Abstract
Introduction:
This study reports for the first time the infection of Rhodnius montenegrensis by Trypanosoma rangeli.
Methods:
The triatomines were manually collected in Attalea speciosa in the municipality of Buritis, Rondônia. The identification of the trypanosomatid species was confirmed by multiplex PCR.
Results:
All of the collected triatomines were R. montenegrensis. The analysis confirmed that all of the adults were infected with the epimastigote form of T. rangeli.
Conclusions:
This report of a new vector of T. rangeli raises a warning for the State of Rondônia because the simultaneous presence of T. rangeli with T. cruzi in the same geographic region enables the occurrence of mixed infections in hosts and vectors, which complicates the differential diagnosis.
Triatominae; Trypanosoma rangeli; Rhodnius montenegrensis; Western Amazon
Trypanosoma rangeli is a heterogeneous hemoflagellate protozoan discovered in Venezuela in the intestinal contents of Rhodnius prolixus and, in addition to Trypanosoma cruzi, is the only trypanosome parasite of man found in Central and South America11. Ramirez LE, Machado MI, Maywald PG, Matos A, Chiari E, Silva EL. Primeira evidência de Trypanosoma rangeli no sudeste do Brasil, região endêmica para doença de Chagas. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 1998; 31:99-102..
Trypanosoma rangeli has been reported in Colombia, Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Guyana, Fr Guyana, Uruguay, Paraguay, Peru, Chile, Venezuela, Trinity, Argentina, Ecuador, Bolivia and Brazil22. Vargas PAO. Genes de Cisteíno Proteases (Catepsina L-like) de Trypanosoma rangeli: Polimorfismo, Relações Filogenéticas e Alvos Para Diagnóstico e Genotipagem. [Dissertation]. [São Paulo]: Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas da Universidade de São Paulo; São Paulo, 2008. , 33. Guhl F, Vallejo GA. Trypanosoma (Herpetosoma) rangeli Tejera, 1920: an updated review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2003; 98:435-442.. In Brazil, it was found in wild animals and triatomines in the south (Santa Catarina), southeast (Minas Gerais), northeast (Ceará, Alagoas and Bahia), central west (Federal District, Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul) and north (Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Acre and Tocantins) regions22. Vargas PAO. Genes de Cisteíno Proteases (Catepsina L-like) de Trypanosoma rangeli: Polimorfismo, Relações Filogenéticas e Alvos Para Diagnóstico e Genotipagem. [Dissertation]. [São Paulo]: Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas da Universidade de São Paulo; São Paulo, 2008. , 44. Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Cura C, Schijman AG, Cuba CAC. Infestation of Mauritia flexuosa palms by triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian savanna. Acta Trop 2012; 121:105-111. , 55. Diotaiuti I, Silveira AC, Elias M, Steindel M. The possibility of occurrence of Trypanosoma rangeli in the State of Tocantins, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1992; 87:451..
From the earliest reports of human infection by T. rangeli in the Americas, more than 2,700 cases of human rangeliosis have been confirmed66. Grisard EC, Steindel M. Trypanosoma (Herpetossoma) rangeli. In: Neves PN, Melo AL, Linarde PM, Vitor RWA, editors. Parasitologia Humana. Vol XI. São Paulo: Atheneu 2005 ; p. 109-113. . The only cases of human infection reported in Brazil have been in the States of Amazonas and Bahia77. Coura JR, Fernandes O, Arboleda M, Barrett TV, Carrada N, Degrave W, et al. Human Infection by Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian Amazon. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1996; 90:278-279. , 88. Sousa MA, Silva Fonseca T, Santos BN, Santos Pereira SM, Carvalhal C, Hasslocher Moreno AM. Trypanosoma rangeli Tejera, 1920, in chronic Chagas disease patients underambulatory care at the Evandro Chagas Clinical Research Institute (IPEC-FIOCRUZ, Brazil). Parasitol Res 2008; 103:697-703. , but in contrast to T. cruzi, T. rangeli is not considered pathogenic to its vertebrate hosts33. Guhl F, Vallejo GA. Trypanosoma (Herpetosoma) rangeli Tejera, 1920: an updated review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2003; 98:435-442..
