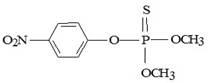
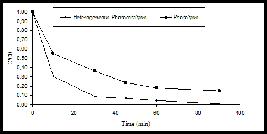
This paper describes solar heterogeneous photocatalysis using immobilized TiO2 applied in the treatment of agricultural waste resulting from the application of commercial formulations of methyl parathion. The disappearance of the insecticide, as well as the formation of its metabolite, was monitored by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), while mineralization efficiency was monitored by measurements of total organic carbon (TOC). Toxicity studies were performed using the microcrustacean Artemia salina. The TOC removal efficiency by photocatalytic process was 48.5%. After 45 minutes of treatment, the removal efficiency of methyl parathion was 90%, being completely mineralized at the end of treatment. The formation and removal of the metabolite methyl paraoxon was observed during the photocatalytic process. The photocatalytic treatment resulted in increased microcrustacean mobility, indicating a reduction of acute toxicity.
Keywords:
methyl parathion; solar photocatalysis; toxicity.

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail



