Abstracts
We report a case of a 19-year-old woman presenting bilateral neurosensorial hearing loss, mental abnormalities, and loss of visual field in the left eye. Visual acuity was 20/20 in OD and 20/25 in OS. Patient was examined systemically. Audiometry showed sensorineural hearing loss in both ears. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain revealed multiple small lesions in the white matter in both cerebral hemispheres and at the corpus callosum. Fundoscopy showed bilateral normal optic disc and sheathing of the arterioles in the middle periphery of OD. Retinal edema and cotton-wool spots were observed. Fluorescein angiography showed bilateral peripheral occlusive arterial vasculopathy. The patient was diagnosed with Susac syndrome and treated with quetiapine fumarate, flunitrazepam, and prednisone, which resulted in stabile outcome. This case shows that a high index of suspicion leading to early recognition and treatment is important to avoid irreversible damage.
Susac syndrome; Retinal artery occlusion; Hearing loss; Corpus callosum; Fluorescein angiography; Humans; Female; Adult; Case reports
Relatamos o caso de uma mulher de 19 anos apresentando perda auditiva neurossensorial bilateral, anormalidades mentais e perda de campo visual no olho esquerdo. A acuidade visual era 20/20 em OD e 20/25 em OE. Paciente foi sistematicamente investigada, audiometria mostrou perda auditiva neurossensorial nos dois ouvidos e ressonância magnética nuclear (RNM) cerebral mostrou múltiplas pequenas lesões na substância branca em ambos os hemisférios cerebrais e no corpo caloso. A fundoscopia mostrou disco óptico normal bilateral, e embainhamento das arteríolas na média periferia do olho direito. Edema de retina e exsudatos algodonosos foram vistos. Angiofluoresceinografia mostrou vasculopatia arterial obstrutiva periférica bilateral. A paciente foi diagnosticada com síndrome Susac e tratada com fumarato de quetiapina, flunitrazepam e prednisona resultando em estabilização do quadro. Este caso mostra que um alto índice de suspeita levando ao reconhecimento precoce e tratamento é importante para evitar o diagnóstico tardio.
Síndrome de Susac; Oclusão da artéria retiniana; Perda auditiva; Corpo caloso; Angiofluoresceinografia; Humano; Femino; Adulto; Relatos de casos
INTRODUCTION
Susac syndrome (SS), also known as retinal-cerebral-cochlear disease, although rare, needs to be considered as a differential diagnosis when unexplained visual field or visual acuity loss is detected in a patient. The triad of clinical symptoms that may not all be present at initial stages include diffuse encephalopathy, branch retinal artery occlusion, and sensorineural hearing loss(11 Rennebohm R, Susac JO, Egan RA, Daroff RB. Susac's Syndrome-update. J Neurol Sci. 2010;299(1-2):86-91.).
The etiology and pathogenesis of SS are not clearly understood. Autoimmune processes leading to the damage and inflammation-related occlusion of the microvessels in the brain, retina, and inner ear may play a causal role(22 Susac JO, Egan RA, Rennebohm RM, Lubow M. Susac syndrome: 1975-2005 microangiopathy/autoimmune endotheliopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2007;257(1-2):270-2.). Electroencephalogram, audiometry, fluorescein angiography (FA), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain sensitively detects the lesions(33 Dorr J, Jarius S, Wildemann B, Ringelstein EB, Schwindt W, Deppe M, et al. [Susac syndrome: an interdisciplinary challenge]. Nervenarzt. 2011;82(10):1250-63. Epub 2011/04/12. Susac-Syndrom: Eine interdisziplinare Herausforderung.).
Retinal abnormalities may have different clinical features. When arteriolar abnormalities are observed close to the central vision, symptoms of visual loss are more evident and the diagnosis may be faster. However, most cases have peripheral arteriolar micro-occlusive events, resulting in late ophthalmologic evaluation(44 Milbratz GH, Marquardt FA, Guimaraes Neto HP, Marquardt DA, Souza ES. Retinal vasculitis in Susac syndrome: case report. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009;72(3):397-9. Epub 2009/08/12.).