The transmission of T. rangeli to vertebrates is mainly related to species of triatomines of the genus Rhodnius, with 12 species reported as their natural vectors; of these 12 species, 6 are found in Brazil (Rhodnius neglectus, Rhodnius nasutus, Rhodnius neivai, Rhodnius domesticus, Rhodnius pictipes and Rhodnius robustus)22. Vargas PAO. Genes de Cisteíno Proteases (Catepsina L-like) de Trypanosoma rangeli: Polimorfismo, Relações Filogenéticas e Alvos Para Diagnóstico e Genotipagem. [Dissertation]. [São Paulo]: Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas da Universidade de São Paulo; São Paulo, 2008. , 99. Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Galvão C, Costa J, Peterson AT. Geographic distribution of Chagas disease vectors in Brazil based on ecological niche modeling. J Trop Med 2012: 1-15. , 1010. Barrett TV, Oliveira TS. A trypanosome, indistinguishable from Trypanosoma rangeli, in the haemolymph of Rhodnius domesticus from Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1977; 71:445-446. The latter species may have been erroneously described in the State of Rondônia by some researchers1111. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Rosa RM, Camargo LMA. First report of Eratyrus mucronatus, Stal, 1859, (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) in the State of Rondonia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2011; 44:511-512 , 1212. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Camargo LMA, Rosa RM. Natural infection of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) by trypanosomatids in two different environments in the municipality of Ouro Preto do Oeste - Rondônia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2012; 45:395-398. because of its similarity to R. montenegrensis, which had not been described at that time.
Rhodnius montenegrensis was first described in 2012 from specimens collected in the municipality of Monte Negro, Rondônia, Brazil. Initially, it was identified as R. robustus, but subsequent studies showed that it was a new species1313. Rosa JA, Rocha CS, Sueli G, Mara CP, Vagner JM, Júlio CRFF, et al. Description of Rhodnius montenegrensis n.sp. (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) from the state of Rondônia, Brazil. Zootaxa 2012; 3478:62-76..
The present study reports the first documented infection of Rhodnius montenegrensis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) by Trypanosoma rangeli.
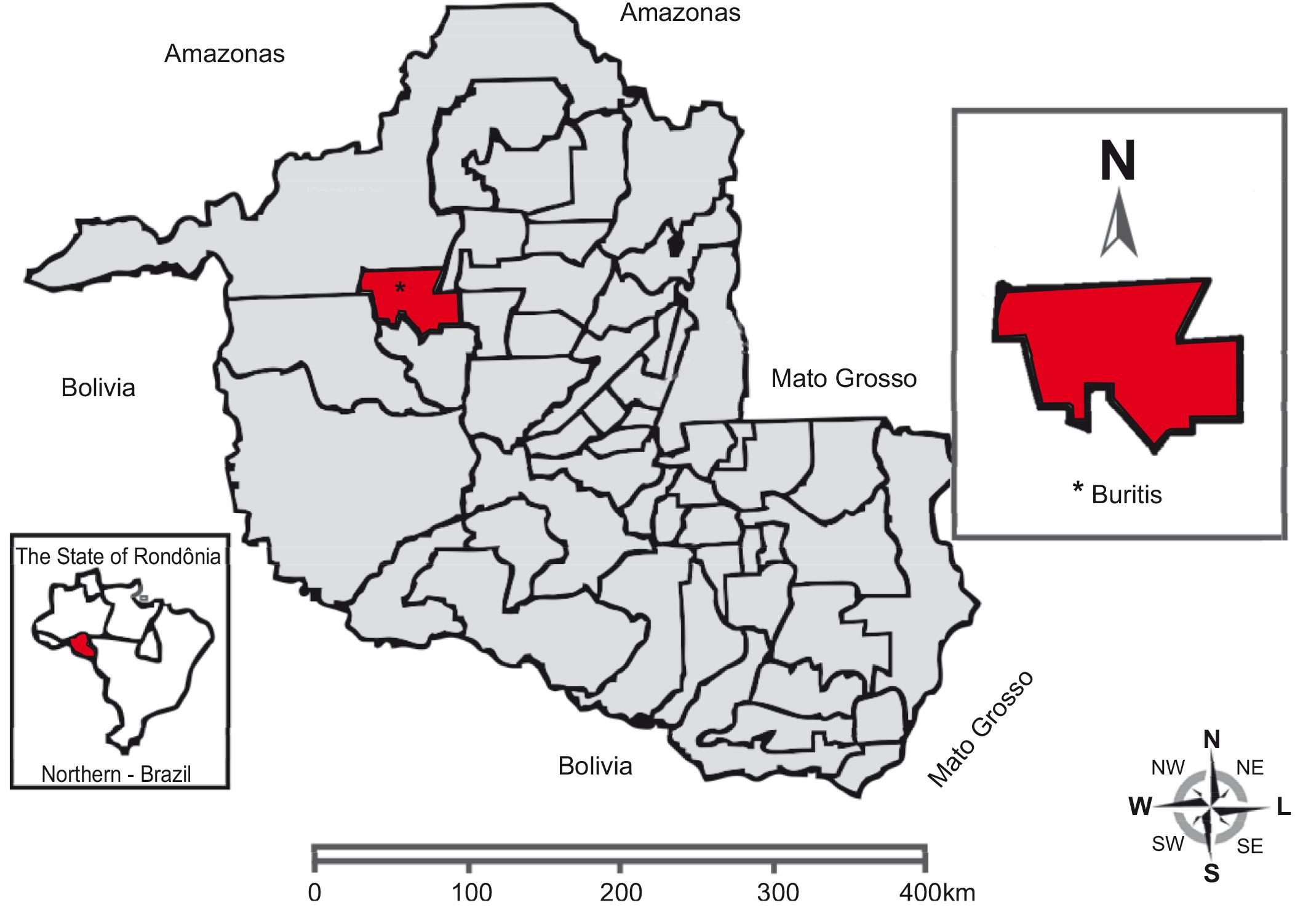
Monthly collections were performed with permission from the Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis - IBAMA), permanent license No. 14934-1 from June to December of 2012 in the rural pasture area in the municipality of Buritis, Rondônia (Latitude 9º57'32.3"S - Longitude 64º08'05.2"W) (Figure 1).
