ABSTRACT:
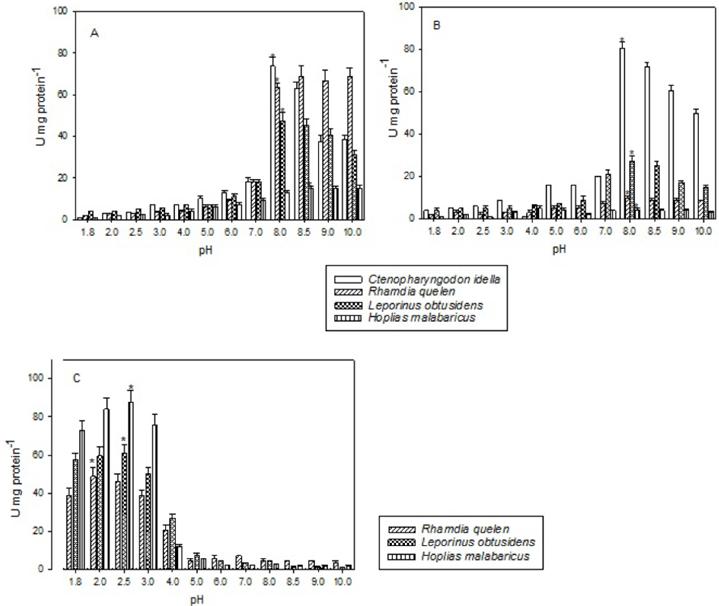
The aim of this study was to verify the activity of some digestive enzymes in four fish species with different feeding habits. Knowledge of these enzymatic activities can help us to understand the species' digestive processes. The species chosen for this study wereCtenopharyngodon idella (herbivore),Rhamdia quelen (omnivore),Leporinus obtusidens (omnivore) andHoplias malabaricus (carnivore). The digestive tract of these species was divided into four portions to estimate enzymatic activity: stomach, anterior, mid and posterior intestine. Ctenopharyngodon idella had the highest amylase and maltase activities in all portions of the gut, followed byL. obtusidens . The highest trypsin activity was observed in all gut portions of H. malabaricus, followed by the mid intestine of L. obtusidens and the anterior intestine of C. idella . The highest chymotrypsin activity was found in all portions of C. idella followed by the anterior intestines ofR. quelen, L. obtusidens andH. malabaricus . In the stomach, acid protease activity was significantly lower in R. quelen andL. obtusidens compared toH. malabaricus. Ctenopharyngodon idella showed high activity of enzymes that hydrolyze carbohydrates, represented in this study by amylase and maltase andH. malabaricus showed higher protease activity and low amylase activity.
Key words:
freshwater fishes; feeding habits; enzymatic activity; amylase; alkaline protease; maltase; trypsin

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail