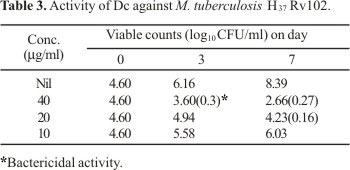
Diclofenac sodium, an antiinflammatory agent, exhibited remarkable inhibitory action against both drug sensitive and drug resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, as well as other mycobacteria. This drug was tested in vitro against 45 different strains of mycobacteria, most of which were inhibited by the drug at 10-25 µg/ml concentration. When tested in vivo, diclofenac, injected at 10 µg/g body weight of a Swiss strain of white mice, could significantly protect them when challenged with 50 median lethal dose of M. tuberculosis H37 Rv 102. According to chi2 test, the in vivo data were highly significant (p<0.01). Diclofenac was further tested for synergism with the conventional antimycobacterial drug streptomycin against M. smegmatis 798. When compared with their individual effects, synergism was found to be statistically significant (p<0.05). By the checkerboard assessment procedure, the fractional inhibitory concentration index of this combination was found to be 0.37, confirming synergism.
antiinflammatory drug; diclofenac sodium; antimycobacterial activity; streptomycin; synergism; non-antibiotic