Abstract
The gluten protein was exposed to the X-ray radiations for different time range, comprising 1 and 3 seconds. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of x-ray radiations on the physicochemical properties of gluten protein. Different functional properties of proteins like water and oil holding capacities, protein solubility, emulsification activity, and stability index, foaming action and stability, water solubility, protein, and moisture content, along with SDS PAGE, FTIR, Xeta potential net charge was carried out to evaluate the effect of X-ray radiation on gluten protein. Results showed that the enhancement of water holding capacity up to 38.12%, as well as oil holding capacity up to 35% could be seen, whereas a significant decrease in emulsification activity and stability index, foaming capacity and stability, even protein content could be observed in treated samples. The net charge on protein in water solution was found to increase towards the positive side. The structure of the protein remained unchanged based on no change was observed in SDS PAGE electrograph, FTIR secondary structure region. Hence, X-ray treatment can be a possible way to alter the protein structure for “tailor-made applications” in food industries.
Keywords:
Gluten; X-ray; Protein structure; Water and oil holding; Foaming capacity and stability; Emulsion capacity and stability; Net charge
Resumo
A proteína do glúten foi exposta à radiação de raios X por diferentes intervalos de tempo, entre 1 e 3 segundos. O objetivo deste estudo foi determinar o efeito das radiações de raios X nas propriedades físico-químicas da proteína do glúten. Diferentes propriedades funcionais de proteínas como capacidade de retenção de água, capacidade de retenção de óleo, solubilidade de proteínas, atividade de emulsificação e índice de estabilidade, ação e estabilidade da espuma, solubilidade em água, teor de proteína e de umidade, juntamente com SDS PAGE, FTIR, carga líquida do potencial Xeta foram analisadas para avaliar o efeito da radiação de raios X na proteína de glúten. Os resultados mostraram um aumento da capacidade de retenção de água em até 38,12%, da capacidade de retenção de óleo em até 35%, enquanto verificou-se uma diminuição significativa na atividade de emulsificação e no índice de estabilidade, na capacidade de formação e estabilidade de espuma e no teor de proteína das amostras tratadas. Verificou-se que a carga líquida sobre a proteína na solução aquosa aumentou para o lado positivo. A estrutura da proteína ficou inalterada com base em nenhuma alteração foi observada no eletrógrafo SDS PAGE, região da estrutura secundária do FTIR. Portanto, o tratamento com raios X pode ser utilizado para alterar a estrutura da proteína visando aplicações específicas na indústria de alimentos.
Palavras-chave:
Glúten; Raios X; Estrutura de proteínas; Retenção de água e óleo; Capacidade de formação e estabilidade de espuma; Capacidade e estabilidade de emulsões; Carga líquida
1 Introduction
Food irradiation includes the exposure of macronutrient to gamma rays or high energy electrons or X-rays. It has been proved that irradiation changes food properties and functions. According to codex general standard for irradiated food, the X-rays can be used up to 7.5 MeV. X-rays are considered as the optimum choice for radiation treatment because they do not cause induced radioactivity in food products; in addition, the cost of production of X-ray is less expensive when compared to gamma radiation. The penetrating power of X-ray creates an excellent way to modify the macromolecules of food (Farkas, 2006Farkas, J. (2006). Irradiation for better foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 17(4), 148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.003
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12...
).
The ionization energy of X-rays reduces when it passes through the food. This absorbed energy produced by the radiation creates an effect on macromolecules like protein, which can achieve the ionic state in food. The radicals like OH, e-aq, H, with H2O2, H3O+ may be formed during the exposure reactions. These radicals react with amino acids of protein and cause decarboxylation reaction, which produces amine and aldehydes. Sulfur-containing and aromatic amino acids are most susceptible to irradiation (Molins, 2001Molins, R. A. (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications. New York: Wiley.). The changes in optical properties are also observed due to oxidation of amino acids, as well as to the formation of dimers with irreversible changes in proteins (Barron & Finkelstein, 1952Barron, E. S. G., & Finkelstein, P. (1952). Studies on the mechanism of action of ionizing radiations. X. Effect of x-rays on some physicochemical properties of proteins. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 41(1), 212-232. PMid:12997265. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(52)90521-3
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(52)9...
). The accumulation of a large number of energy results in the denaturation of protein consisting of changes in the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins, however, without changing the nutritional values of them. Currently, ionizing radiation (X-ray) is only using for Radio pasteurization, Radurization, Radappertization (Harder et al., 2015Harder, M. N. C., Arthur, V., & Arthur, P. B. (2015). Irradiation of foods: processing technology and effects on nutrients: effect of ionizing radiation on food components. In B. Caballero, P. M. Finglas & F. Toldrá (Eds.), Encyclopedia of food and health (pp. 476-471). Amsterdam: Academic Press.). About 80% of the protein of wheat flour is composed of gluten. Gluten proteins are formed from gliadins and glutenins. They are profoundly characterized as polymorphic polypeptides of molecular weight about 30,000 to 90,000 kDa. These protein subunits are functional subunits for viscosity, elasticity (Kovacs et al., 2004Kovacs, M. I. P., Fu, B. X., Woods, S. M., & Khan, K. (2004). Thermal stability of wheat gluten protein: its effect on dough properties and noodle texture. Journal of Cereal Science, 39(1), 9-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(03)00058-4
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(03)...
).