Multifocal arteriolar wall hyperfluorescence and peripheral branch artery occlusion can occur in normal-appearing fundus. Gass plaques (GP), which are yellow-white deposits seen at the mid segments of the arteriole, are a helpful finding for the diagnosis(55 Egan RA, Ha Nguyen T, Gass JD, Rizzo JF, 3rd, Tivnan J, Susac JO. Retinal arterial wall plaques in Susac syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135(4):483-6. Epub 2003/03/26.). If an initial FA is normal, it should be repeated at intervals during the early course of definite or suspected SS. FA abnormalities serve as a valuable biomarker, and serial FA may be useful in monitoring the effect of the treatment(11 Rennebohm R, Susac JO, Egan RA, Daroff RB. Susac's Syndrome-update. J Neurol Sci. 2010;299(1-2):86-91.).
The natural history and outcomes of SS are not fully understood. The disease may be active for several months and the time to remission can be long(44 Milbratz GH, Marquardt FA, Guimaraes Neto HP, Marquardt DA, Souza ES. Retinal vasculitis in Susac syndrome: case report. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009;72(3):397-9. Epub 2009/08/12.). After remission it results in various cognitive and functional damages. However, serious loss of vision is not observed in the majority of the patients.
The objectives of this study were to report a case of SS, its clinical manifestations, and to discuss the variability in clinical findings as well as management.
RESULTS
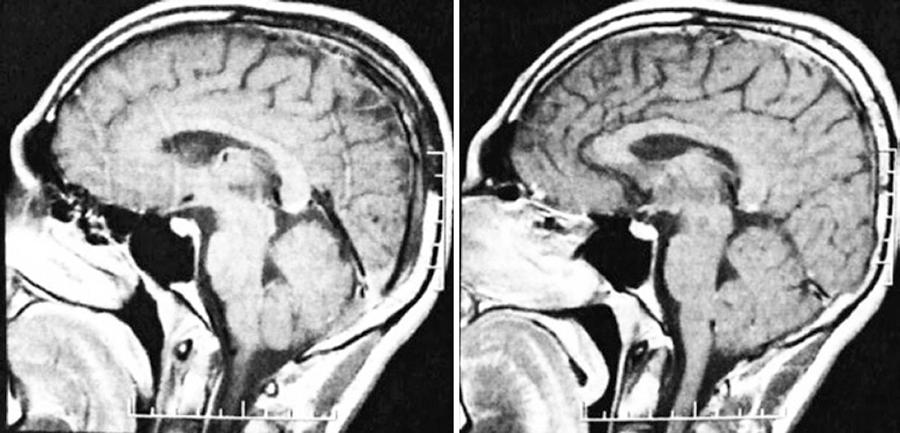
A 19-year-old female was referred by a neurologist because of visual field loss in the left eye that lasted for 10 days. Three months earlier, the patient was examined for neurological abnormalities associated with bilateral hearing loss and underwent audiometry, impedance testing, brain MRI, and laboratory evaluations. The audiometry showed severe sensorineural hearing loss in the right ear and moderate sensorineural hearing loss in the left ear. The brain MRI showed multiple small lesions in the white matter in both cerebral hemispheres and at the corpus callosum (Figure 1). The total complement, complement 3 and 4, antinuclear factor, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and T4 thyroid level were normal.
Ophthalmologic examination showed best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of 20/20 in OD and 20/25 in OS. Fundoscopy showed bilateral normal optic disc and sheathing of the arterioles in the middle periphery of OD. Retinal edema was seen in the temporal inferior quadrant and at the mid-peripheral temporal superior region associated with cotton-wool spots and sheathing of the arterioles nasally in the left eye.
FA showed bilateral normal choroidal perfusion-arterial nonperfusion at the peripheral superior and nasal inferior areas in right eye (OD) and in late phase temporal and inferiorly in left eye (OS), suggesting bilateral peripheral occlusive arterial vasculopathy, which was more evident in the left eye. Unusual leakage pattern of arterial wall in the temporal inferior area, but not located in the arterial occlusion area was noted in the right eye (Figure 2).
FA images of both eyes of patient 2 shows microarterial nonperfusion in the peripheral retina. A) Microarterial occlusion in the peripheral retina temporosuperiorly in the left eye. B) A similar image of the peripheral retina temporally in the left eye shows a clearer image of the nonperfused arterioles. C) Unusual leakage pattern of arterial wall hyperfluorescence in the temporal inferior area not located in the arterial occlusion area. D) FA of the right eye shows important nonperfusion of the arterioles in the temporosuperior quadrant of the retina.
The clinical findings and the exclusion of other diseases resulted in the diagnosis of SS. Quetiapine fumarate (100 mg/day), flunitrazepam (0.5 mg/day), and prednisone (40 mg/day) were prescribed. Photocoagulation was applied to the ischemic areas to prevent retinal neovascularization.