Triatomines were collected from 14 specimens of Attalea speciosa (babassu) twice a month in the morning after downing a tree with a chainsaw and removing the bracts. Triatomines were manually collected through active searching. The A. speciosa were randomly selected, drawing any 1 from a group of 20.
The collected specimens were sent in a cooler at room temperature to the microscopy laboratory at the School of Education and Environment (Faculdade de Educação e Meio Ambiente - FAEMA) in the municipality of Ariquemes, Rondônia, where wet mount analysis and smear analysis of the adult triatomines' rectal contents were performed with an optical microscope at 1600X magnification after staining with triarylmethane (0.1%), xanthene (0.1%) and thiazine (0.1%) (Figure 2).
The identification of the trypanosomatid species was confirmed by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in collaboration with the Department of Parasitology at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, São Paulo University (ICB-USP), São Paulo (SP), Brazil.
Parasite deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was extracted from the triatomine rectal samples using a Qiagen DNA extraction kit. The multiplex PCR was performed according to Fernandes et al.1414. Fernandes O, Santos SS, Cupolillo E, Mendonça B, Derre R, Junqueira ACV, et al. A mini-exon multiplex polymerase chain reaction to distinguish the major groups of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian Amazon. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001; 95:97-99.. This method amplifies a portion of the non-transcribed spacer of the mini-exon gene that varies between T. cruzi and T. rangeli species and between lines 1 and 2 of T. cruzi. The following primers were used: TC1, 5'-ACACTTTCTGGCGCTGATCG-3'; TC2, 250bp, 5'-TTGCTCGCACACTCGGCTGCAT-3'; Z3, 150bp, 5'-CCGCGCACAACCCCTATAAAAATG-3'; TR, 100bp, 5'-CCTATTGTGATCCCCATCTTCG-3' and EXON, 5'-TACCAATATAGTACAGAACTG-3'. The reaction mixture consisted of 100pmol of each primer and 150μM dNTPs in a buffer composed of 10mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 1.5mM MgCl2, 25mM KCl, 0.1mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 2.5U of Taq DNA polymerase and 10ng of genomic DNA in a total volume of 50μL. The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: an initial step of 5min at 95°C, 34 cycles of 30sec at 94°C, 30sec at 55°C and 30sec at 72°C and a final extension of 10min at 72°C. The following reference strains were used as controls in each reaction: TC1, X10 Clone 1; TC2, Strain Y; Z3, Emerald Clone 1 and T. rangeli R1625. The amplified products were subjected to electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel at 100V for 1h. After electrophoresis, the DNA was stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under ultraviolet light. A molecular marker of 50 base pairs was used as a size control for the amplified fragments.
The identification of the adult triatomine species was conducted based on the keys previously described by and Rosa et al.1212. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Camargo LMA, Rosa RM. Natural infection of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) by trypanosomatids in two different environments in the municipality of Ouro Preto do Oeste - Rondônia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2012; 45:395-398..
A total of 120 triatomines were collected, providing an average of 8.6 specimens per Attalea speciosa, which is below the average reported by other studies in the state99. Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Galvão C, Costa J, Peterson AT. Geographic distribution of Chagas disease vectors in Brazil based on ecological niche modeling. J Trop Med 2012: 1-15. , 1111. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Rosa RM, Camargo LMA. First report of Eratyrus mucronatus, Stal, 1859, (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) in the State of Rondonia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2011; 44:511-512. Of those triatomines, only 13 (10.8%) were adults, and all were R. montenegrensis.
The analysis confirmed that all of the adults were infected with trypanosomatids, with the T. rangeli in the epimastigote form. This work is the first report of the infection of R. montenegrensis by T. rangeli, which increases the total number of species of triatomines of the genus Rhodnius infected by this protozoan to 13, including 7 species found specifically in Brazil.
