ABSTRACT:
Find shade-tolerant species is essential to the success of silvopastoral systems, increasingly frequent in recent years. In legumes, which have potential of biological nitrogen fixation, there is a great lack of knowledge when in shaded environments.The cultivation of four tropical forage (Neonotonia wightii, Pueraria phaseoloides, Macrotyloma axilare and Arachis pintoi) was evaluated when submitted to artificial shade levels (30, 50 and 70% shade) and in full sun during water and drought seasons. The design used was in randomized complete blocks in a sub-divided plot scheme with four replications. In the Water-season the Forage Peanuts had higher forage production in full sun (11 ton ha-1 DM), and under shade did not differ from Perennial Soybean, higher than the others in all levels of shade. In Drought-season the forage production was 61% lower than in Water-season. The highest crude protein levels were reported in Forage Peanuts, Tropical Kudzu and Perennial Soybean, 19.0; 18.3 and 18.2% respectively in the Water-season. Forage Peanuts is a good option for use in silvopastoral systems although there is a small reduction in forage production (average of 23.7%). In general, species of fabaceae showed a greater reduction in forage production in the period of water deficit; however, shading at levels of 30% to 50% contribute to mitigation of water shortage. Although, there is a small reduction in forage production, withexception of perennial soybeans in dry season, it is advisable to use tropical forage legumes in silvopastoral systems, since forage quality is not affected by shade.
Key words:
Fabaceae; forage production; chemical composition
RESUMO:
Encontrar espécies tolerantes ao sombreamento é essencial para o sucesso dos sistemas silvipastoris, cada vez mais frequentes nos últimos anos. Em se tratando de leguminosas, que possuem potencial de fixação biológica de nitrogênio, há uma grande carência de conhecimento em ambientes sombreados. Objetivou-se avaliar o cultivo de quatro leguminosas forrageiras tropicais (Neonotonia wightii, Pueraria phaseoloides, Macrotyloma axilare e Arachis pintoi) submetidas a diferentes níveis de sombreamento artificial (30, 50 e 70% de sombra) e em pleno sol durante as estações de água e seca. O delineamento utilizado foi o de blocos completos casualizados, em esquema de parcelas subdivididas, com quatro repetições. Na estação das águas, o Amendoim Forrageiro teve maior produção de forragem a pleno sol (11 ton ha-1 MS), e sob sombreamento não diferiu da Soja perene, superiores às demais em todos os níveis de sombra. Na estação de seca, as espécies apresentaram produção de forragem 61% menor do que a estação da água. Os níveis mais altos de proteína bruta foram encontrados em Amendoim Forrageiro, Kudzu tropical e Soja Perene, 19,0; 18,3 e 18,2%, respectivamente, na estação da água. O Amendoim Forrageiro é uma boa opção para uso em sistemas silvipastoris, embora haja uma pequena redução na produção de forragem (média de 23,7%). Em geral, espécies de Fabaceae apresentaram maior redução na produção de forragem no período de déficit hídrico, porém o sombreamento em níveis de 30% a 50% contribuiram para a mitigação da escassez hídrica. Embora haja uma pequena redução na produção de forragem, com exceção da Soja Perene na estação seca, é aconselhável o uso dessas leguminosas forrageiras tropicais nos sistemas silvipastoris, uma vez que a qualidade da forragem é pouco afetada pela sombra.
Palavras-chave:
Fabaceae; produção de forragem; composição bromatológica
INTRODUCTION:
Brazil has great potential in terms of animal production, a result of interaction between large territorial extensions and tropical climate, which provides an excellent condition for animal exploitation. These characteristics make possible the use of pasture production systems, considering the development that is presented by tropical forages, which constitutes a low cost food and is the main component of cattle feeding (EUCLIDES, 2000EUCLIDES, V.P.B. Alternativas para intensificação da produção de carne bovina em pastagem. Campo Grande: Embrapa Gado de Corte, 2000. 65p. Available from: <Available from: https://www.embrapa.br/gado-de-corte/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/324156/alternativas-para-intensificacao-da-producao-de-carne-bovina-em-pastagem
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://www.embrapa.br/gado-de-corte/bus...
). Although, it occupies a prominent position on the world stage in animal production, Brazil still has unsatisfactory productivity indexes; however, it has been undergoing an accelerated modernization process (VILELA et al., 2006VILELA, D. et al. Desempenho de vacas da raça Holandesa em pastagem de Coastcross. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.35, p.555-561. 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/%0D/rbz/v35n2/a31v35n2.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.br/pdf/%0D/rbz/v35n2/a...
).
The Southeastern region of Brazil has a diverse climatic characteristic, due to its topography, its geographic position and, mainly, the dynamic aspects of the atmosphere, which include the meteorological systems of micro, meso and large scales, that act directly or indirectly in the pluvial regime, such as the South Atlantic Convergence Zone and the Cold Fronts, mainly responsible for rainfall and the South Atlantic Subtropical cyclone and the Upper Air Cyclonic Vortex, which, depending on their positions, cause great periods of drought (MINUZZI et al., 2007MINUZZI R.B et al. Climatologia do comportamento do período chuvoso da região sudeste do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, 2007, v.22, n.3, p.338-344. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-77862007000300007
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-77862007...
).
According to ALVES et al. (2005ALVES, L.M. et al. Início da estação chuvosa na região Sudeste do Brasil: Parte 1 - Estudos observacionais. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, v.20, n.3, p.385-394, 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://www.rbmet.org.br/port/revista/revista_artigo.php?id_artigo=143
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.rbmet.org.br/port/revista/rev...
) and PAIVA (1997PAIVA, C.M. Determinação das datas de início e fim da estação chuvosa e da ocorrência de veranicos na Bacia do Rio Doce. 1997. 65f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Meteorologia Agrícola) - Faculdade de Engenharia Agrícola, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, 1997. Available from: <Available from: http://www.locus.ufv.br/handle/123456789/11418
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.locus.ufv.br/handle/123456789...
), the rainy season in the Southeast region of Brazil is concentrated between October and March, when more than 80% of the annual rainfall occurs. Due to this characteristic, this well-defined precipitation regime is characterized as a monsoon system, similar to that of a monsoon region of Southeast Asia (VEIGA et al., 2002VEIGA, J.A.P. et al. A influência das anomalias de TSM dos oceanos Atlântico e Pacífico sobre as chuvas de monção da América do Sul. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, v.17, n.2, p.181-194, 2002. Available from: <Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37679270_A_influencia_das_anomalias_de_TSM_dos_Oceanos_Atlantico_e_Pacifico_sobre_as_chuvas_de_moncao_da_America_do_Sul
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication...
).
An interesting alternative to improve pasture efficiency, minimize production costs and make the pasture environment more sustainable it is by recommending to introduce legumes which contribute to diversifying the forage system, reducing risks of pests, diseases and degradation of pastures (SILVA & SALIBA, 2007SILVA, J.J.; SALIBA, E.O.S. Pastagens consorciadas: uma alternativa para sistemas extensivos e orgânicos. Veterinária e Zootecnia, v.14, p.8-18, 2007.). In addition, these forages present characteristics that make possible to increase the performance of grazing animals, such as: biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) in the soil, which positively influences pasture persistence and productivity, and improvement in nutritional value (FREITAS et al., 2011FREITAS, A.D.S. et al. Nodulação e fixação de nitrogênio por forrageiras da caatinga cultivadas em solos do semiárido paraibano. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.40, n.9, p.1856-1861, 2011.).
