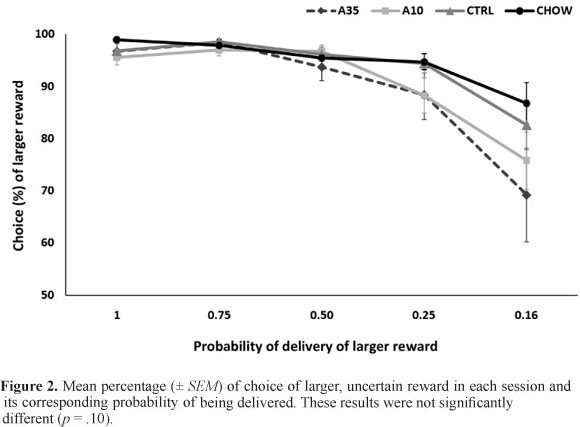
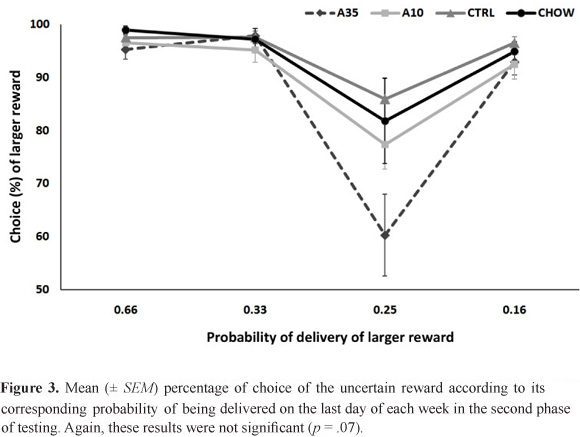
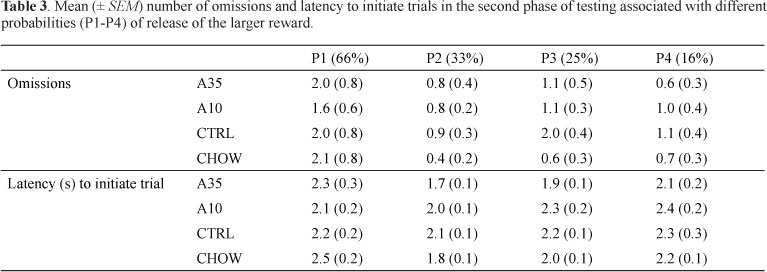
Individuals who fall under the spectrum of the Fetal Alcohol Syndrome have a higher prevalence of several cognitive disturbances, including a greater probability of being diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Some of these effects, such as hyperactivity and attentional impairments, are already well established in the literature. The assessment of impulsive choice, however, has received little attention in human and animal studies. In the present study, we attempted to investigate the effects of prenatal ethanol exposure on two tasks related to impulsive choice that have never been studied in this condition: delay and probability discounting. METHOD: Rats prenatally exposed to ethanol (liquid diets with 0%, 10%, or 35% ethanol-derived calories [EDC] or laboratory chow) were trained to respond for food in either delay (n = 21) or probability (n = 48) discounting tasks performed in computer-controlled operant conditioning chambers. RESULTS: Prenatal treatment failed to differentiate the rates at which the rats chose the larger reinforcer associated with delay - in a task in which 35% EDC was not tested - or risk, although the results suggest that further tests are warranted.
delay discounting; probability discounting; Fetal Alcohol Syndrome; prenatal ethanol exposure; impulsivity