This report of a new vector of T. rangeli presents a warning to the State of Rondônia because the simultaneous presence of T. rangeli and T. cruzi in the same geographic region enables the occurrence of mixed infections in both vertebrate hosts and vectors, which complicates the differential diagnosis of an infection1515. Miles MA, Arias JR, Valente SAS, Naiff RD, Souza AA, Povoa MM, et al. Vertebrate hosts and vetors of Trypanosoma rangeli in the Amazon basin of Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1983; 32:1251-1259.. This possibility is concerning, especially in a state where there are reports of other vector species of T. rangeli, such as R. pictipes and R. robustus 1111. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Rosa RM, Camargo LMA. First report of Eratyrus mucronatus, Stal, 1859, (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) in the State of Rondonia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2011; 44:511-512,1212. Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Camargo LMA, Rosa RM. Natural infection of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) by trypanosomatids in two different environments in the municipality of Ouro Preto do Oeste - Rondônia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2012; 45:395-398. .
REFERENCES
-
1Ramirez LE, Machado MI, Maywald PG, Matos A, Chiari E, Silva EL. Primeira evidência de Trypanosoma rangeli no sudeste do Brasil, região endêmica para doença de Chagas. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 1998; 31:99-102.
-
2Vargas PAO. Genes de Cisteíno Proteases (Catepsina L-like) de Trypanosoma rangeli: Polimorfismo, Relações Filogenéticas e Alvos Para Diagnóstico e Genotipagem. [Dissertation]. [São Paulo]: Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas da Universidade de São Paulo; São Paulo, 2008.
-
3Guhl F, Vallejo GA. Trypanosoma (Herpetosoma) rangeli Tejera, 1920: an updated review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2003; 98:435-442.
-
4Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Cura C, Schijman AG, Cuba CAC. Infestation of Mauritia flexuosa palms by triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian savanna. Acta Trop 2012; 121:105-111.
-
5Diotaiuti I, Silveira AC, Elias M, Steindel M. The possibility of occurrence of Trypanosoma rangeli in the State of Tocantins, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 1992; 87:451.
-
6Grisard EC, Steindel M. Trypanosoma (Herpetossoma) rangeli. In: Neves PN, Melo AL, Linarde PM, Vitor RWA, editors. Parasitologia Humana. Vol XI. São Paulo: Atheneu 2005 ; p. 109-113.
-
7Coura JR, Fernandes O, Arboleda M, Barrett TV, Carrada N, Degrave W, et al. Human Infection by Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian Amazon. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1996; 90:278-279.
-
8Sousa MA, Silva Fonseca T, Santos BN, Santos Pereira SM, Carvalhal C, Hasslocher Moreno AM. Trypanosoma rangeli Tejera, 1920, in chronic Chagas disease patients underambulatory care at the Evandro Chagas Clinical Research Institute (IPEC-FIOCRUZ, Brazil). Parasitol Res 2008; 103:697-703.
-
9Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Galvão C, Costa J, Peterson AT. Geographic distribution of Chagas disease vectors in Brazil based on ecological niche modeling. J Trop Med 2012: 1-15.
-
10Barrett TV, Oliveira TS. A trypanosome, indistinguishable from Trypanosoma rangeli, in the haemolymph of Rhodnius domesticus from Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1977; 71:445-446
-
11Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Rosa RM, Camargo LMA. First report of Eratyrus mucronatus, Stal, 1859, (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) in the State of Rondonia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2011; 44:511-512
-
12Meneguetti DUO, Trevisan O, Camargo LMA, Rosa RM. Natural infection of triatomines (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) by trypanosomatids in two different environments in the municipality of Ouro Preto do Oeste - Rondônia, Brazil. Rev Soc Bra Med Trop 2012; 45:395-398.
-
13Rosa JA, Rocha CS, Sueli G, Mara CP, Vagner JM, Júlio CRFF, et al. Description of Rhodnius montenegrensis n.sp. (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) from the state of Rondônia, Brazil. Zootaxa 2012; 3478:62-76.
-
14Fernandes O, Santos SS, Cupolillo E, Mendonça B, Derre R, Junqueira ACV, et al. A mini-exon multiplex polymerase chain reaction to distinguish the major groups of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli in the Brazilian Amazon. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001; 95:97-99.
-
15Miles MA, Arias JR, Valente SAS, Naiff RD, Souza AA, Povoa MM, et al. Vertebrate hosts and vetors of Trypanosoma rangeli in the Amazon basin of Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1983; 32:1251-1259.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
Mar 2013 -
Date of issue
May-Jun 2014
History
-
Received
07 Sept 2013 -
Accepted
27 Nov 2013