The interest in shade foraging has been growing in the last years, mainly due to the desire to associate pastures with trees (BARRIOS et al., 2008BARRIOS, R. et al. Efecto del sombreamiento artificial sobre el establecimiento de leguminosas promisorias como cobertura en palma aceitera en el estado Monagas. Agronomía Tropical, v.58, n.1, p. 31-34, 2008. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0002- 192X2008000100007&lng=es&nrm=iso
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?scri...
, GOBBI et al., 2010GOBBI, K.F. et al. Valor nutritivo do capim-braquiária e do amendoim forrageiro submetidos ao sombreamento. Archivos de Zootecnia, v.59, n.227, p-809-818, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/azoo/v59n227/art6.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/azoo/v59n227...
, NICODEMO et al., 2015NICODEMO, M.L.F. et al. Frequências de cortes em nove leguminosas forrageiras tropicais herbáceas cultivadas ao sol e sob plantação florestal. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia, v.67, n.3, p.809-818, 2015. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119...
) constituting silvopastoral systems (SSPs). In the case of forage species, is necessary to choose shade-tolerant species, with good productive capacity, adapted to the management and acclimated to the soil-climatic conditions (GARCIA & ANDRADE, 2001GARCIA, R.; ANDRADE, C.M.S. Sistemas silvipastoris na Região Sudeste. In: CARVALHO, M.M.; ALVIM, M.J.; CARNEIRO, J.C. (Ed.). Sistemas agroflorestais pecuários: opções de sustentabilidade para áreas tropicais e subtropicais. Juiz de Fora: Embrapa-CNPGL; FAO, 2001. p.173-187. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982011000900003
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982011...
).
Neonotonia wightii, Pueraria phaseoloides, Macrotyloma axilare, and Arachis pintoi belong to the Fabaceae family and are often used as forage legumes and are beneficial to agroforestry activities, including soil conservation, weed management, and increases in organic matter and nitrogen in the soil (SANTOS, et al., 2015SANTOS, L.D.T. et al.Phenotypic plasticity of Neonotoniawightii and Puerariaphaseoloides grown under different light intensities.Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences, v.87, n.1, p.520-528, 2015. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201520140017
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0001-376520152...
). Difficulties in the management of Fabaceae as well as high rates of weed infestation during the cultivation of these species are some of the obstacles of their use, as reported in sugarcane producing areas in Brazil (KUVA et al., 2007KUVA, M.A, et al. 2007. Fitossociologia de comunidades de plantas daninhas em agroecossistema cana-crua. Planta Daninha, v.25, n.3, p.501-511, 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/pd/v25n3/09.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.br/pdf/pd/v25n3/09.pdf...
). For VALLE and ZIMMER (2013VALLE, C.B.; ZIMMER, A.H.Leguminosas forrageiras em pastos consorciados: experiências do passado que podem fomentar o futuro. In: AS FORRAGEIRAS E AS SUAS RELAÇÕES COM O SOLO, O AMBIENTE E O ANIMAL. Anais... Lavras: UFLA, 2013. pp.17-28.), the main legume failures in pasture in the last 3 decades are the result of the use of genotypes with low resistance to diseases, low reser-voirtion rate in grazed pastures, inadequate animal management (super or sub grazing) and inadequate legume implantation and maintenance techniques in poor and acidic pastures.
ANDRADE et al. (2004ANDRADE, C.M.S. de; et al. Crescimento de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras tropicais sob sombreamento. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v.39, n.3, p.263-270, 2004. Available from> <Available from> http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab/article/view/6766/3822
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab...
) reported that the increase in the level of shade causes decrease of dry matter production. For this reason, it is necessary to identify the species that tolerate the best shade cultivation, as well as the levels of shading that interferes on the forage to obtain the advantages offered by the existing consortium in the SSPs (SOARES et al., 2009SOARES, A. B. et al. Influência da luminosidade no comportamento de onze espécies forrageiras perenes de verão. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.38, n.3, p.443-451, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000300007
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009...
), in this sense, the objective of this study was to evaluate the forage production and quality of Neonotonia wightii, Pueraria phaseoloides, Macrotyloma axilare and Arachis pintoi submitted to different levels of shading (30, 50 and 70% shading) and full sun.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The present study was carried out in the Forage and Pasture Sector of the Animal Science Institute of Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro, Seropédica - RJ, Brazil, located at latitude 22º45`S, longitude 43º41’W, with an average altitude of 33 meters between 2015 and 2016. The Fabaceae species used were Perennial Soybean (Neonotonia wightii Lackey), Tropical Kudzu (Pueraria phaseoloides Benth.), Macrotilom (Macrotylom aaxillare Verdc.) and Forage Peanut (Arachis pintoi Krapov. & Greg.), submitted to shading levels of 30, 50 and 70% from the use of polypropylene screens (“black plastic screen”) plus control treatment (full sun). The experiment carried out in a randomized complete block design with subdivided plots, with shade in the plot and the Fabaceae in the subplot, with four replications in repeated measure analysis.
The soil of the experimental area was analyzed in the laboratory of chemical analysis of the Department of Soil Fertility at the Institute of Agronomy of the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro and based on results obtained the soil was corrected and fertilized. The soil was plowed and barred to facilitate the planting and germination of forages.
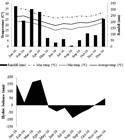
The climate of the region is Aw type according to the Köppen classification, with a dry season from April to September and a rainy season from October to March, which we call the “Drought-season” and “Water-season”, respectively. The Drought-season is characterized by a negative hydric balance, presented in the figure 1-B. The means of temperature and rainfall are presented in the figure 1-A.
Means of temperature and rainfall (A) and hydric balance (B) of the experimental period obtained by the Ecologia Agrícola station, Seropédica-RJ, Brazil. Source: National Meteorology Institute (INMET).
Implantation was carried out using seeds of Neonotonia wightii cv. “Common”, Pueraria phaseoloides cv. “Common”, Macrotylomaaxilare cv. Java and Arachis pintoi cv. Belmonte. Fabaceae planted at the beginning of the water-season (September 2015) in beds of 2x3 m with planting lines spaced of 0.5 m, totaling an area of 720 m2. After planting of the Fabaceae, a “black plastic screen” cover was installed at a height of 1.5 m from the ground. After the species were fully established (around 60 days latter), uniformity cut was performed using a costal brush at a height of 5 cm from the soil.
