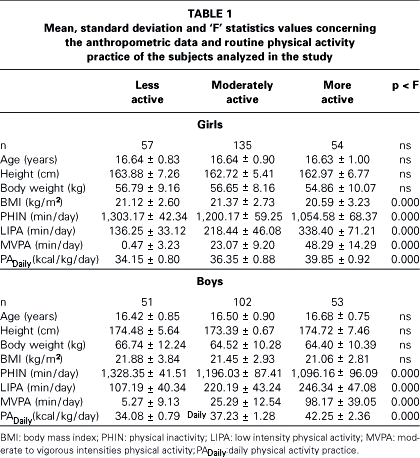
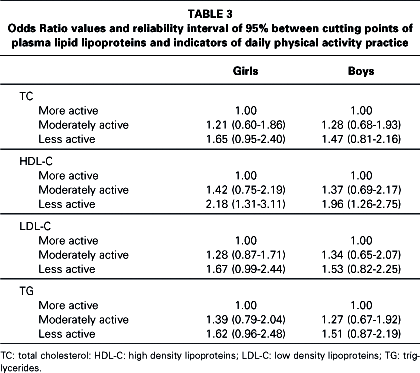
The aim of the present study was to analyze the impact of regular practice of physical activity facing estimates of daily energy expenditure (EEdaily) in the plasmatic lipid-lipoprotein profile in a representative sample of adolescents. The sample consisted of 452 subjects (246 females and 206 males), age between 15 and 18 years. The plasmatic lipid-lipoprotein concentrations were established through laboratory procedures. The data concerning the regular practice of physical activity were obtained though a retrospective instrument of self-recording. Estimates concerning the EEdaily were established based on the caloric cost associated with the type and the duration of the activities registered by the adolescents. The sample was divided in three groups of regular practice of physical activity: the least active, < 25º percentile of the EEdaily; the moderately active, 25-75º percentile of the EEdaily; and the most active, > 75º percentile of the EEdaily. Cutting points for an atherogenic lipid-lipoprotein risk were also established. The results of the analysis of covariance, having the participation of the body mass index controlled, showed that the HDL-C concentrations were significantly different according to the growing groups of EEdaily in females (p = 0.009) and in males (p = 0.010). However, the variation behavior of the values observed was different in the two sexes. The analysis of logistic regression showed that the relative risk for lower values of HDL-C was two times higher among the least active adolescents comparing with the most active ones. In both sexes the concentrations of total cholesterol, LDL-C and triglycerides did not present significant differences among the groups of EEdaily. In conclusion, more intense regular practice of physical activity as well as higher EEdaily are associated with higher concentrations of HDL-C in adolescents of both sexes, regardless of the variations of body weight. The associations between EEdaily and the other plasmatic components of lipid-lipoproteins treated in the present study were weak and inconsistent.
Physical activity; Sedentarism; Cardiovascular risk factors; Cholesterol; Triglycerides