Abstract
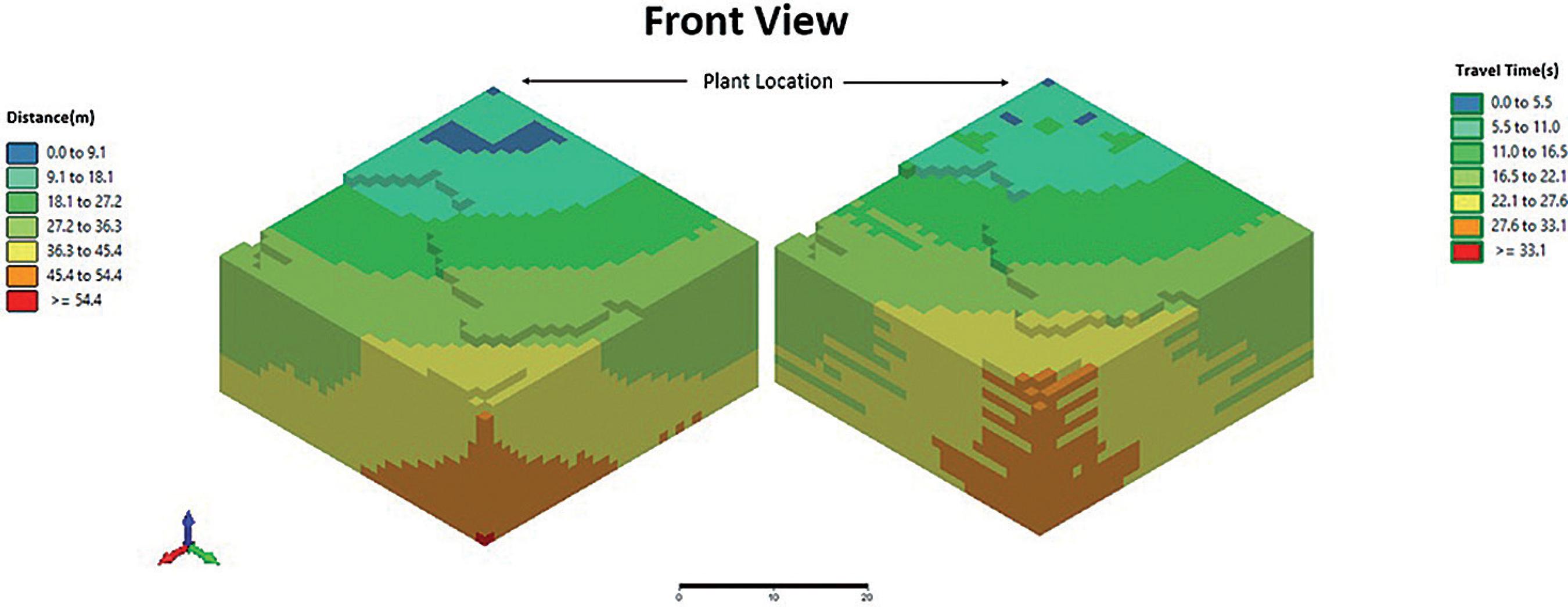
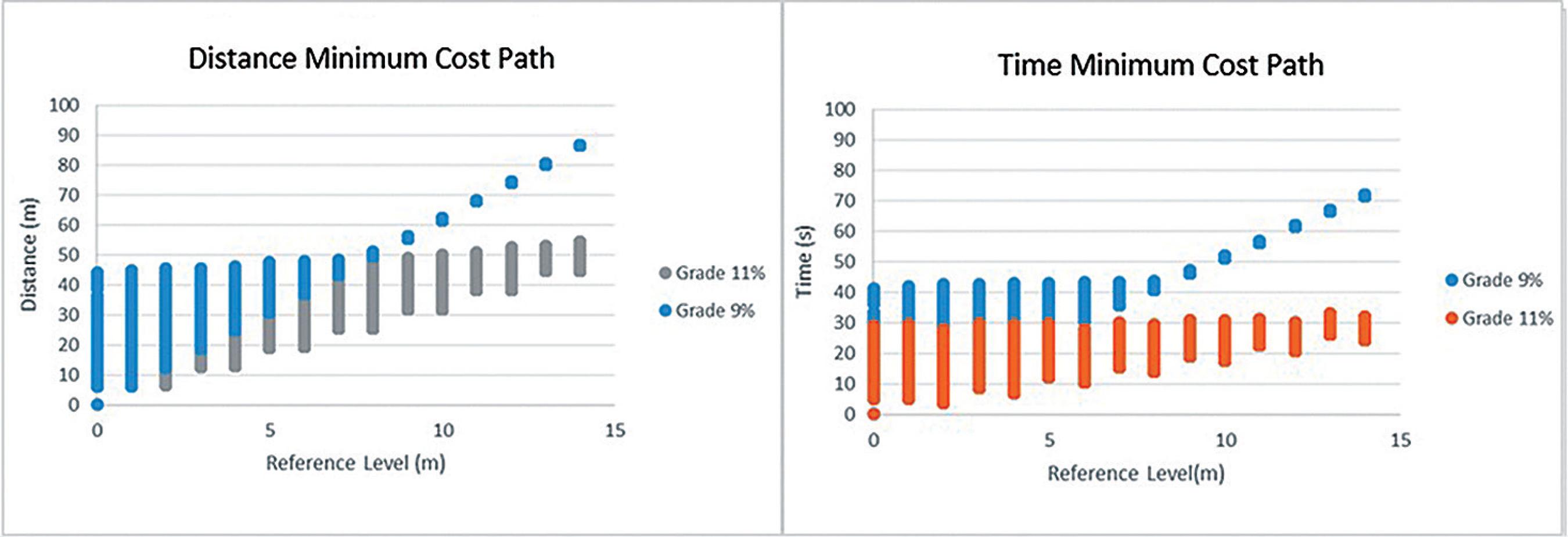
The transport distance in a mining operation strongly influences a mine operation revenue and its operational cycle because it is a fundamental part of the total mining costs. Generally, the transport route is determined based on an engineer's practical knowledge, which does not consider any mechanism to optimize the possible routes to be taken. In an attempt to establish a methodology for calculating the path that results in minimum costs