The first cut was performed on 01/13/2016 with two samples at the center of the plot using a 0.25 m2 (0.5 x 0.5 m) frame, according to MCMENIMAN (1997McMENIMAN, N.P. Methods of estimating intake of grazing animals.In: REUNIÃO ANUAL DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE ZOOTECNIA, 34., Juiz de fora, 1997. Anais... Juiz de Fora: Sociedade Brasileira de Zotoecnia, 1997. p.131-168.). The evaluations were carried out with a fixed interval of 60 (sixty) days until one year of evaluation was completed and a the similar interval was used by ANDRADE et al. (2004ANDRADE, C.M.S. de; et al. Crescimento de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras tropicais sob sombreamento. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v.39, n.3, p.263-270, 2004. Available from> <Available from> http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab/article/view/6766/3822
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab...
). A cover fertilization (150 kg KCl.ha-1) was carried out after the standardization cut and two more cover of fertilizations of the same magnitude throughout the year.
After cutting, the material was taken to the Laboratory for weighing and separation in leaves (leaf blade + petiole) and stalk. The material subjected to drying in a forced ventilation oven at a temperature of 55 oC for 72 h to determine the dry matter. After, the material (all components) was milled with a 1 mm sieve screen. Afterwards, the determinations of dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), mineral matter (MM), cellulose and lignin according to manual described by SILVA & QUEIROZ (2006SILVA, D.J.; QUEIROZ, A.C. Análise de alimentos: métodos químicos e biológicos. 3.ed. Viçosa, MG: UFV, 2006. 235p.) were performed.
Forage mass was estimated from the weight of DM produced by the area of the square used (0.25 m2) and converted to the hectare. The forage production was calculated multiplying the forage mass by the number of cut. The relation of leaf/stalk was calculated based on the weight of leaf fractions (leaf blade + petiole) and stalk corrected for DM.
The data were analyzed using the MIXED procedure of the statistical program SAS (Statistical Analysis System) version 9.2 for Windows. Choice of variance and covariance matrix was based on the Akaike’s Information Criterion (WOLFINGER, 1993WOLFINGER, R. Covariance structure selection in general mixed models.Communications in Statistics - Simulation, v.22, n.4, p.1079-1106, 1993. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/03610919308813143
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1080/0361091930881314...
) and the analysis of variance was based on the following causes of variation: Fabaceae species, shade level, period of the year, and the interactions between them. Effects of Fabaceae species, shade level and period of the year and their interactions were considered fixed and the effects of blocks and their interactions considered as random. The treatment averages were estimated by the LSMENS and compared by PDIFF (p<0.05).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
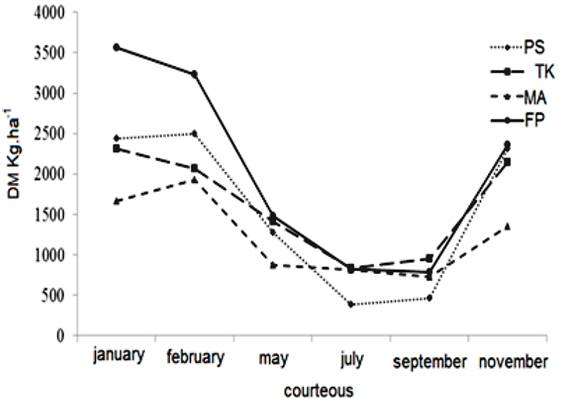
Forage mass (FM) varied with the interaction between the Fabaceae species, shade level and period of the year (p=0.0235). In the figure 2 are presented the production curves at the different times of the year. Forage Peanuts presented the highest forage mass (3.1 ton DM.ha.cut-1) than other species (2.4, 2.2 and 1.6 DM ha.cut-1 to Perennial soybean, Kudzu Tropical and Macrotilom, respectively) in the Water-season. In the Drought-season the Forage Peanuts and Kudzu Tropical had greater forage mass (1.0 ton DM ha.cut-1) than the Perennial soybean and Macrotilom (0.8 ton DM ha.cut-1).
Production curve of Perennial Soybean (PS), Tropical Kudzu (TK), Macrotilom (MA) and Forage Peanut (FP) under shade.
Forage production varied with the interaction between Fabaceae species, shade level and period of the year (p=0.0095). Results obtained are presented in table 1.
In the Water-season, the Forage Peanut presented the highest forage production (11 ton ha-1 DM) in the full sun while the other Fabaceae species had a mean of 6.5 ton ha-1 DM. Under artificial shading, the Forage Peanut stood out again, presenting the higher yields with average of 8.5 ton ha-1 DM, but was similar to Perennial Soybean (average of 7.6 ton ha-1 DM).
During this period, Tropical Kudzu and Forage Peanut showed a negative linear behavior with a reduction of 34 and 25 percent, respectively, in level at 70% shade in relation to the full sun. With regard to the means of forage production in the levels of shading, it was possible to notice that there was an average reduction of 0.99, 3.47 and 12.49% at levels 30, 50 and 70% of shading, respectively, relative to the forage production obtained in full sun. In general, in the Water-season, an average reduction of 5.7% in forage production was observed when forages received some type of shading.
In the Water-season, the Forage Peanut in the full sun presented the higher forage production, which was also higher in the Drought-season, but with a reduction of 65.5%. In this period the Forage Peanut presented a linear negative behavior with mean determination coefficient of ≅80%. The Perennial Soybean presented positive quadratic response, with an increase of 39.6, 20 and 3.7% relative to treatment in full sun. With regard to the means of forage production in the levels of shading, it was possible to notice that there was a mean reduction of 2.2, 2.3 and 0.39% at levels 30, 50 and 70% shading, respectively, relative to forage production obtained in full sun. In general, during Drought-season, a mean reduction of 1.36% in forage production observed when forages received some type of shading.
Probably these results are justified by the variation of the intensity, duration and period of occurrence of the water deficit and its interaction with other factors that determine the final yield (CUNHA & BERGAMASCHI, 1992CUNHA, G.R.; BERGAMASCHI, H. 1992. Efeito da disponibilidade hídrica sobre o rendimento das culturas. In: BERGAMASCHI, H. (Coord.). Agrometeorologia aplicada à irrigação. Porto Alegre: UFRGS-Ed. Universitária. p.85-97.). However, it should note that in the present study polypropylene screens was used to analyze the response of plants to shade. And according to WILSON & LUDLOW (1991WILSON, J.R. et al. Temperature effects on anatomy and digestibility of leaf and stem of tropical and temperate forage species. Netherlands Journal of Agricultural Science, v.39, n.1, p.31-48. 1991.), this technique presents some drawbacks, one of them is that natural shading provided by trees alters both the intensity and the quality (red: distant red) radiation in the understorey, while polypropylene screens; although is efficient in reducing radiation intensity, do not change their quality (HUBER & STUEFER, 1997HUBER, H.; STUEFER, J. F. Shade-induced changes in the branching pattern of a stoloniferous herb: functional response or allometric effect? Oecologia, v.110, n.4, p.478-486, 1997. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004420050183
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004420050183...
