Abstract
Objective
To compare the growth of very low birth weight preterm infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit, fed with pasteurized human milk and pasteurized human milk plus a commercial supplement.
Methods
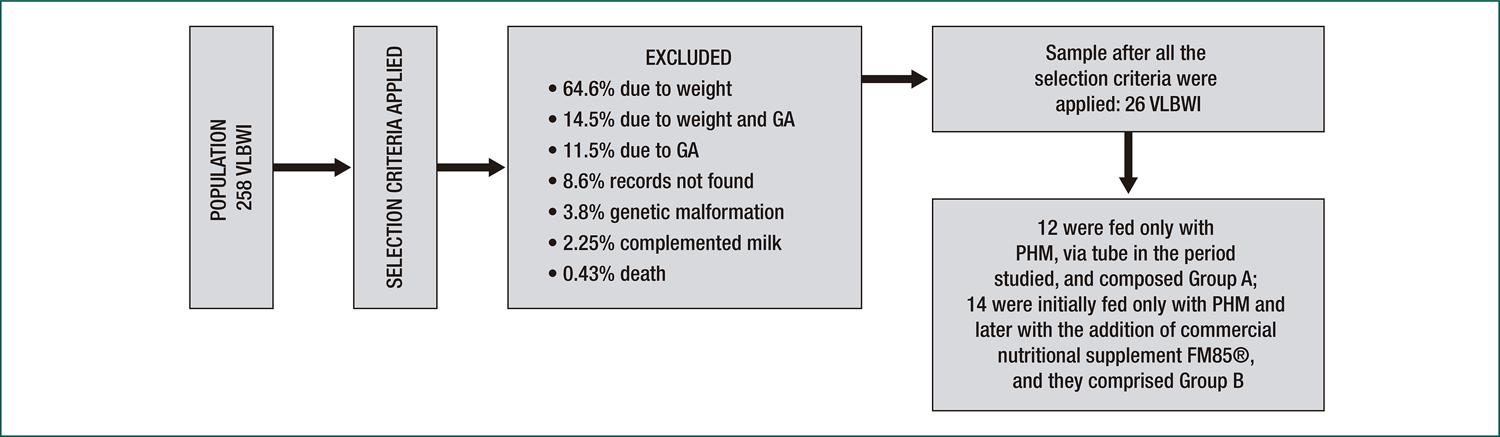
This was a series of cases, with a longitudinal design. Population and sample were comprised of all the records of infants less than 36 weeks gestational age, weighing less than 1,500 grams, who met the following inclusion criteria: clinically stable, of either sex, without diseases that could interfere in the growth and weight gain, using any type of tube through which they received pasteurized human milk and/or pasteurized human milk enhanced with FM85®, a commercial fortifying additive. Two groups were created: very low birth weight infants who received pasteurized human milk (Group A) and those who received pasteurized human milk enhanced with FM85® (Group B).
Results
No statistically significant difference was found between the two groups of very low preterm newborns, with the different diets evaluated at two different times. The gestational age influenced daily weight gain in both comparisons.
Conclusion
No statistically significant difference in growth was identified when comparing the two groups.
Infant, premature; Milk, human; Milk banks; Food additives; Nursing