DISCUSSION
Susac syndrome has an unknown etiology and is associated with varying outcomes(22 Susac JO, Egan RA, Rennebohm RM, Lubow M. Susac syndrome: 1975-2005 microangiopathy/autoimmune endotheliopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2007;257(1-2):270-2.,44 Milbratz GH, Marquardt FA, Guimaraes Neto HP, Marquardt DA, Souza ES. Retinal vasculitis in Susac syndrome: case report. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009;72(3):397-9. Epub 2009/08/12.,66 Rennebohm RM, Susac JO. Treatment of Susac syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2007;257(1-2):215-20.). If not suspected of having the syndrome, the diagnosis may be delayed. Once the diagnosis is made, close neurologic, otorhinolaryngologic, and ophthalmologic follow-up examinations are very important(33 Dorr J, Jarius S, Wildemann B, Ringelstein EB, Schwindt W, Deppe M, et al. [Susac syndrome: an interdisciplinary challenge]. Nervenarzt. 2011;82(10):1250-63. Epub 2011/04/12. Susac-Syndrom: Eine interdisziplinare Herausforderung.) since the damage could be irreversible.
A specific routine for the management of this disease has not been described and
approaches can be didactically divided into two strategies, namely the management of
complications and the prevention of recurrences. The complications must be evaluated and
treated according to the preference of the ophthalmologist to reestablish function. ASA,
anticoagulants, steroids, immunosuppressors, and immunoglobulins have been shown to be
effective for the prevention of recurrence(66 Rennebohm RM, Susac JO. Treatment of Susac syndrome. J Neurol Sci.
2007;257(1-2):215-20.
7 Naacke H, Heron E, Bourcier T, Borderie V, Laroche L. [A new case of
Susac syndrome and a review of the literature]. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2003;26(3):284-9.
French.-88 Coppeto JR, Currie JN, Monteiro ML, Lessell S. A syndrome of
arterial-occlusive retinopathy and encephalopathy. Am J Ophthalmol.
1984;98(2):189-202.).
We observed no neovascularization in the peripheral retina and a BCVA of 20/20 in the case.
The current study was limited by the retrospective design, the diversity of the therapeutic approaches, and the difficulties in evaluating the efficacy of treatment. However, the results of our study, which analyzed the diversity in systemic manifestations from early symptoms are important due to the low disease prevalence.
Susac syndrome is considered as a rare disease. A high index of suspicion, which could lead to early recognition and treatment is important to avoid late diagnosis and to minimize the risk for persistent impairment. Prospective studies analyzing the effectiveness of the proposed treatments are critical for the establishment of therapeutic approaches for each clinical finding.
-
Study conducted at Department of Ophthalmology, Hospital Evangélico, Curitiba, PR and Department of Ophthalmology, Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil.
REFERENCES
-
1Rennebohm R, Susac JO, Egan RA, Daroff RB. Susac's Syndrome-update. J Neurol Sci. 2010;299(1-2):86-91.
-
2Susac JO, Egan RA, Rennebohm RM, Lubow M. Susac syndrome: 1975-2005 microangiopathy/autoimmune endotheliopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2007;257(1-2):270-2.
-
3Dorr J, Jarius S, Wildemann B, Ringelstein EB, Schwindt W, Deppe M, et al. [Susac syndrome: an interdisciplinary challenge]. Nervenarzt. 2011;82(10):1250-63. Epub 2011/04/12. Susac-Syndrom: Eine interdisziplinare Herausforderung.
-
4Milbratz GH, Marquardt FA, Guimaraes Neto HP, Marquardt DA, Souza ES. Retinal vasculitis in Susac syndrome: case report. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009;72(3):397-9. Epub 2009/08/12.
-
5Egan RA, Ha Nguyen T, Gass JD, Rizzo JF, 3rd, Tivnan J, Susac JO. Retinal arterial wall plaques in Susac syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135(4):483-6. Epub 2003/03/26.
-
6Rennebohm RM, Susac JO. Treatment of Susac syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2007;257(1-2):215-20.
-
7Naacke H, Heron E, Bourcier T, Borderie V, Laroche L. [A new case of Susac syndrome and a review of the literature]. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2003;26(3):284-9. French.
-
8Coppeto JR, Currie JN, Monteiro ML, Lessell S. A syndrome of arterial-occlusive retinopathy and encephalopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984;98(2):189-202.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
May-Jun 2014
History
-
Received
02 Dec 2013 -
Accepted
06 Dec 2013