). The reduction of the red: distant red ratio provided by natural shading has important effects on plant morphogenesis. The other error of this technique (artificial shading) is the alteration of the canopy microclimate, reducing evapotranspiration (WILSON & LUDLOW, 1991WILSON, J.R.; LUDLOW, M.M. The environment and potential growth of herbage under plantations. In: SHELTON, H. M.; STÜR, W. W. (Eds.). Forages for plantation crops. Canberra: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, 1991. p.10-24. (ACIAR Proceedings, 32).), but there is no interference of the arboreal component, intercepting the rainwater in its canopy and competing with the forage for the water from the soil.
The overall response of the study to forage production, reported that the depressant effect of shading in relation to full-sun cultivation is of greater magnitude in the Water-season (reduction of 5.7%) than in the Drought-season (reduction of 1.36%). In addition, considering forage production of the Water-season plus the AP of Drought period, a general average reduction of 3.6% observed when the plants are subjected to shading. These results corroborate with the affirmation of ANDRADE et al. (2004ANDRADE, C.M.S. de; et al. Crescimento de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras tropicais sob sombreamento. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v.39, n.3, p.263-270, 2004. Available from> <Available from> http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab/article/view/6766/3822
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab...
), which under these conditions, there is a reduction of water stress of shaded plants during Drought-season, at a level probably higher than that provided by natural shading.
GOBBI et al. (2009GOBBI, K.F. et al. Características morfológicas, estruturais e produtividade do capim-braquiária e do amendoim forrageiro submetidos ao sombreamento. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.38, n.9, p.1645-1654, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000900002
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009...
) observed that the dry matter production of Forage Peanuts decreased by 21 and 17% with shading of 50 and 70%, respectively, relative to the full sun production. In a study conducted by ANDRADE and VALENTIM (1999ANDRADE, C.M.S.; VALENTIM, J.F. Adaptação, produtividade e persistência de Arachis pintoi submetido à diferentes níveis de sombreamento. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.28, n3. p.439-445, 1999. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35981999000300001
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35981999...
), the production of Arachis pintoi BRA - 031143 reduced linearly with shade levels in the rainy season and increased linearly in the dry period. In the Belmonte cultivar, the levels of 30, 50 and 70% of shading caused a reduction of 5, 26 and 60%, respectively, in the dry matter accumulation rates.
Fabaceae are physiologically more adapted to low light conditions due to the C3 photosynthetic mechanism when compared to the tropical grasses (C4), as a consequence, their forage production may be less affected in shaded environments. Results suggested that there are differences between the need for incident radiation for each plant. As for example, NICODEMO et al. (2015NICODEMO, M.L.F. et al. Frequências de cortes em nove leguminosas forrageiras tropicais herbáceas cultivadas ao sol e sob plantação florestal. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia, v.67, n.3, p.809-818, 2015. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119...
) studying mass of forage plants harvested at intervals of 30, 60, 90 and 180 days, with additional cuts at 120 and 150 days, it verified that under full sun the tested Fabaceae tolerated more frequent cuts (intervals of 30 - 90 days), except Lablab.
In this sense, there are species with less need for light radiation (about 30% light) to develop, such as Perennial Soybean and Macrotilom in waters and Tropical Kudzu and Macrotilom during the Drought-season, other species would need a greater contribution (approximately 70% light). Tropical Kudzu and Macrotilom would require 50% light to have their production increased. These results are in accordance with the classification described by SHELTON et al. (1986SHELTON, H. M. et al. Pasture in the plantations of Asia and the Pacific performance and prospect. Tropical Grassland, v.21, n.4, p. 159-168, 1986.) that reported higher tolerance to shade of Perennial Soybean compared to the others. Other studies have shown that shading results in decreased DM only in poaceae, and this effect is lower in Fabaceae (ERIKSEN & WHITNEY, 1982ERIKSEN, F.I., WHITNEY, A.S. Growth and fixation of some tropical forage legumes as influenced by solar radiation regimes. Agronomy Journal, v.4, n.4, p.703-709, 1982. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400040026x
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.000...
). However, influence of shading on forage production is still not very well defined in the literature.
The Drought-season is the period where the water deficit in plants can be observed in a more common way, because the water present in the soil is not available for small or long periods, causing a reduction of the physiological activities of the plant (CAVALCANTE et al. 2009CAVALCANTE, A.C.R. et al. Estresse por déficit hídrico em plantas forrageiras. Documentos/Embrapa Caprinos, Sobral-CE, 2009. 50p. Available from: <Available from: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/CNPC-2010/23051/1/doc89.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/...
).
Thus, this period is characterized by significant changes in the proportion and distribution of leaves, stems and dead material in the vertical profile of the canopy, in relation to the blade: stem and the final length of the leaf blades, among others (DA SILVA & NASCIMENTO JUNIOR, 2007DA SILVA, S.C.; NASCIMENTO JÚNIOR, D. Avanços na pesquisa com plantas forrageiras tropicais em pastagens: características morfofisiológicas e manejo do pastejo. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.36, suplemento especial, p.121-138. 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982007001000014
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982007...
).
In general, the leaf area index (LAI) of pastures increases as forage abundance increases and this increase occurs at decreasing rates. So that a plateau is reached and from that moment there is a reduction of the liquid accumulation of leaves due to senescence losses and excessive accumulation of stalks and dead material, mainly due to the limiting conditions of quantity and quality of light inside forage canopy (DA SILVA & PEDREIRA, 1997DA SILVA, S.C.; PEDREIRA, C.G.S. Princípios de ecologia aplicados ao manejo de pastagem. In: SIMPÓSIO SOBRE ECOSSISTEMAS DE PASTAGENS, 3., Jaboticabal, 1997. Anais… Jaboticabal: Funep, 1997. p.1-12.). During this process, the leaves located in the lower strata are shaded and, once competition for light is established (ROBSON, 1981ROBSON, M.J. Potential production - what is it and can we increase it?. In: OCCASIONAL SYMPOSIUM - PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND HERBAGE PRODUCTION, 13., 1981, England. Proceedings... England: British Grassland Society, 1981. p. 5-17.), there is an increase in stem elongation as a means of exposing the new leaves to the upper canopy and optimizing the photosynthetic capacity of the pasture (DA SILVA et al., 2009DA SILVA, S.C. et al. Sward structural characteristics and herbage accumulation of Panicum maximum cv. Mombaça subjected to rotational stocking managements. Scientia Agricola, v.66, p.8-19, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162009000100002
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162009...
).
Therefore, a balance determined by the availability and quality of light inside the forage canopy, and other factors (such as water, temperature and nutrients) act as modulators of the speed. These processes occur from the point of view of the forage plant, and the volumetric density of pasture has a high correlation with LAI, height, light interception and vertical distribution of morphological components in forage mass, as especially the leaf/stem ratio (DA SILVA & CARVALHO, 2005DA SILVA, S.C.; CARVALHO, P.C.F. Foraging behaviour and intake in the favorable tropics/sub-tropics. In: McGILLOWAY, D.A. (Ed.) Grassland: a global resource. Wageningen: Netherlands, Academic Publishers, p.81-95, 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.511.4117&rep=rep1&type=pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/dow...
).
