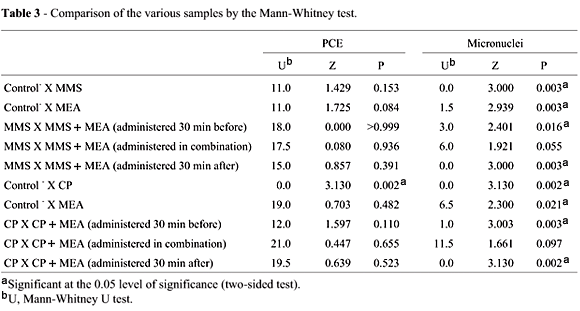
Cysteamine or 2-mercaptoethylamine (MEA) is an aminothiol with a well-known radioprotective action. No specific information is available in the literature about the possible chemoprotective action of MEA against genotoxic chemical agents. This paper presents the results of studies on the ability of MEA to protect mouse bone marrow polychromatic erythrocytes against the induction of micronuclei by alkylating agents such as methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) and cyclophosphamide (CP). We observed that MEA administered intraperitoneally 30 min before or 30 min after the administration of MMS or CP significantly reduced the frequency of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes (MNPCEs) induced by the alkylating agents. When MEA was administered in combination with MMS or CP the reduction in the frequency of MNPCEs did not reach statistically significant levels, although it reached values close to significance. With respect to the polychromatic erythrocyte/normochromatic erythrocyte (PCE/NCE) ratio, we observed that MEA did not provide significant protection against the bone marrow toxicity induced by CP.
cysteamine; MEA; micronuclei; amifostine; WR-2721