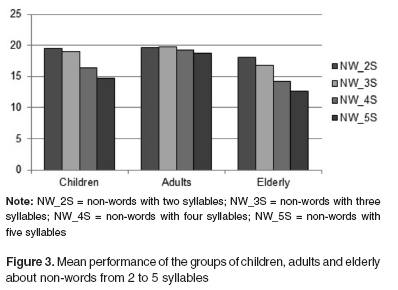
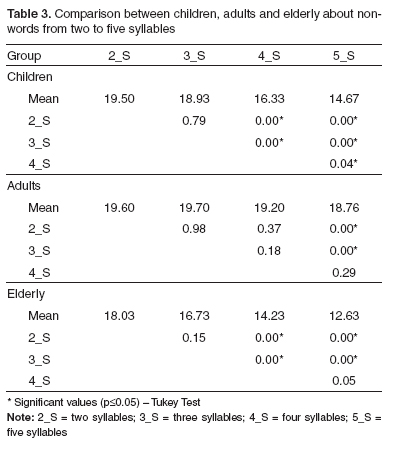
PURPOSE: Considering phonological working memory abilities extend until a certain age and can decline with aging, this study had the aim to verify the performance of individuals without language deficits at different ages in tasks that assess the phonological working memory (non-words and digits). METHODS: The study involved 90 normal individuals: 30 children (with ages between 6 and 8 years), 30 adults (ages between 19 and 35 years), and 30 elderly (60 years old or older). The selected subjects were submitted to a phonological working memory assessment that included a task of non-words repetition, consisting of the repetition of 40 invented two- to five-syllable words, and a task of repetition of digits, which should be repeated in direct and reverse order. The results were statistically analyzed. RESULTS: There were differences between the groups of children, adults and elderly (elderly < children < adults) in the total score of the non-words repetition task. In the digits repetition task, the difference occurred in all groups in the direct order, in the reverse order, and in the total score (children < elderly < adults). CONCLUSION: The elderly have worse performance in phonological working memory tasks, suggesting that this ability declines with the aging process. The adults present better performance, evidencing that they have better abilities to store verbal material.
Language development; Memory; Cognition; Aging; Evaluation; Age effect