In the present study, the leaf/stalk ratio (LSR) varied with the interaction between Fabaceae species, shade level and period of the year (p<0.0001). The results are presented in table 2. During the Water-season, the Perennial Soybean presented a positive linear effect for the leaf/stem ratio, the Macrotilom and the Tropical Kudzu presented quadratic behavior as a function of shade level (0, 30, 50 and 70% light retention).
In the Drought-season, only the Forage Peanuts presented a positive linear effect for leaf/stalk ratio as a function of shading level, the other species presented a quadratic effect, positive to Macrotilom and negative to Perennial Soybean and Kudzu Tropical. However, in general, in the period of the waters, the species had an average increase of 1.5% in the LSR with a mean determination coefficient of ≅60% and in the dry period presented a 4.7% reduction in the LSR with a mean determination coefficient of ≅50%.
This suggested a low but significant influence of shading on leaf morphology as a function of shading levels, precisely because the shaded plants invest relatively higher proportion of photoassimilates in the increase of leaf area, in order to maximize the capture of available light, presenting thinner leaves and bigger specific leaf area (SLA) and leaves with lower mass density (LAMBERS et al., 1998LAMBERS, H. et al. Plant physiological ecology. New York: Springer, 1998. 540p.).
Increase of SLA in low light conditions is directly related to the anatomical alterations that can occur in shaded plants such as thinner cuticles and epidermis, lower mesophilic thickness and lower proportion of palindromic parenchyma, conductive and sustentation tissues, higher proportion of intercellular spaces and lower stomatal density (BERLYN & CHO, 2000BERLYN, G.P.; CHO, J. Light, moisture, and nutrient use by plants. In: ASHTON, M.S., MONTAGNINI, F. (Eds.) The silvicultural basis for agroforestry systems. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000. p.9-39.).
However, changes in the LSR when comparing the periods (of water and drought) are a consequence of the low availability of water. In additional also causes a high leaf senescence and restriction to the appearance of new leaves, and the degree of these changes is due to the intensity of the Water stress and depends on the genotype (SMIT & SINGELS, 2006SMIT, M.A.; SINGELS, A. The response of sugarcane canopy development to water stress. Field Crops Research, v.98, p.91-97, 2006. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.009
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.00...
).
Crude protein (CP) content varied with the interaction between Fabaceous species, shade level and period of the year (p=0.0085). Results achieved are shown in table 3. The highest levels of CP were observed for the forage peanut, Tropical Kudzu and Perennial Soybean in the Water-season (19.0, 18.3 and 18.2%, respectively), however, did not differ (p>0.05). The Macrotilom had the lowest CP content (13.8%), differed (p>0.05) from the contents of the other species.
During the Water-season the Perennial Soybean presented a positive linear effect for the CP, especially to the increment of LSR (Table 2). The Tropical Kudzu and Macrotilom presented a quadratic behavior for the LSR; however, this behavior not reflected when checking the CP contents. The Macrotilom presented lowest CP in drought and water seasons. In the Drought-season, Forage Peanuts presented higher CP levels, probably in response to morphological changes during the period. GOBBI et al. (2009GOBBI, K.F. et al. Características morfológicas, estruturais e produtividade do capim-braquiária e do amendoim forrageiro submetidos ao sombreamento. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.38, n.9, p.1645-1654, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000900002
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009...
), evaluating Forage Peanuts in response to three levels of artificial shading (0, 50 and 70%) in the dry-water transition period and verified that the leaf: stalk ratio was not affected by shading but showed a significant reduction in dry matter production with shading.
Regarding the neutral detergent insoluble fiber (NDF) content variation was observed with the interaction between fabaceous species, shade level and period of the year (p<0.0001). Results achieved are shown in table 4.
For the NDF content as a function of the species effect, in the Water-season, forage peanut and Macrotilom showed the lowest values (45.7 and 45.3%, respectively) differing (p<0.05) from the others. Perennial Soybean and Tropical Kudzu presented the highest levels (51.7 and 54.6% NDF, respectively), both did not differ (p>0.05) from each other. PÁDUA et al. (2006PÁDUA, F.T. et al. Produção de matéria seca e composição químico-bromatológica do feno de três leguminosas forrageiras tropicais em dois sistemas de cultivo. Ciência Rural, v.36, n.4, p.1253- 1257, 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/cr/v36n4/a32v36n4.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.br/pdf/cr/v36n4/a32v36...
) reported a lower NDF content for the Macrotilom (50.42%), compared to the levels observed for Perennial Soybean and Tropical Kudzu (60.29 and 62.47%, respectively). When comparing results obtained for the NDF content and leaf/stalk ratio it confirmed that the difference between species came as a function of the proportion of stalks on the number of leaves of each species.
Thus, the higher NDF levels reached by Perennial Soybean and Tropical Kudzu are associated with a greater presence of stalks in relation to the number of leaves. Positive linear response was observed for the NDF content, as a function of shade levels studied, with an average increase of 4.1; 8.3 and 6% in the Water-season when submitted to levels of 30, 50 and 70% of shade, respectively, in relation to the response of the treatment without shading in the Water-season, a negative linear response was observed for the NDF content, as a function of shade levels studied.
Presenting an average decrease of 0.6; 2.7 and 4.0%, when submitted to the levels of 30, 50 and 70% of shade, respectively, in relation to the response of the treatment without shading. In the Drought-season, this species loses leaves, avoiding excessive loss of moisture (DUBEUX JÚNIOR et al., 2010DUBEUX JÚNIOR, J.C.B. et al. Deposição e composição química de serapilheira em um bosque de sabiá. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.39, n.8, pp.1650-1658, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000800005
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010...
), thus increasing the NDF contents in this period is probably due to the average reduction of 4.7% in LSR, according to table 5.
The fall of leaves and of some branches forms a layer called litter which accumulates on the ground, forming a dead vegetation cover. This loss of leaves occurs to avoid excessive water loss in this period (OLIVEIRA & PRISCO (1967). During the Drought-season, FERREIRA et al. (2007FERREIRA, R.L.C. et al. Deposição e acúmulo de matéria seca e nutrientes em serapilheira em um bosque de sabiá (Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth). Revista Árvore, v.31, n.1, p.7-12, 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622007000100002
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622007...
) observed that in a forest of sage (Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth) in Itambé city - PE, Brazil, occurred a deposition of 1,624 kg.ha.Month-1 of litter . Period in which the plants lost their leaves with the beginning of water scarcity, and after the onset of rains the foliage reappeared again.
SANTOS et al. (2010SANTOS, M. E. R. et al. Correlações entre número de perfilhos, índice de tombamento, massa dos componentes morfológicos e valor nutritivo da forragem em pastos diferidos de capim-braquiária. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.39, n.3, p.487-483, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000300006
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010...
) evaluating the morphological components and chemical composition of plants of Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth submitted to phosphate fertilization and at different times of the year, observed a significant difference for NDF ofleaves according the time of year, occurring higher values for drought-season, regardless of the fraction of the plant. The values reported for NDF in the present study were higher than those reported by Mimosa caesalpiniifoliaVIEIRA et al., (2005VIEIRA, E.L. et al. Composição química de forrageiras e seletividade de bovinos em bosque-de-Sabiá (Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth.) nos períodos chuvoso e seco. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.34, p.1505-1511. 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v34n5/26630.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v34n5/26630...
