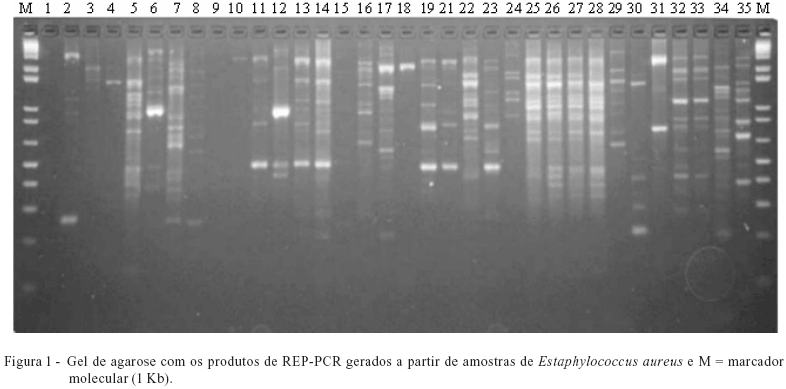
Este estudo foi realizado com o objetivo de aplicar a técnica de REP-PCR no monitoramento da qualidade do leite de cabra por meio da detecção de Staphylococcus aureus em amostras de mãos de ordenhador, tetos das cabras, leite, ordenhadeira e água para estabelecimento e implantação do sistema de Análise de Perigos e Pontos Críticos de Controle (APPCC). Verificaram-se vários fingerprints de todos os isolados coletados das diferentes fontes estudadas (mãos de ordenhador, tetos das cabras, leite, ordenhadeira e água). Observaram-se comportamentos muito similares das bandas, o que indica que os isolados podem ser relatados como clones epidemiológicos. As mãos do ordenhador caracterizaram-se como ponto crítico de controle, pois se destacaram como iniciador de contaminação nas amostras Staphylococcus aureus. A técnica demonstrou ser eficiente para a análise da similaridade entre indivíduos da espécie Staphylococcus aureus e, portanto, constitui ferramenta útil para investigação de falhas no manejo e na busca de controle mais eficiente para evitar ou reduzir a disseminação de microrganismos patogênicos causadores de sérias enfermidades em humanos e animais, que muitas vezes podem ser transmitidas por produtos como o leite e seus derivados.
epidemiologia molecular; identidades genômicas; manejo