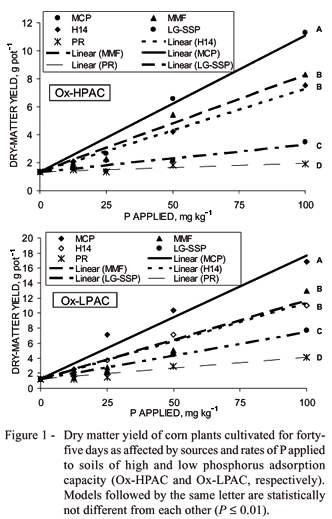
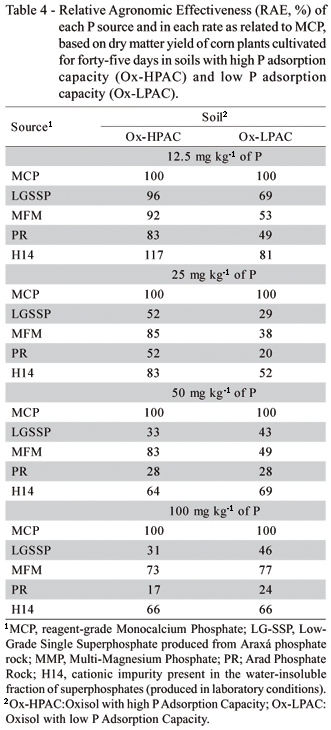
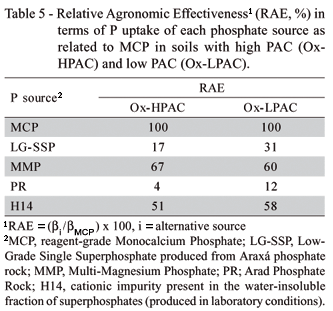
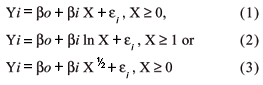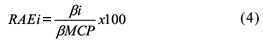Phosphate fertilizers should match soil attributes to enhance agronomic effectiveness and recovery by plants. The purpose of this study was to test the agronomic effectiveness of P sources varying in water solubility on two soils differing widely in P adsorption capacity (PAC). Soils selected for the study were Oxisols with very low available P and presenting low and high PAC (Ox-LPAC and Ox-HPAC, respectively). Both were limed to pH 5.4 in a greenhouse study conducted utilizing corn as the test crop. Treatments consisted of the two soils interacting with five P sources (monocalcium phosphate - MCP, low-grade single superphosphate - LG-SSP, multimagnesium phosphate - MMP, Arad phosphate rock - PR and a P impurity in triple superphosphate - H14), and four rates of P (12.5, 25.0, 50.0 and 100.0 mg kg-1). A control with no P was added for each soil. The treatments were arranged as blocks with three replicates. Plants were harvested 45 d after germination. Dry-matter yield and P uptake were measured and the relative agronomic effectiveness (RAE) compared with MCP as the standard. When applied in low rates of P (12.5 and 25.0 mg kg-1) the RAE of the alternative sources was higher in the soil with high PAC (45, 66, 39 and 65% in the Ox-HPAC for the LG-SSP, MMP, PR and H14, respectively, as opposed to 24, 40, 14 and 47% in the Ox-LPAC). Results suggest that sources of P with low water solubility can be agronomically more effective in soils with high PAC.
alternative phosphorus sources; relative efficiency; solubility