) that found values of 44.39 and 39.05% of NDF for rainy and Drought-season, respectively. These differences are probably associated to the determination of the whole plant in this research, as well as to the effects of plant age, precipitation and tannin complex: protein in the proportion of cell wall. SANTOS et al. (2010)SANTOS, M. E. R. et al. Correlações entre número de perfilhos, índice de tombamento, massa dos componentes morfológicos e valor nutritivo da forragem em pastos diferidos de capim-braquiária. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.39, n.3, p.487-483, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000300006
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010...
.
The cellulose content (CEL) varied with the interaction between the Fabaceae species and the period of the year (p<0.0001), only for the Tropical Kudzu was observed effect of shading levels; however, only in the Water-season, the results reported are shown in table 5.
Tropical Kudzu presented a negative linear behavior as a function of the shading levels. But with a low coefficient of determination of ≅33%, but in general the species had an increase of the CEL contents of 7.6 and 0.83 at the levels of 30 and 50%, respectively, and a reduction of 0.93% when subjected to 70% shading, in relation to the treatment of full sun in the Water-season.
Some authors reported morphophysiological alterations performed by the plant to aid the search for luminosity, as well as to increase the efficiency of the capture of the incident radiation, which may include stems stretching, leaf/stem ratio decrease and leaf area increase (WILSON & WONG, 1982WILSON, J.R., WONG, C.C. Effect of shade on some factors influencing nutritive quality of green panic and siratro pastures. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, v.33, n.10, p.937-949, 1982. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9820937
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9820937...
; CARVALHO et al., 1995).
During Drought-season, species showed no difference in the CEL content due to the different levels of shading in relation to the treatment with full sun. However, the difference in morphological response between the studied species was confirmed as a response to water deficit, in which greater or less leaf loss, stems increase and/or probably roots have a close correlation with MF, with AF and LSR, but with maintenance of CEL levels at different levels of shading.
When contrasting the MF responses (Table 1) with the CEL values (Table 5), in the dry period, it can see that results are in accordance with the hypothesis of ESPINDOLA et al. (2006ESPINDOLA, J.A.A. et al. Decomposição e liberação de nutrientes acumulados em leguminosas herbáceas perenes consorciadas com bananeira. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, v.30, n.2, p.321-328, 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832006000200012
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832006...
). These authors carried out a study with the objective of evaluating the decomposition and the release of nutrients by aerial part of perennial herbaceous Fabaceae, verified that the CEL contents were correlated with losses of the production during the Drought-season with greater emphasis on Tropical Kudzu and Siratro, and lower for Macrotilom.
Lignin content (LIG) varied with the interaction between Fabaceous species, shade level and period of the year (p=0.0005). Table 6 presents the results obtained in this study.
In the Water-season, the Perennial Soybean, for the LIG, did not present difference in relation to the levels of shading, presenting an average of 8.5% of LIG. Tropical Kudzu and Macrotilom showed positive linear behavior as a function of shade levels with a mean determination coefficient of ≅ 86 and 99%, respectively. Forage Peanut showed a positive quadratic behavior as a function of shading level (0, 30, 50 and 70% light retention) with a mean determination coefficient of ≅96%. The Macrotilom at the 70% level of shading was the one that presented the highest levels of LIG (10%) not differing from Tropical Kudzu (9.2%), possibly because under shading conditions or when reaching the critical leaf area index more vertical growth with greater stalk elongation and lower leaf density. This search for luminosity called phenotypic plasticity, whose habit of escape also develops as a function of intensive grazing (BRIGGS & WALTERS, 1997BRIGGS, D.; WALTERS, S.M. Plant variation and evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 3rd Edition, 1997. pp. 264-269; 309-352. ).
Luminosity of the habitat can promote phenotypic changes in both the morphology and the physiology of the individuals (LÜTTE, 1997; LARCHER, 2006LARCHER, W. Ecofisiologia vegetal.Tradução: Prado, C. H. B. A. São Carlos: Ed. Rima, 2006. 531p.). In this case, it presents reductions in leaf size and inter-node spacing for greater protection of growth points, ensuring greater persistence. Most likely, these results are due to the contribution of the NDF content in the chemical composition of the species, since there is a high correlation between the NDF contents between the LIG contents (PACIULLO et al., 2001PACIULLO, D.S.C. et al. Correlações entre Componentes Anatômicos, Químicos e Digestibilidade In Vitro da Matéria Seca de Gramíneas Forrageiras. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.30, n.3, p.955-963, 2001. Supl 1. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v30n3s1/5513.pdf
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v30n3s1/551...
). In the Drought-season, there was no difference in the LIG content for all the species studied, due to the different levels of shading in relation to the full sun treatment.
Growth season influenced the lignin contents, with the highest values observed in the summer (average of 8.07%). The literature demonstrated the intense deposition of lignin under high temperature conditions (WILSON et al., 1991WILSON, J.R. et al. Temperature effects on anatomy and digestibility of leaf and stem of tropical and temperate forage species. Netherlands Journal of Agricultural Science, v.39, n.1, p.31-48. 1991.); however, in the present study the difference between the periods was small (≅8% in the Water-season and ≅7.3% in the Drought-season).
Results of concentrations of mineral matter (MM), are shown in table 7, and varied with the interaction between the species of Fabaceae and shade level (p=0.0118) and between the fabaceae species and period of the year (p<0, 0001).
Nevertheless, in unfolding the interaction between Fabaceae and shade levels, it observed that at all levels of shading the Macrotilom presented the lowest concentrations of MM than the other species. However, the Macrotilom was the only species that presented a positive linear behavior as a function of shading levels, but with a low average determination coefficient of ≅28%.
In the present study the concentrations of MM also varied between species and period of the year (p<0.0001) and the results are arranged in table 8. Forage Peanuts presented no difference between the periods of the year for MM maintaining an average of 9.3% of MM. The Macrotilom showed a reduction of 19.67% of MM from the period of water to the dry period, while Perennial Soybean and Tropical Kudzu presented increases of 20.83 and 16.18% of MM, respectively. Thus, even though it is reported that there is a stimulus of luminosity on the concentrations of MM of the plants, the controversies remain, since the increase f MM is not stimulated by luminosity alone (ERIKSEN & WHITNEY, 1982ERIKSEN, F.I., WHITNEY, A.S. Growth and fixation of some tropical forage legumes as influenced by solar radiation regimes. Agronomy Journal, v.4, n.4, p.703-709, 1982. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400040026x
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.000...
).
However, CARVALHO et al. (1995) pointed out that forages grown under shade conditions tend to have a higher percentage of green leaves, lower percentage of dry matter and higher concentrations of MM in leaves than plants grown in full sun. However, the alteration in the MM content could be related to morphological changes of the forage to the shade (KOUKOURA et al., 2009KOUKOURA, Z. A. et al. Growth characteristics and nutrient content of some herbaceous species under shade and fertilization.Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, v.7, n.2, p.431-438, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://revistas.inia.es/index.php/sjar/article/view/433
>. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
http://revistas.inia.es/index.php/sjar/a...
