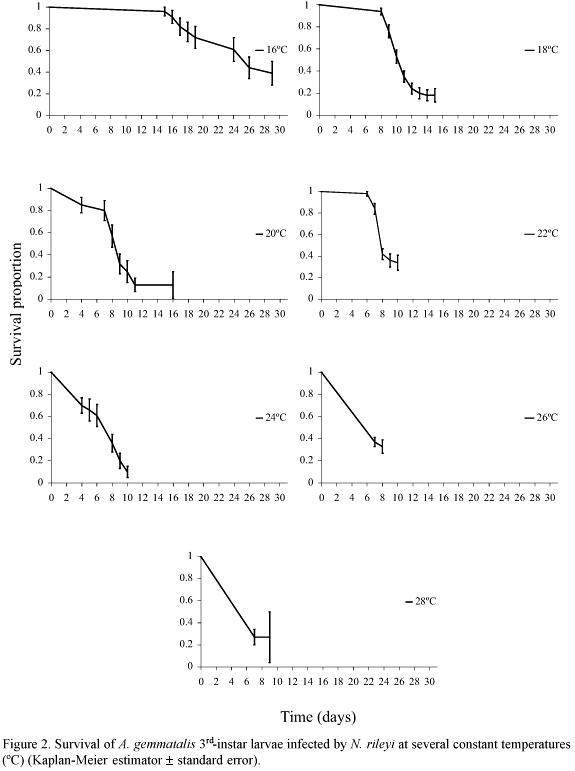
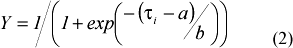The influence of temperature on the development rate of the entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi (Farlow) Samson in Anticarsia gemmatalis (Hübner) 3rd-instar larvae was studied under constant temperature regimes. A non linear model was used to describe temperature-dependent vegetative and reproductive development rates of the fungus. The temperature required to reach the highest vegetative development rate was estimated to be 25.5ºC while lower and upper developmental thresholds were 11ºC and 30ºC, respectively. The rate of development for conidia release was stable from 18ºC to 26ºC. The estimated lower and upper thresholds of vegetative development coincide with conditions during the natural epizootics in central Argentina. Non-linear effects of temperature on vegetative and reproductive development rates and probability distributions of N. rileyi under in vivo conditions are described.
Biological control; mathematical model; population dynamics; natural enemy