ABSTRACT
Introduction
Aging is a natural process and marked by changes and adaptations of both a biological and physiological nature. As regards adaptations, there are numerous works that address these responses following various types of training programs. Resistance training (RT) can be assessed by biochemical parameters such as creatine kinase (CK), which is a major marker of stress in the skeletal muscles. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a biochemical marker used to assess damage to the cardiac muscles.
Objective
To evaluate the influence of CK on CRP in elderly female subjects undergoing RT.
Methods
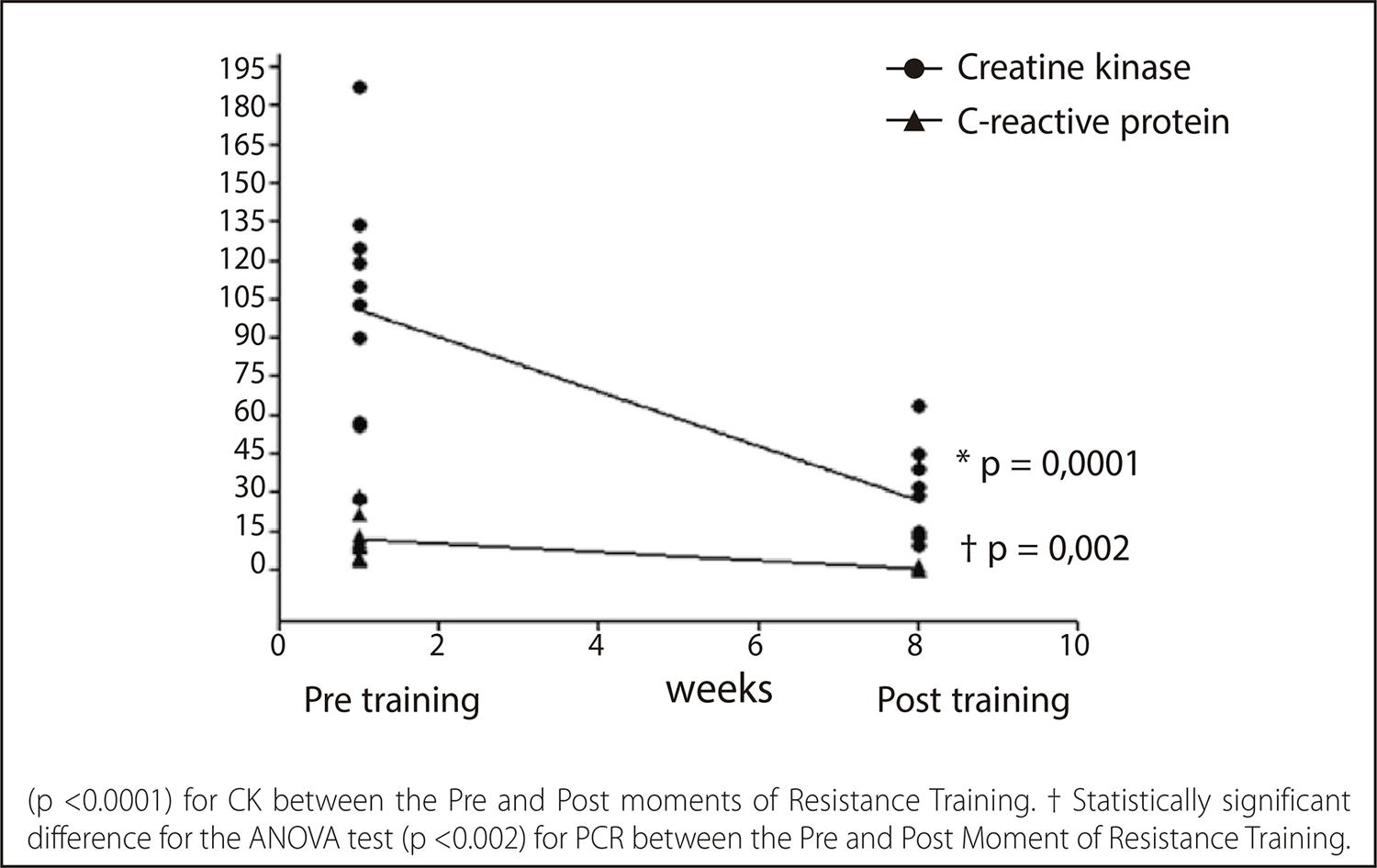
An experimental study was carried out with 10 elderly women (61 ± 1.8 years). Peripheral venous blood was collected for the CK and CRP analysis both before and 24 hours after 8 weeks of RT. Anthropometric measurements involved BMI (Body Mass Index), WHR (waist-to-hip ratio) and body composition. The RT involved combined series - Bi-Set. For statistical analysis, the Shapiro-Wilk normality test was conducted first and presented p >0.05, confirming the use of parametric tests. Group variables were presented as mean and standard deviation. To compare the load-dependent samples, the repeated measures one-way ANOVA was performed first, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. For CK and CRP variables, we conducted the paired Student’s t-test for the timepoints pre- and post-eight weeks of RT along with the one-way ANOVA test, also conducting Tukey’s post-test when necessary. The level of significance was set at p ≤0.05.
Results
There was a statistically significant decrease in both serum CK and CRP, which indicated a reduction of 73.14% and 75%, respectively.
Conclusion
Long-term RT promoted influences among biomarkers assessed through skeletal muscle (CK) and cardiac muscle (CRP) damage, determining adaptation and muscle remodeling in any age group. Level of evidence II, Investigation of treatment results.
Creatine kinase; C-reactive protein; Myalgia; Aged