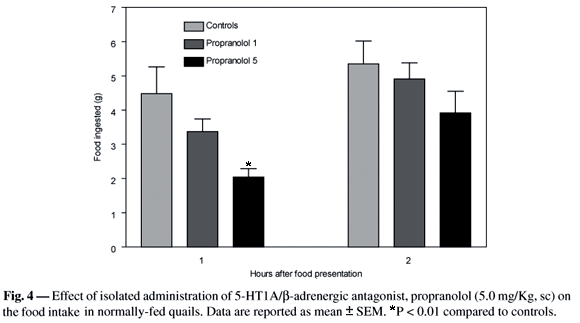
In this study, we investigate the effect of serotonin receptor 5-HT1A stimulation on the feeding behavior of quails (Coturnix japonica). The administration of 5-HT1A agonist, 8-OH-DPAT (0.05 to 5.0 mg/Kg) dose-dependently inhibited the food intake in normally fed quails. Greater inhibition was attained with 5.0 mg/kg (0.93 ± 0.21 g vs. 5.83 ± 0.25 g, P < 0.05, 2 h after food offer). A comparable response was obtained from previously fasted quails. At end of 2 h, a higher dose of 8-OH-DPAT induced more intense hypophagy (1.59 ± 0.41 g vs. 6.85 ± 1.04 g, P < 0.0001). Previous treatment with the antagonist 5-HT1A/beta-adrenergic, propranolol, failed to block the inhibitory action of 8-OH-DPAT, but instead, intensified it (controls, 5.22 ± 1.09 g; 8-OH-DPAT, 1.41 ± 0.19 g; propranolol + 8-OH-DPAT, 0.44 ± 0.25 g, P < 0.01, for all comparisons). The administration of an isolated higher dose of propranolol induced a hypophagic action (controls, 4.5 ± 0.8 g vs. propranolol, 2.0 ± 0.2 g, P < 0.01). Current outcomes suggest a possible role of 5-HT1A receptor on the feeding behavior of quails, as opposed to mammals. On the other hand, the intensified hypophagy induced by previous administration of propranolol raises the hypothesis of a beta-adrenergic excitatory mechanism that controls the feeding behavior of quails.
feeding behavior; 5-HT1A receptor; serotonergic system; quails; Coturnix japonica