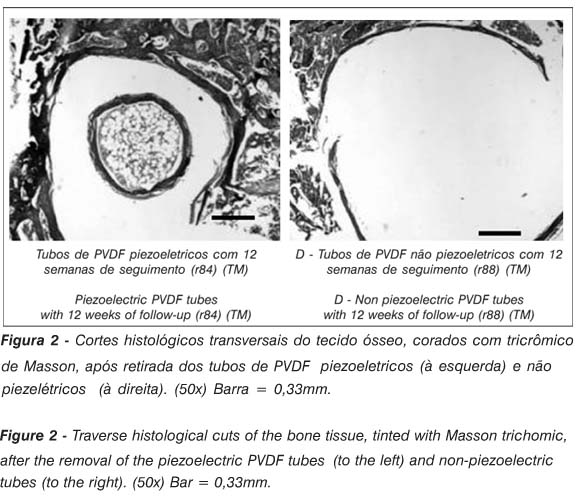
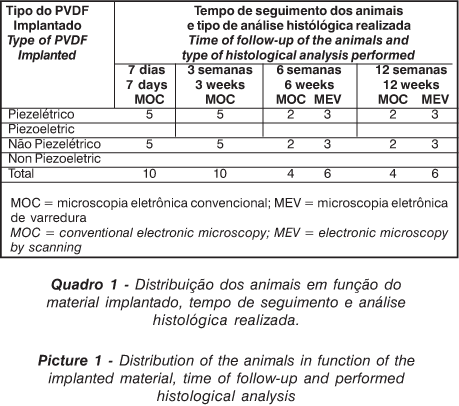
The objective of this study was to evaluate the interface formed between the poli (viniilidene) fluoride (PVDF-piezoelectric and non-piezoelectric) and cap rats' bone tissue. Twenty tubes of PVDF [P (VDF-TrFE)] piezoelectric, (d3h = 2,5 pC/N and capacitance 800 pF/m), and twenty tubes of non-piezoelectric PVDF were implanted in the intercondilian notch of the left femur of 40 rats. The animals of both groups were subdivided in four subgroups, followed up for 7 days, 3, 6 and 12 weeks. The interface found between bone and tubes was studied by conventional optical microscopy (MOC) (n=28) and by backscattered electronic scanning microscopy (MEV) (n=12). Bone tissue growth was observed inside the tubes of piezoelectric PVDF followed up during 12 weeks, both by MOC and by MEV backscattering. The results indicate that the piezoelectric effect had an important role in the new bone tissue formation inside the piezoelectric tubes. Probably, that bone formation was a result from the electrets effect or from micro deformations produced in the piezoelectric tubes, due to the intra-articular pressure variation on the knee movement during gait.
Piezoelectric effect; Bone growth; Artificial implants