Abstract
Introduction:
several birth defects associated to congenital Zika virus infection have been reported, although the clinical features have not been fully characterized.
Description:
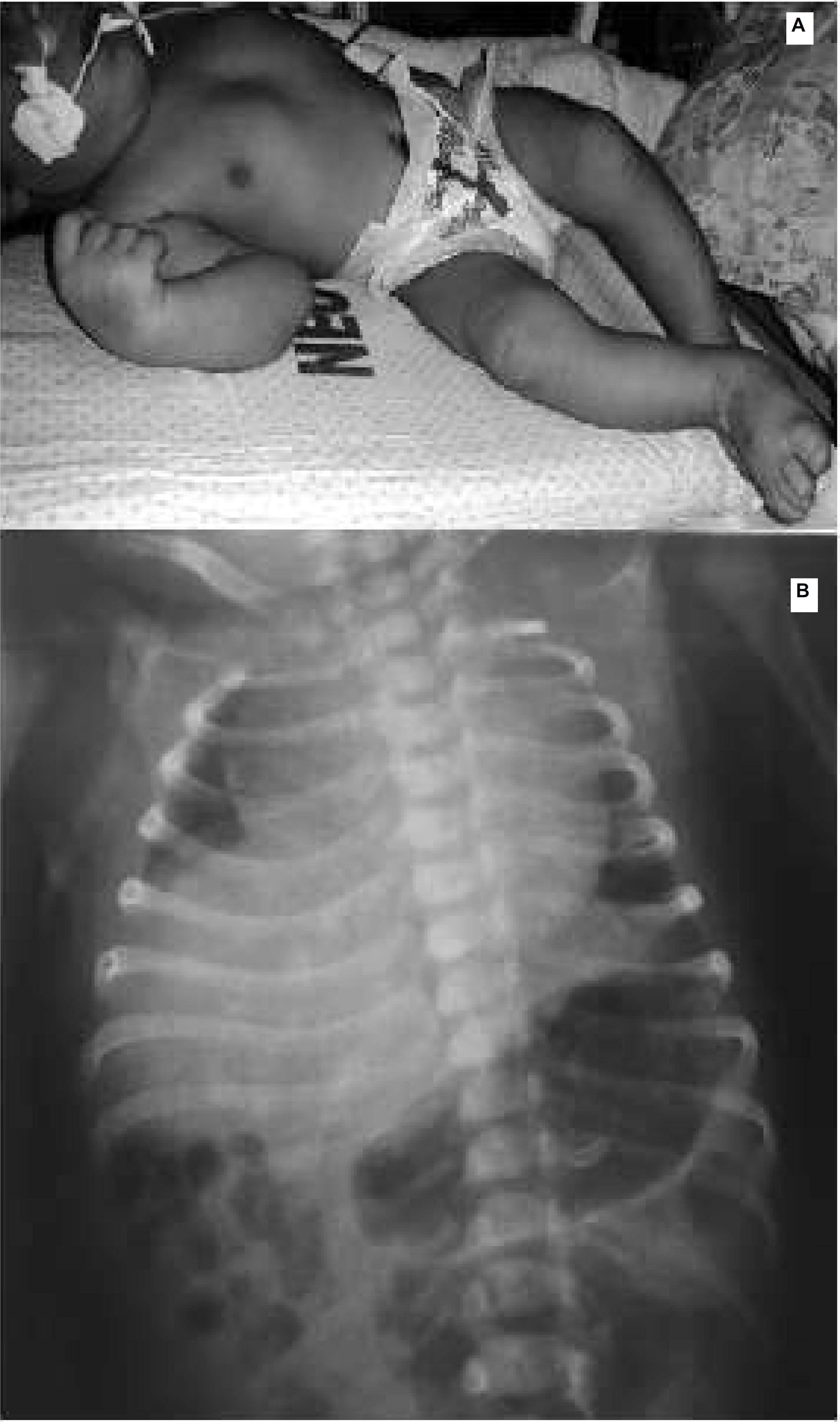
this is the first case report on unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis diagnosed on a neonate with congenital Zika confirmed by the examination of the amniotic fluid through polymerase chain reaction (ZIKV RT-PCR) and the examination of cerebrospinal fluid by serological test (IgM ZIKV-ELISA) after birth. The main manifestations detected by intrauterine ultrasound were: microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, intracranial calcifications, enlarged cisterna magna, increased amniotic fluid index and fetal akinesia syndrome. The newborn had acute respiratory failure in the first hours of life, requiring mechanical ventila-tion. The X- ray of the chest showed unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis and cardiomegaly.
Discussion:
diaphragmatic palsy in congenital Zika has not been previously reported, the etiopathogenic mechanisms of this event in congenital Zika virus needs to be elucidated.
Key words:
Microcephaly; Arbovirus infections; Arthrogryposis; Prenatal ultrasound; Respiratory paralysis