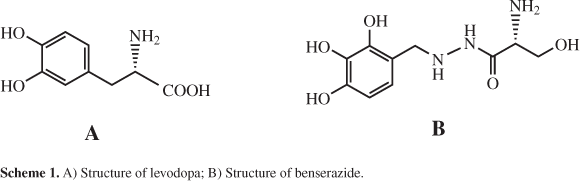
An electrochemical method is described for the sequential voltammetric determination of benserazide and levodopa using chloranil (CA) as an electrocatalyst. Cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to investigate the suitability of CA as a mediator for the electrocatalytic oxidation of benserazide and levodopa in an aqueous solution. The oxidation peak potential of levodopa and benserazide shifted at about 230 and 480 mV to a less positive potential, respectively, than with the unmodified carbon paste electrode. Under optimum conditions, the electrocatalytic oxidation peak current of levodopa and benserazide showed two linear dynamic ranges with limit of detection of 0.65 μmol L-1 and 0.95 μmol L-1, respectively. The relative standard deviations for the determination of 5.0 × 10-5 mol L-1 benserazide and 5.0 × 10-4 mol L-1 levodopa were 2.0 and 2.0% (n = 5), respectively. The linear calibration ranges were 1.0-500 μmol L-1 for benserazide and 3-500 μmol L-1 for levodopa using differential pulse voltammetry. The proposed method has been successfully applied for the determination of levodopa and benserazide in urine samples, demonstrating the feasibility and reliability of the proposed method.
levodopa and benserazide; sequential determination; cyclic voltammetry; chloranil; electrocatalysis; differential pulse voltammetry