). Thus, the increase observed in the concentrations of the minerals studied in the four Fabaceae in this research is probably related to the morphophysiological changes promoted by shading, mainly based on the LSR response.
CONCLUSION:
The Forage Peanuts has been shown to be a good option for use in silvopastoral systems since it presents high forage production and good nutritive value even though it has a reduction in production under shading. These Fabaceae species presented a higher reduction in the forage production in the Drought-season (average 61%) but only Perennial Soybean is favored by the shading at levels of 30% and 50% in this season. Macrotilom was little affected by the shading with less production in Water-season and with great reduction in nutritive value in the Drought-season in relation to others species. Although, there is a small reduction in forage production, except for Perennial Soybean in the Drought-season, it is advisable to use these tropical forage legumes in silvopastoral systems since the quality of the forage is little affected by the shade.
REFERENCES
- ALVES, L.M. et al. Início da estação chuvosa na região Sudeste do Brasil: Parte 1 - Estudos observacionais. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, v.20, n.3, p.385-394, 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://www.rbmet.org.br/port/revista/revista_artigo.php?id_artigo=143 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.rbmet.org.br/port/revista/revista_artigo.php?id_artigo=143 - ANDRADE, C.M.S.; VALENTIM, J.F. Adaptação, produtividade e persistência de Arachis pintoi submetido à diferentes níveis de sombreamento. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.28, n3. p.439-445, 1999. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35981999000300001 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35981999000300001 - ANDRADE, C.M.S. de; et al. Crescimento de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras tropicais sob sombreamento. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v.39, n.3, p.263-270, 2004. Available from> <Available from> http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab/article/view/6766/3822 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://seer.sct.embrapa.br/index.php/pab/article/view/6766/3822 - BARRIOS, R. et al. Efecto del sombreamiento artificial sobre el establecimiento de leguminosas promisorias como cobertura en palma aceitera en el estado Monagas. Agronomía Tropical, v.58, n.1, p. 31-34, 2008. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0002- 192X2008000100007&lng=es&nrm=iso >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.org.ve/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0002- 192X2008000100007&lng=es&nrm=iso - BERLYN, G.P.; CHO, J. Light, moisture, and nutrient use by plants. In: ASHTON, M.S., MONTAGNINI, F. (Eds.) The silvicultural basis for agroforestry systems. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000. p.9-39.
- BRIGGS, D.; WALTERS, S.M. Plant variation and evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 3rd Edition, 1997. pp. 264-269; 309-352.
- CAVALCANTE, A.C.R. et al. Estresse por déficit hídrico em plantas forrageiras. Documentos/Embrapa Caprinos, Sobral-CE, 2009. 50p. Available from: <Available from: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/CNPC-2010/23051/1/doc89.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/CNPC-2010/23051/1/doc89.pdf - CUNHA, G.R.; BERGAMASCHI, H. 1992. Efeito da disponibilidade hídrica sobre o rendimento das culturas. In: BERGAMASCHI, H. (Coord.). Agrometeorologia aplicada à irrigação. Porto Alegre: UFRGS-Ed. Universitária. p.85-97.
- DA SILVA, S.C.; NASCIMENTO JÚNIOR, D. Avanços na pesquisa com plantas forrageiras tropicais em pastagens: características morfofisiológicas e manejo do pastejo. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.36, suplemento especial, p.121-138. 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982007001000014 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982007001000014 - DA SILVA, S.C. et al. Sward structural characteristics and herbage accumulation of Panicum maximum cv. Mombaça subjected to rotational stocking managements. Scientia Agricola, v.66, p.8-19, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162009000100002 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162009000100002 - DA SILVA, S.C.; CARVALHO, P.C.F. Foraging behaviour and intake in the favorable tropics/sub-tropics. In: McGILLOWAY, D.A. (Ed.) Grassland: a global resource. Wageningen: Netherlands, Academic Publishers, p.81-95, 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.511.4117&rep=rep1&type=pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.511.4117&rep=rep1&type=pdf - DA SILVA, S.C.; PEDREIRA, C.G.S. Princípios de ecologia aplicados ao manejo de pastagem. In: SIMPÓSIO SOBRE ECOSSISTEMAS DE PASTAGENS, 3., Jaboticabal, 1997. Anais… Jaboticabal: Funep, 1997. p.1-12.
- DUBEUX JÚNIOR, J.C.B. et al. Deposição e composição química de serapilheira em um bosque de sabiá. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.39, n.8, pp.1650-1658, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000800005 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000800005 - ERIKSEN, F.I., WHITNEY, A.S. Growth and fixation of some tropical forage legumes as influenced by solar radiation regimes. Agronomy Journal, v.4, n.4, p.703-709, 1982. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400040026x >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/agronj1982.00021962007400040026x - ESPINDOLA, J.A.A. et al. Decomposição e liberação de nutrientes acumulados em leguminosas herbáceas perenes consorciadas com bananeira. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, v.30, n.2, p.321-328, 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832006000200012 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832006000200012 - EUCLIDES, V.P.B. Alternativas para intensificação da produção de carne bovina em pastagem. Campo Grande: Embrapa Gado de Corte, 2000. 65p. Available from: <Available from: https://www.embrapa.br/gado-de-corte/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/324156/alternativas-para-intensificacao-da-producao-de-carne-bovina-em-pastagem >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://www.embrapa.br/gado-de-corte/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/324156/alternativas-para-intensificacao-da-producao-de-carne-bovina-em-pastagem - FERREIRA, R.L.C. et al. Deposição e acúmulo de matéria seca e nutrientes em serapilheira em um bosque de sabiá (Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth). Revista Árvore, v.31, n.1, p.7-12, 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622007000100002 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622007000100002 - FREITAS, A.D.S. et al. Nodulação e fixação de nitrogênio por forrageiras da caatinga cultivadas em solos do semiárido paraibano. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.40, n.9, p.1856-1861, 2011.
- GARCIA, R.; ANDRADE, C.M.S. Sistemas silvipastoris na Região Sudeste. In: CARVALHO, M.M.; ALVIM, M.J.; CARNEIRO, J.C. (Ed.). Sistemas agroflorestais pecuários: opções de sustentabilidade para áreas tropicais e subtropicais. Juiz de Fora: Embrapa-CNPGL; FAO, 2001. p.173-187. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982011000900003 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982011000900003 - GOBBI, K.F. et al. Características morfológicas, estruturais e produtividade do capim-braquiária e do amendoim forrageiro submetidos ao sombreamento. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.38, n.9, p.1645-1654, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000900002 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000900002 - GOBBI, K.F. et al. Valor nutritivo do capim-braquiária e do amendoim forrageiro submetidos ao sombreamento. Archivos de Zootecnia, v.59, n.227, p-809-818, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/azoo/v59n227/art6.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/azoo/v59n227/art6.pdf - HUBER, H.; STUEFER, J. F. Shade-induced changes in the branching pattern of a stoloniferous herb: functional response or allometric effect? Oecologia, v.110, n.4, p.478-486, 1997. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004420050183 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004420050183 - KOUKOURA, Z. A. et al. Growth characteristics and nutrient content of some herbaceous species under shade and fertilization.Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, v.7, n.2, p.431-438, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://revistas.inia.es/index.php/sjar/article/view/433 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://revistas.inia.es/index.php/sjar/article/view/433 - KUVA, M.A, et al. 2007. Fitossociologia de comunidades de plantas daninhas em agroecossistema cana-crua. Planta Daninha, v.25, n.3, p.501-511, 2007. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/pd/v25n3/09.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.br/pdf/pd/v25n3/09.pdf - LAMBERS, H. et al. Plant physiological ecology. New York: Springer, 1998. 540p.