to transport the mined block to its destination, the Dijkstra methodology is applied to a tree graph analysis, where the mining blocks are analysed as nodes of the tree. The transport cost is reflected as the arc of the graphs, which can use the Euclidean distance or the transport time for the calculation of the minimum path. The result obtained from the Dijkstra algorithm provided a non-operational route; to overcome this problem, an adjustment was performed through non-parametric equations. In this manner, it was possible to determine the transport costs for each block of the model. The paths based on Euclidean distance and transport time showed a tendency to increase for deeper mining regions. Identifying areas of largest growth and correctly quantifying their values increase the efficiency of mining planning.
keywords:
fleet costs; Dijkstra; optimized path; transport time; transport distance

 (Source: Authors)
(Source: Authors)
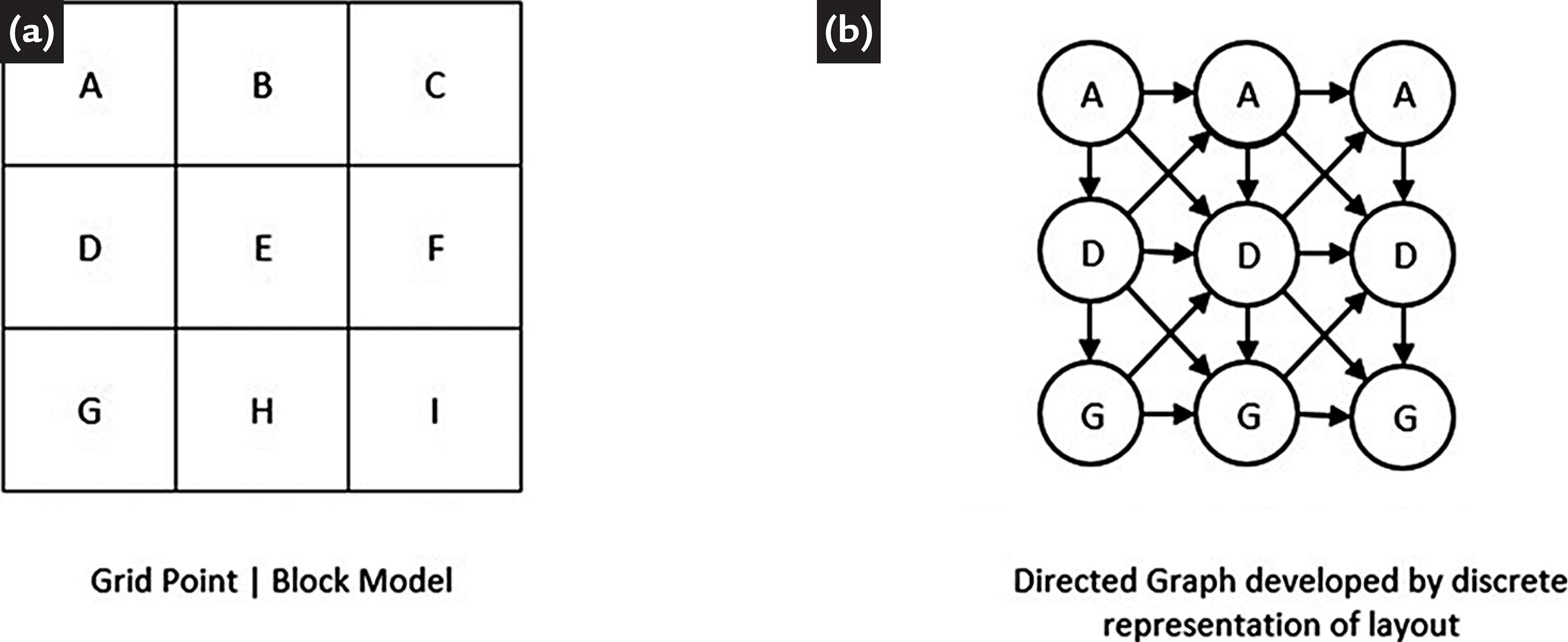
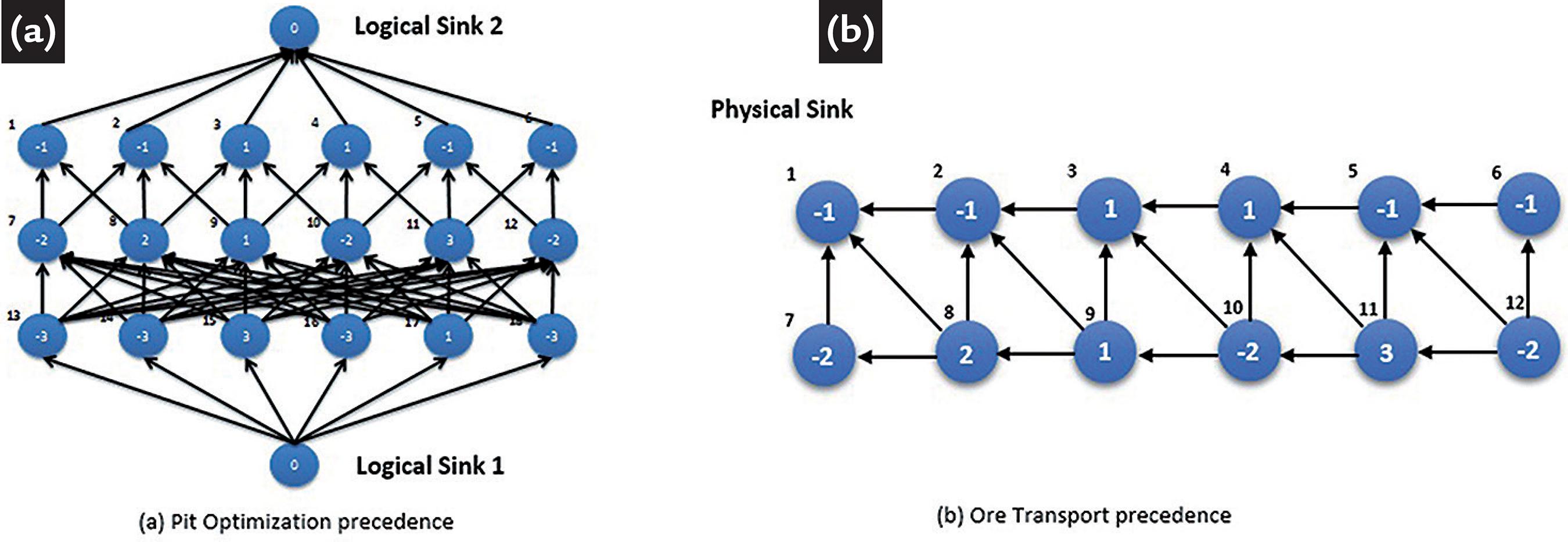 (Adapted from Souza (
(Adapted from Souza (