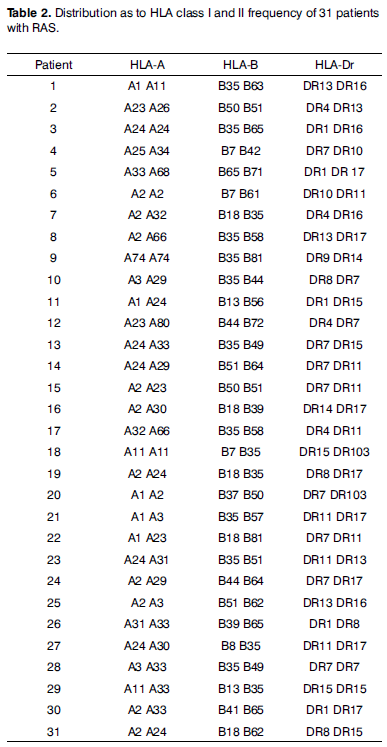
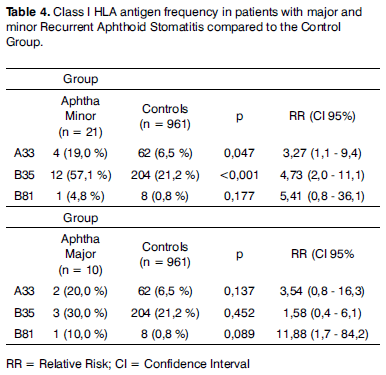
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis is a common oral mucosa disorder that affects 20% of the world's population, characterized by recurring painful ulcers in the mouth. The diagnosis is primarily based on the patient's clinical history. Inheritance may pose as a risk factor for the disease; however, the studies available are inconclusive as to the results attained, and they vary according to the population studied. AIM: to typify class I and class II HLA molecules and to assess how frequent these molecules are present in the Brazilian population with Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis, compared to healthy controls. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this prospective, cross-sectional and investigative study, thirty one patients with diagnostic hypothesis of recurrent aphthous stomatitis were seen from February of 2004 to May of 2006. We obtained the DNA from those patients who matched the inclusion criteria and typified their HLA by PCR. RESULTS: In those patients with Recurrent Minor Aphthous Stomatitis we found statistically significant occurrences of HLA-A33 and HLA-B35. CONCLUSION: HLA-A33 and HLA-B35 may be associated with recurrent minor aphthous stomatitis in the Brazilian's population.
hla antigens; aphthous stomatitis; genetics; stomatology