PURPOSE:
To determine the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of alfa lipoic acid (ALA) on the liver injury induced by methotrexate (MTX) in rats.
METHODS:
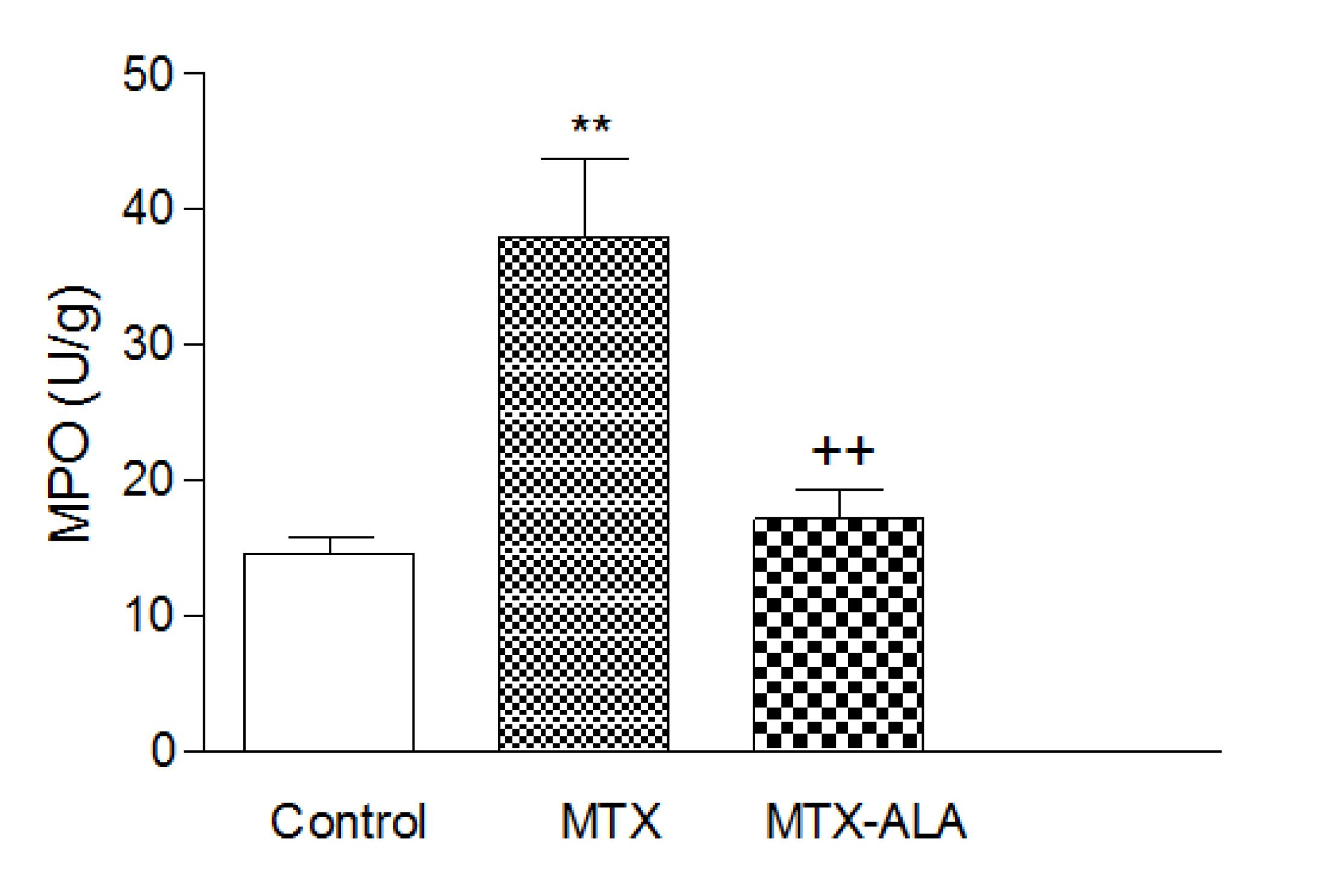
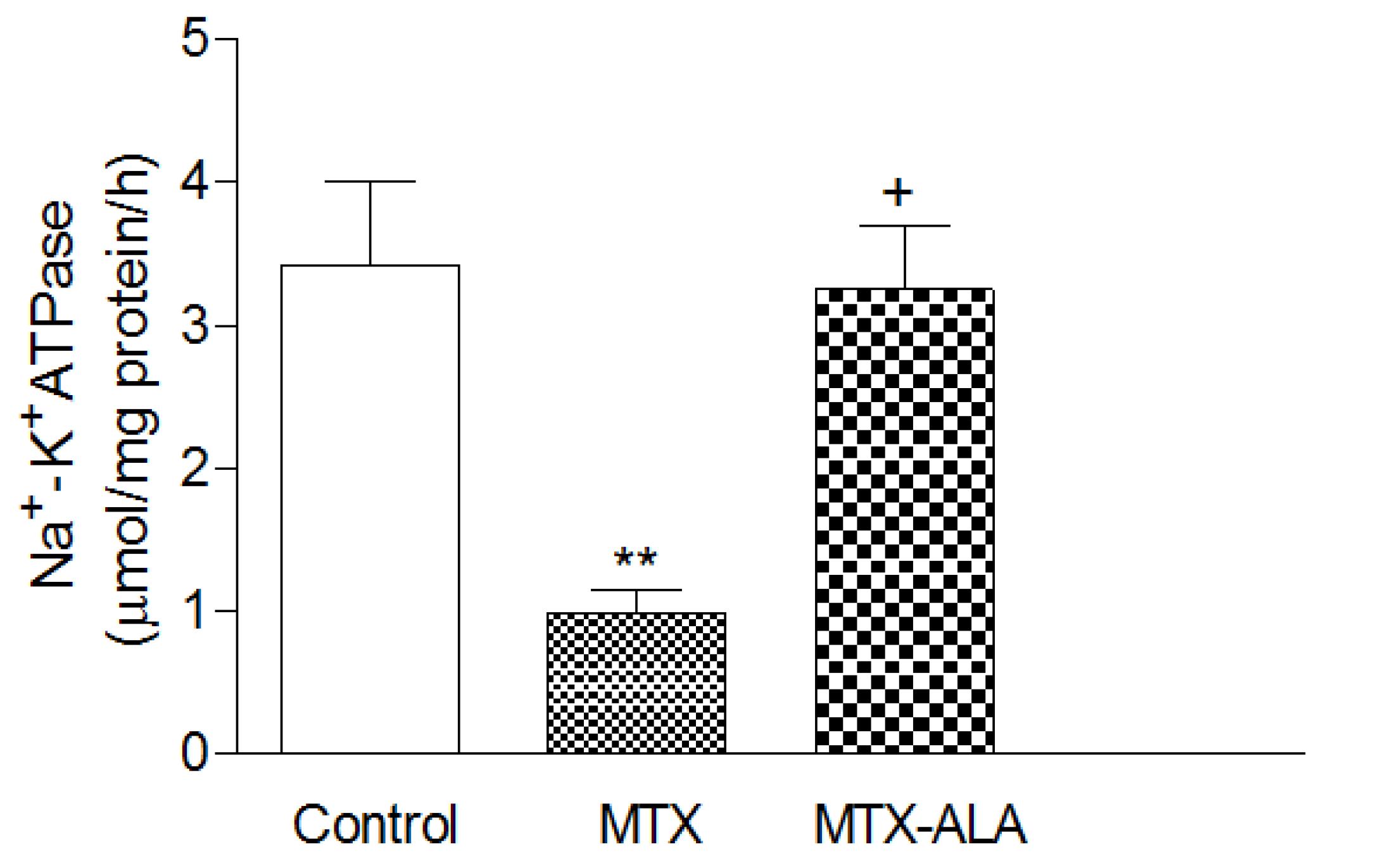
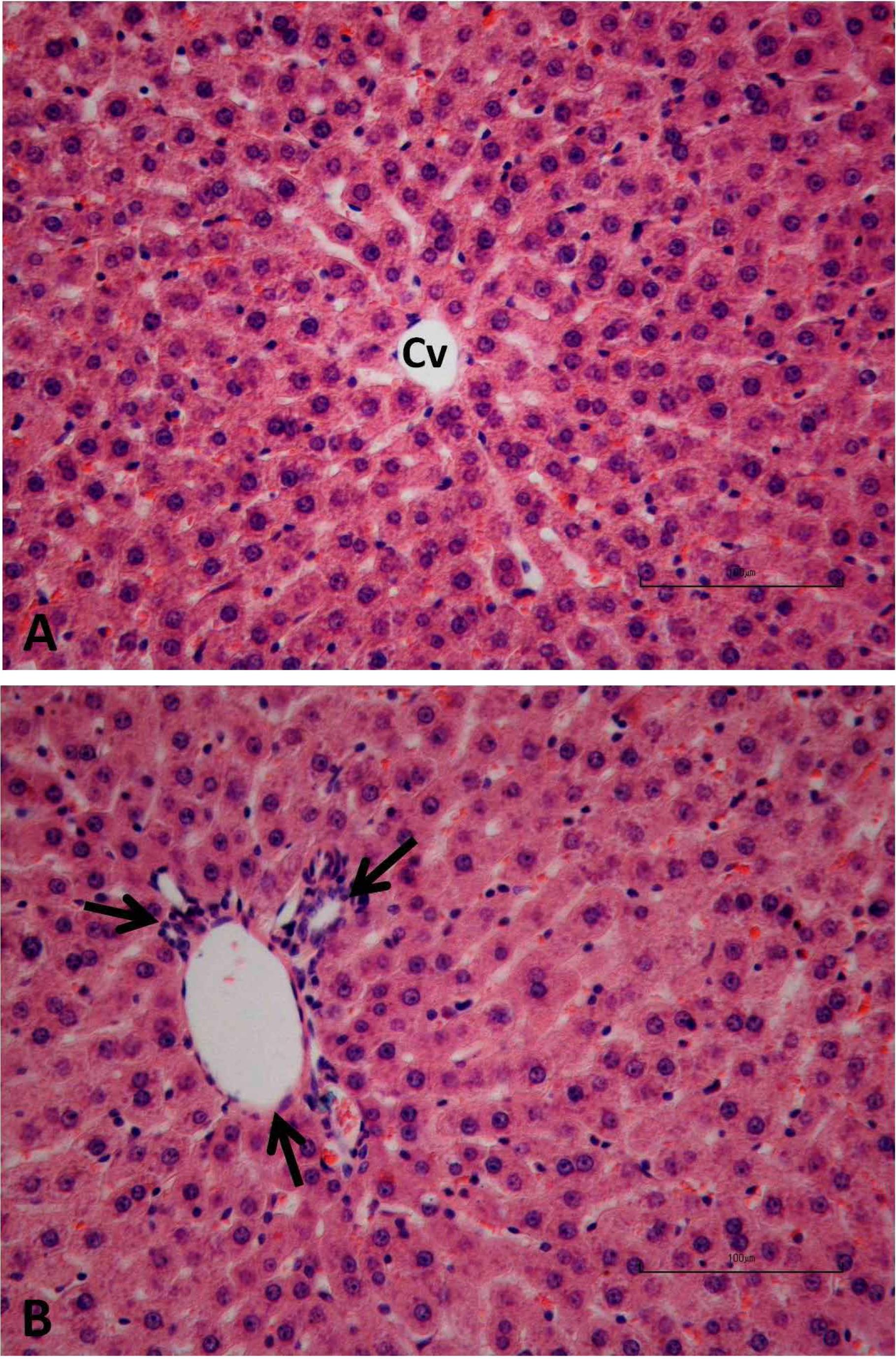
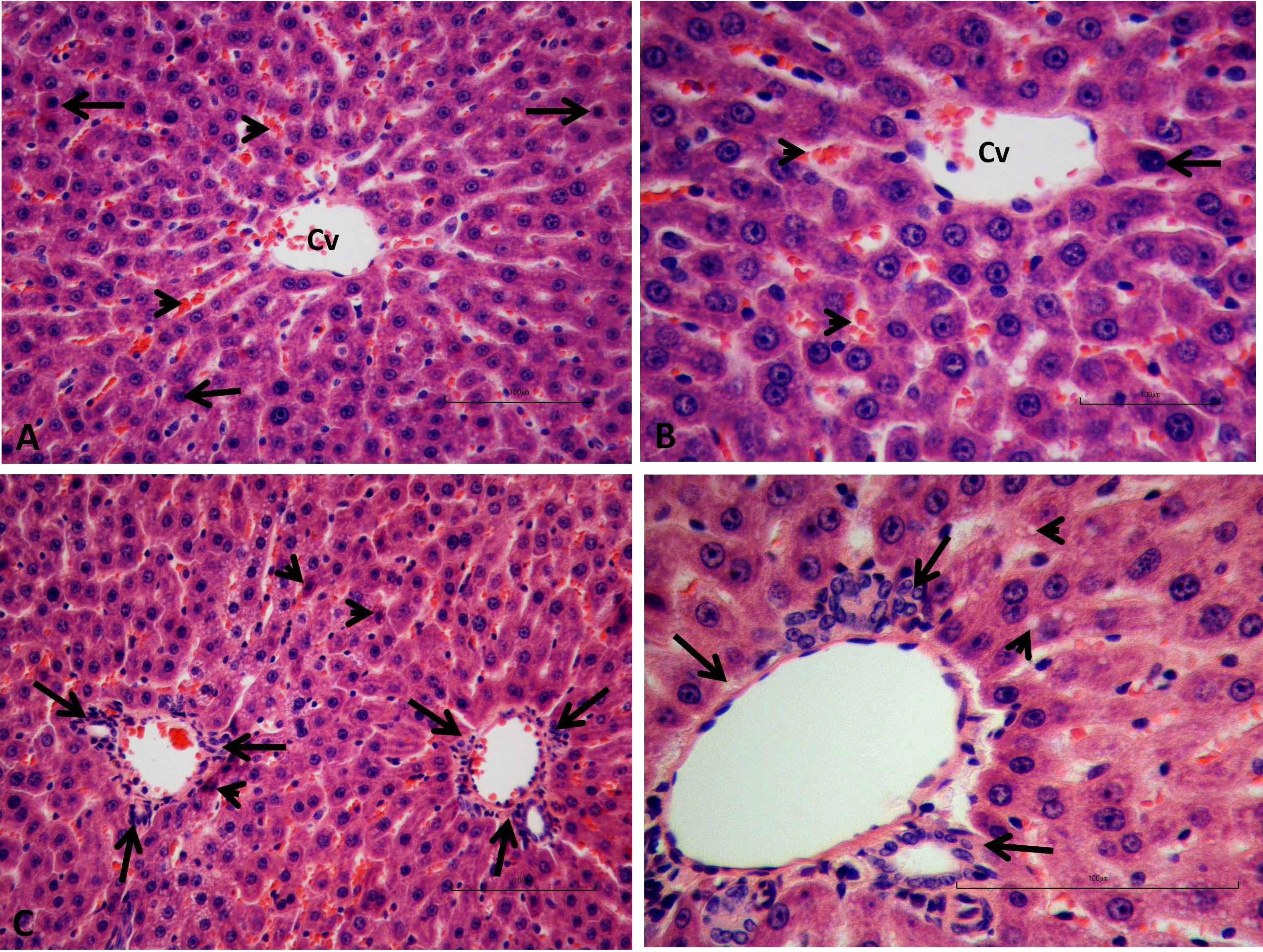
Thirty two rats were randomly assigned into four equal groups; control, ALA, MTX and MTX with ALA groups. Liver injury was performed with a single dose of MTX (20 mg/kg) to groups 3 and 4. The ALA was administered intraperitonealy for five days in groups 2 and 4. The other rats received saline injection. At the sixth day the rats decapitated, blood and liver tissue samples were removed for TNF-α, IL-1β, malondialdehyde, glutathione, myeloperoxidase and sodium potassium-adenosine triphosphatase levels measurement and histological examination.
RESULTS:
MTX administration caused a significant decrease in tissue GSH, and tissue Na+, K+ ATPase activity and which was accompanied with significant increases in tissue MDA and MPO activity. Moreover the pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL- β) were significantly increased in the MTX group. On the other hand, ALA treatment reversed all these biochemical indices as well as histopathological alterations induced by MTX.
CONCLUSION:
Alfa lipoic acid ameliorates methotrexate induced oxidative damage of liver in rats with its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Thioctic Acid; Methotrexate; Liver; Rats