Abstract
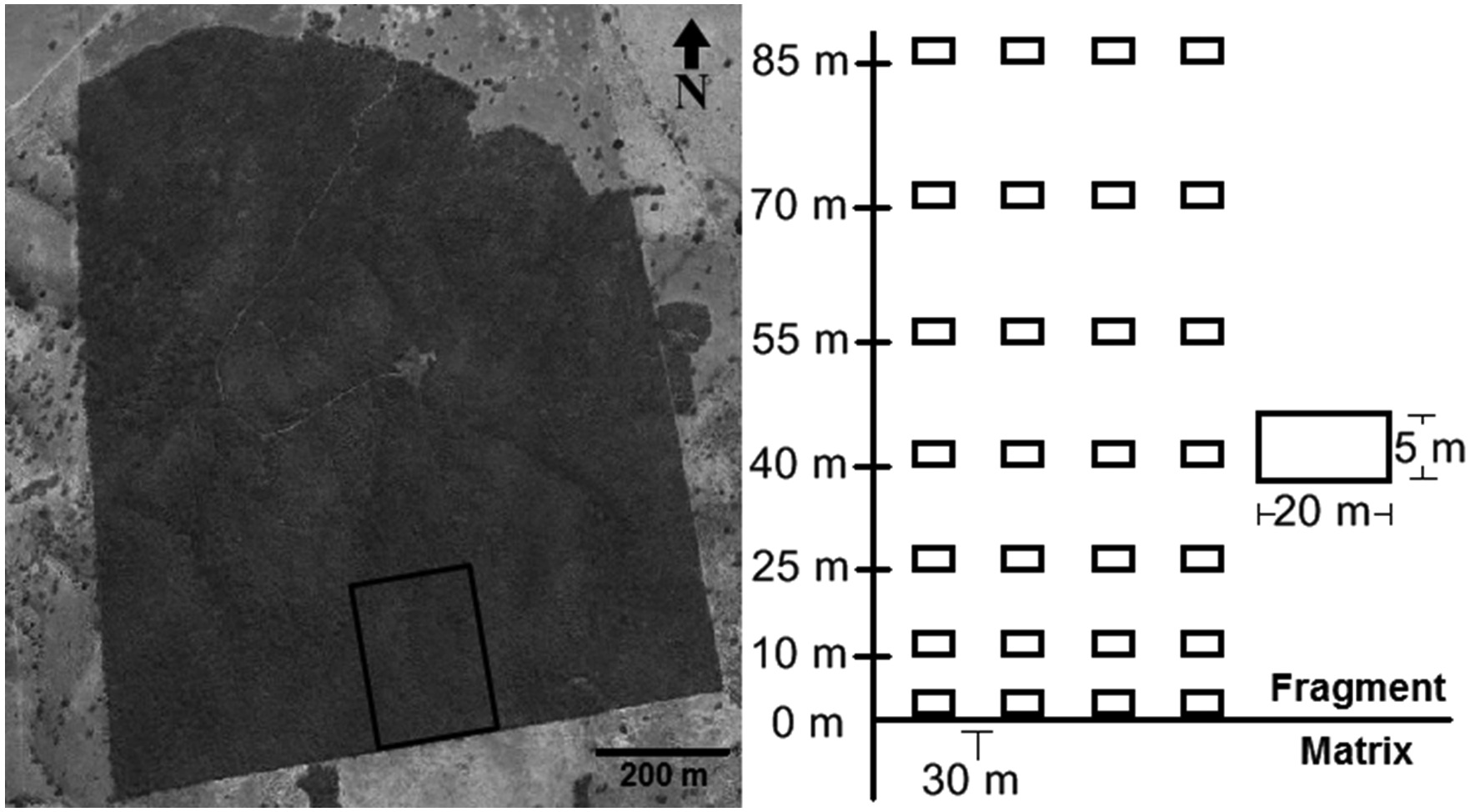
Due to the deciduous nature of dry forests (widely known as seasonally dry tropical forests) they are subject to microclimatic conditions not experienced in other forest formations. Close examinations of the theory of edge effects in dry forests are still rare and a number of questions arise in terms of this topic. In light of this situation we examined a fragment of the dry forest to respond to the following questions: (I) Are there differences in canopy cover along the edge-interior gradient during the dry season? (II) How does the microclimate (air temperature, soil temperature, and relative humidity) vary along that gradient? (III) How does the microclimate influence tree species richness, evenness and abundance along that gradient? (IV) Are certain tree species more dominant closer to the forest edges? Regressions were performed to address these questions. Their coefficients did not significantly vary from zero. Apparently, the uniform openness of the forest canopy caused a homogeneous internal microclimate, without significant differentiation in habitats that would allow modifications in biotic variables tested. We conclude that the processes of edge effect commonly seen in humid forests, not was shared with the dry forest assessed.
Keywords:
boundary effects; canopy cover; deciduous forest; edge influence; microclimatic influences

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail