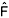The aim of this research was to study the mating system of a natural population of Theobroma grandiflorum (cupuassu) from Nova Ipixuna, Pará state, using microsatellite markers. Eight polymorphic microsatellite loci were analyzed in eight families, each represented by 10 six-month old seedlings derived from open-pollinated pods. The estimation for the multilocus outcrossing rate (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1026" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle>m = 1.0) and individual outcrossing rate (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1027" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle> = 1.0) for this population suggests that T. grandiflorum may be a perfect outbreeding (allogamous) species. Likewise, for the studied population the estimate for single locus outcrossing rate (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1028" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle>S) was elevated (0.946), but lower than <img border=0 id="_x0000_i1029" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle>m, confirming the likely outcrossing character of the species and suggesting the occurrence of 5.4% biparental inbreeding rate (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1030" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle>m - <img border=0 id="_x0000_i1031" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img01.gif" align=absmiddle>S). The estimation of genetic divergence (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1032" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img02.gif" align=absmiddle>st) between allelic frequencies in ovules and pollen revealed a deviation from random mating in 75% of the evaluated loci. Likewise, the estimate of correlation of paternity (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1033" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img03.gif" align=absmiddle>P = 0.930) and the mean coefficient of co-ancestrality within families (<img border=0 id="_x0000_i1034" src="../../img/revistas/gmb/v26n3/a25img04.gif" align=absmiddle>XY = 0.501) indicated that the outcrossings were predominantly correlated, and the offspring were full-sibs. These results suggested that for this particular population of T. grandiflorum, the sampling strategy for genetic conservation and breeding should adopt specific models for families derived from correlated outcrossing (full-sibs) and not the ones usually adopted in classic outcrossing species breeding programs (half-sibs).
Amazonia; germplasm; cupuassu; genetic conservation; simple sequence repeat