- LARCHER, W. Ecofisiologia vegetal.Tradução: Prado, C. H. B. A. São Carlos: Ed. Rima, 2006. 531p.
- McMENIMAN, N.P. Methods of estimating intake of grazing animals.In: REUNIÃO ANUAL DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE ZOOTECNIA, 34., Juiz de fora, 1997. Anais... Juiz de Fora: Sociedade Brasileira de Zotoecnia, 1997. p.131-168.
- MINUZZI R.B et al. Climatologia do comportamento do período chuvoso da região sudeste do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, 2007, v.22, n.3, p.338-344. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-77862007000300007 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-77862007000300007 - NICODEMO, M.L.F. et al. Frequências de cortes em nove leguminosas forrageiras tropicais herbáceas cultivadas ao sol e sob plantação florestal. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia, v.67, n.3, p.809-818, 2015. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1678-4162-7119 - PACIULLO, D.S.C. et al. Correlações entre Componentes Anatômicos, Químicos e Digestibilidade In Vitro da Matéria Seca de Gramíneas Forrageiras. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.30, n.3, p.955-963, 2001. Supl 1. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v30n3s1/5513.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v30n3s1/5513.pdf - PÁDUA, F.T. et al. Produção de matéria seca e composição químico-bromatológica do feno de três leguminosas forrageiras tropicais em dois sistemas de cultivo. Ciência Rural, v.36, n.4, p.1253- 1257, 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/cr/v36n4/a32v36n4.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.br/pdf/cr/v36n4/a32v36n4.pdf - PAIVA, C.M. Determinação das datas de início e fim da estação chuvosa e da ocorrência de veranicos na Bacia do Rio Doce. 1997. 65f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Meteorologia Agrícola) - Faculdade de Engenharia Agrícola, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, 1997. Available from: <Available from: http://www.locus.ufv.br/handle/123456789/11418 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.locus.ufv.br/handle/123456789/11418 - ROBSON, M.J. Potential production - what is it and can we increase it?. In: OCCASIONAL SYMPOSIUM - PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND HERBAGE PRODUCTION, 13., 1981, England. Proceedings... England: British Grassland Society, 1981. p. 5-17.
- SANTOS, L.D.T. et al.Phenotypic plasticity of Neonotoniawightii and Puerariaphaseoloides grown under different light intensities.Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences, v.87, n.1, p.520-528, 2015. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201520140017 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201520140017 - SANTOS, M. E. R. et al. Correlações entre número de perfilhos, índice de tombamento, massa dos componentes morfológicos e valor nutritivo da forragem em pastos diferidos de capim-braquiária. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.39, n.3, p.487-483, 2010. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000300006 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010000300006 - SHELTON, H. M. et al. Pasture in the plantations of Asia and the Pacific performance and prospect. Tropical Grassland, v.21, n.4, p. 159-168, 1986.
- SILVA, D.J.; QUEIROZ, A.C. Análise de alimentos: métodos químicos e biológicos. 3.ed. Viçosa, MG: UFV, 2006. 235p.
- SILVA, J.J.; SALIBA, E.O.S. Pastagens consorciadas: uma alternativa para sistemas extensivos e orgânicos. Veterinária e Zootecnia, v.14, p.8-18, 2007.
- SMIT, M.A.; SINGELS, A. The response of sugarcane canopy development to water stress. Field Crops Research, v.98, p.91-97, 2006. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.009 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.009 - SOARES, A. B. et al. Influência da luminosidade no comportamento de onze espécies forrageiras perenes de verão. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.38, n.3, p.443-451, 2009. Available from: <Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000300007 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982009000300007 - VALLE, C.B.; ZIMMER, A.H.Leguminosas forrageiras em pastos consorciados: experiências do passado que podem fomentar o futuro. In: AS FORRAGEIRAS E AS SUAS RELAÇÕES COM O SOLO, O AMBIENTE E O ANIMAL. Anais... Lavras: UFLA, 2013. pp.17-28.
- VEIGA, J.A.P. et al. A influência das anomalias de TSM dos oceanos Atlântico e Pacífico sobre as chuvas de monção da América do Sul. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, v.17, n.2, p.181-194, 2002. Available from: <Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37679270_A_influencia_das_anomalias_de_TSM_dos_Oceanos_Atlantico_e_Pacifico_sobre_as_chuvas_de_moncao_da_America_do_Sul >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37679270_A_influencia_das_anomalias_de_TSM_dos_Oceanos_Atlantico_e_Pacifico_sobre_as_chuvas_de_moncao_da_America_do_Sul - VIEIRA, E.L. et al. Composição química de forrageiras e seletividade de bovinos em bosque-de-Sabiá (Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth.) nos períodos chuvoso e seco. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.34, p.1505-1511. 2005. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v34n5/26630.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbz/v34n5/26630.pdf - VILELA, D. et al. Desempenho de vacas da raça Holandesa em pastagem de Coastcross. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, v.35, p.555-561. 2006. Available from: <Available from: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/%0D/rbz/v35n2/a31v35n2.pdf >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» http://www.scielo.br/pdf/%0D/rbz/v35n2/a31v35n2.pdf - WILSON, J.R.; LUDLOW, M.M. The environment and potential growth of herbage under plantations. In: SHELTON, H. M.; STÜR, W. W. (Eds.). Forages for plantation crops. Canberra: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, 1991. p.10-24. (ACIAR Proceedings, 32).
- WILSON, J.R., WONG, C.C. Effect of shade on some factors influencing nutritive quality of green panic and siratro pastures. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, v.33, n.10, p.937-949, 1982. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9820937 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9820937 - WILSON, J.R. et al. Temperature effects on anatomy and digestibility of leaf and stem of tropical and temperate forage species. Netherlands Journal of Agricultural Science, v.39, n.1, p.31-48. 1991.
- WOLFINGER, R. Covariance structure selection in general mixed models.Communications in Statistics - Simulation, v.22, n.4, p.1079-1106, 1993. Available from: <Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/03610919308813143 >. Accessed: Mar. 23, 2018.
» https://doi.org/10.1080/03610919308813143
-
CR-2017-0726.R2
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
04 July 2019 -
Date of issue
2019
History
-
Received
10 Oct 2017 -
Accepted
30 Apr 2019 -
Reviewed
03 June 2019