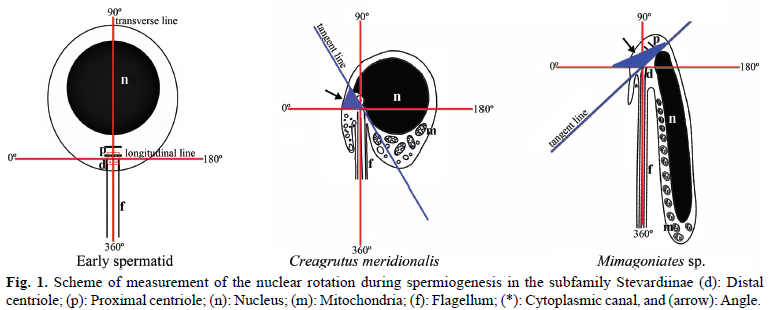
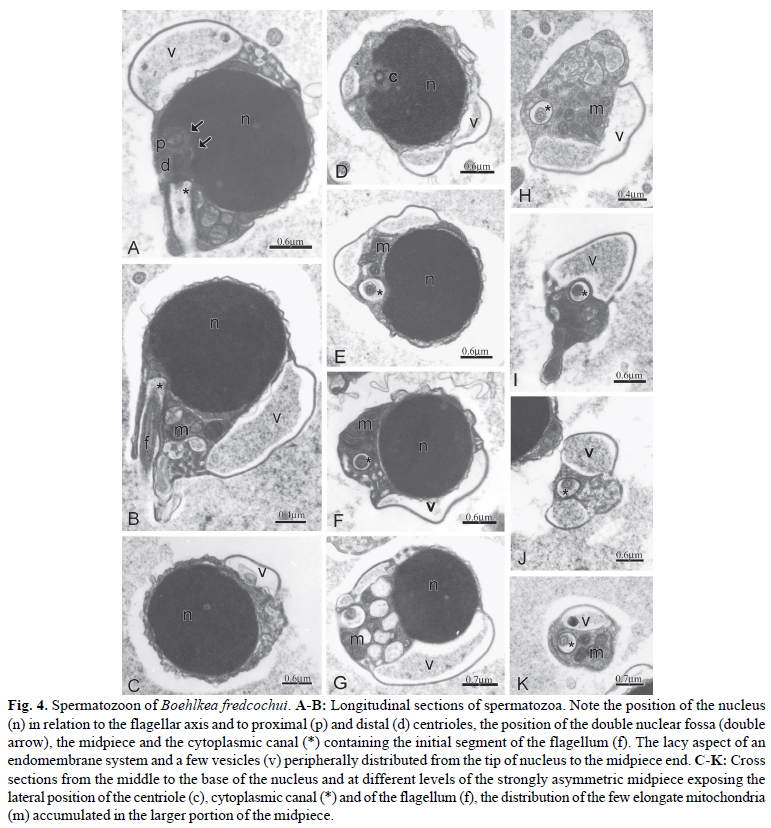
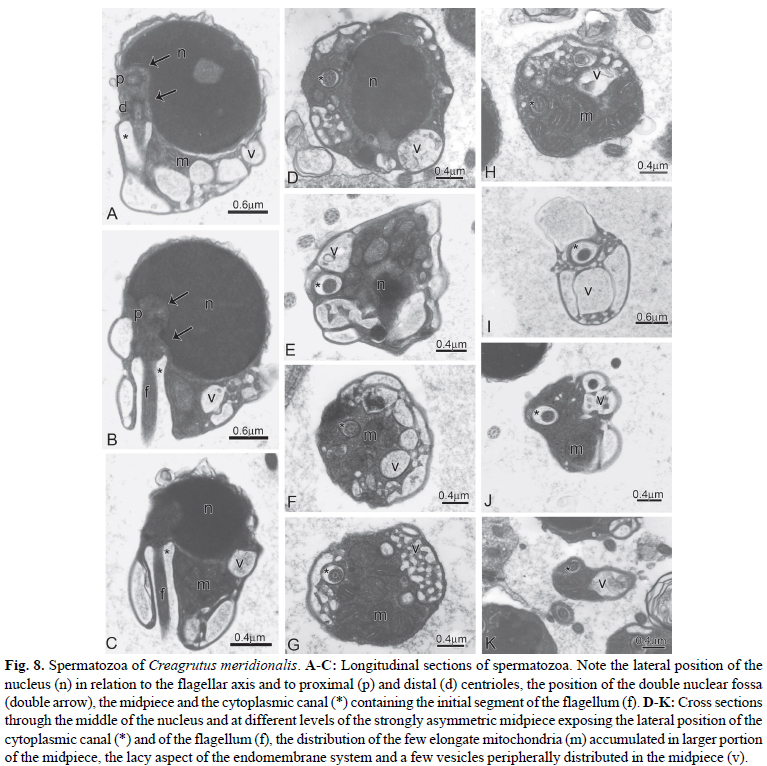
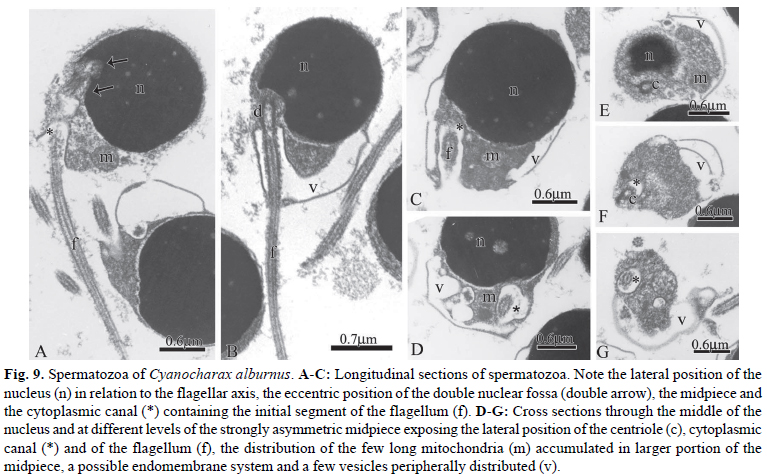
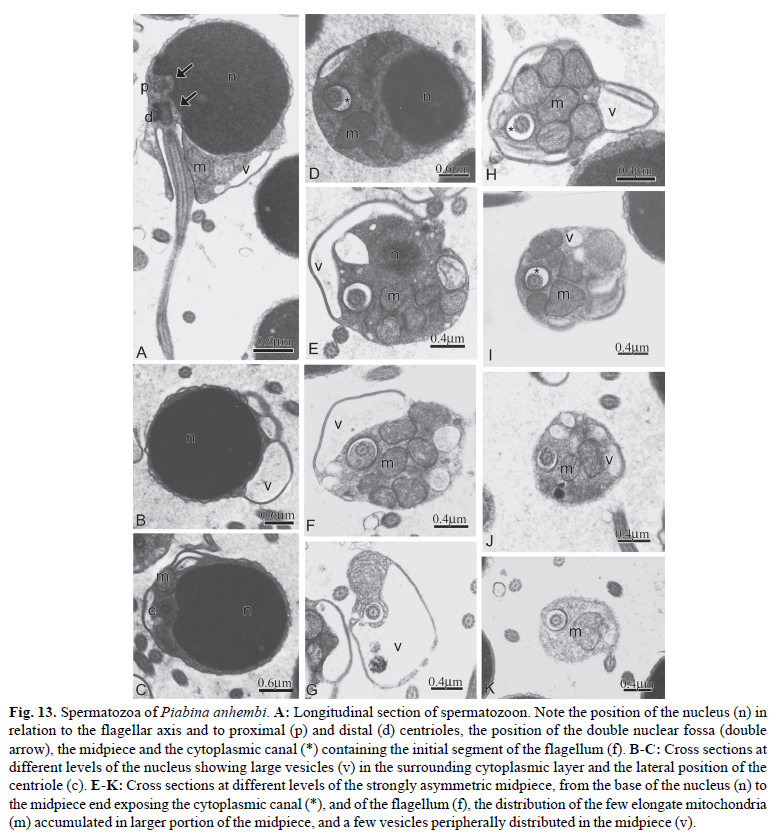
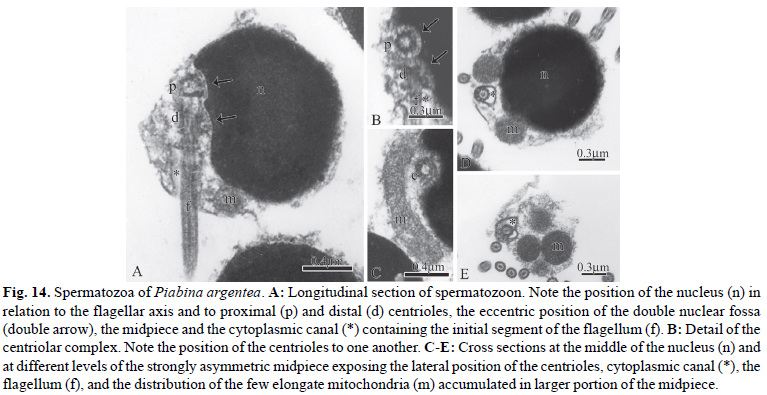
The monophyly and phylogenetic relationships among the members of Clade A characids (sensu Malabarba & Weitzman), later redefined and named as the Stevardiinae (sensu Mirande), have been primarily supported by traditional morphological and molecular data. Herein were examined, described and compared spermiogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of 12 species of the genera Boehlkea, Bryconacidnus, Bryconamericus, Creagrutus, Cyanocharax, Hemibrycon, Knodus, Odontostoechus, Piabina, and Rhinobrycon in order to evaluate possible phylogenetic signals and their potential use in recovering relationships of the Stevardiinae. All examined species demonstrated a nuclear rotation equal or less than 95º resulting in a lateral position of the double nuclear fossa and flagellum. In all species, sperm nuclei are slightly elongate toward the flagellum, the proximal centriole is partially inside the nuclear fossa and lies anterior and oblique to the distal centriole, and the midpiece is short and strongly asymmetric. All species analyzed herein and other species previously examined for these systems in the Stevardiinae share homologous sperm characteristics as evidenced by spermiogenesis, further supporting the monophyly of this clade. Spermatozoa of the Stevardiinae further show three morphotypes (M1, M2, M3) of arrangement of centrioles, flagellum, nucleus and midpiece, hypothesized as successively derived in a series of transformation from the most basal morphotype (M1).
Clade A; Phylogeny; Spermiogenesis; Sperm morphotype