divided by the number of villi in each segment, was measured and used in statistical analysis by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). RESULTS:There were increases in the absolute numbers of cells 30 and 60 days after SG, but statistical analysis by ANOVA showed no significant difference between the groups. CONCLUSION: A compensatory increase in the number of duodenal immunopositive ghrelin cells did not occur as a response to sleeve gastrectomy.
Ghrelin; Gastrectomy; Bariatric Surgery; Rats, Wistar