The functional properties of protein-dependent pathways depend on the structure of the protein. The alternation in protein structure may lead to change in the functionality of protein like protein solubility, emulsification properties, foaming properties (Yalcin et al., 2008Yalcin, E., Sakiyan, O., Sumnu, G., Celik, S., & Koksel, H. (2008). Functional properties of microwave-treated wheat gluten. European Food Research and Technology, 227(5), 1411-1417. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0860-8
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-086...
). Most of the ionization study was focused on gamma radiation based on effects of protein. The need for X-ray analysis based on protein is another area that there is lack of studies regarding the details of vegetable and protein functions. The study has conducted to determine the effect of X-ray radiations on functional properties of proteins like water and oil holding capacities, protein solubility, emulsification activity, and stability, Foaming Capacity (FC) and Foaming Stability (FS).
2 Materials and method
2.1 Materials
Gluten protein powder was purchased from Agridient manufacturers (purity 85%) in Mumbai. Sodium tartrate, copper sulfate, 10% sodium hydroxide, SDS, Acrylamide, Bis-acrylamide, Glycine, Commasiae Brilliant Blue R-250, Methanol, GAA, Glycerol, Bromophenol blue, β-mercaptoethanol, TEMED chemicals were purchased from Himedia, sigma, and SRL laboratory.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Treatment
Around 200 grams of Gluten protein powder were exposed to X-rays at 108 kV for 1 sec and 3 seconds by X-ray machine (Make- RMS) and then they were labeled as GLU 1 and GLU 3 respectively. The functional properties of these gluten protein powder were studied and compared against untreated gluten protein powder. The samples were frozen immediate at -40 °C.
2.2.2 Assays of proximate analysis of x-ray treated sample
The protein was analyzed for protein content changes after X-ray treatment. Protein determination was carried out by Kjheldhal Method (Roger et al., 2007Roger, D. D., Jean-Justin, E. N., & François-Xavier, E. (2007). Nutritive value, toxicological and hygienic quality of some cassava based products consumed in Cameroon. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 6(4), 404-408. http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2007.404.408
http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2007.404.4...
).
2.2.3 Water holding capacity
Water holding capacity was determined by the method outlined by Yu et al. (2007)Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., & Goktepe, I. (2007). Peanut protein concentrate: production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chemistry, 103(1), 121-129. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.08.012
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.200...
. 0.5 grams of gluten protein flour was weighed into pre-weighed 15-mL centrifuge tubes. For each sample, an amount of 5 mL of distilled water was added and mixed using a vortex at the highest speed for 2 min. Samples were allowed to stand at room temperature for 30 min after the mixture was thoroughly wetted. Then centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 30 min. The supernatant was decanted, and the centrifuge tube containing sediment was weighed. Water holding capacity (grams of water per gram of protein) was calculated with Equation 1.
Where W0 is the weight of the dry sample (g), W1 is the weight of the tube plus the dry sample (g), and W2 is the weight of the tube plus the sediment (g). Triplicate samples were analyzed for each sample.
2.2.4 Oil holding capacity
Oil holding was determined by the method outlined by Yilmaz & Emir (2016)Yilmaz, E., & Emir, D. D. (2016). Extraction and functional properties of proteins from pre-roasted and enzyme treated poppyseed (Papaver somniferum L.) press cakes. Journal of Oleo Science, 65(4), 319-329. PMid:26972462. http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228
http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228...
. 0.5 gram of protein sample was weighed into the tube, and an amount of 5 mL of sunflower oil was added into it. The sample was dispersed in oil by vortexing for 30 min; the mixture was allowed to stand for 30 min at room temperature and then centrifuged at 5888 rpm for 15 min. An additional 5 min centrifugation at 17000 rpm was done before inverting the tubes to drain the free oil out for 1 hour. Finally, the absorbed oil was calculated from the weight difference, and Oil Holding Capacity (OHC) was reported as g oil/g protein.
2.2.5 Emulsion activity and stability index
Emulsifying activity and emulsion stability were determined with slight modifications. An emulsion of various concentration 0.25%, 0.5%, 0.75%, and 1% was prepared by mixing 0.5 g of gluten protein sample in 5 mL distilled water and then vortexed for 1 min, then an amount of 5 mL sunflower oil was added and homogenized at 8,000 rpm for 3 min at 25 °C (Ballesteros et al., 2014Ballesteros, L. F., Teixeira, J. A., & Mussatto, S. I. (2014). Chemical, functional, and structural properties of spent coffee grounds and coffee silverskin. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(12), 3493-3503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1349-z
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-134...
; Chau et al., 1997Chau, C.-F., Cheung, P. C. K., & Wong, Y.-S. (1997). Functional properties of protein concentrates from three Chinese indigenous legume seeds. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(7), 2500-2503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf970047c
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf970047c...
). Then 50 µL of the emulsion was diluted with 5 mL of 0.1% (w/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution. The absorbance of the emulsion was measured immediately after emulsion formation using UV-Visible spectroscopy at 500 nm and expressed as emulsion activity of the protein was calculated using Equation 1 (Li et al., 2014Li, C., Huang, X., Peng, Q., Shan, Y., & Xue, F. (2014). Physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-glucomannan conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21(5), 1722-1727. PMid:24703823. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.03.018
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.201...
; Sui et al., 2017Sui, X., Bi, S., Qi, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Li, Y., & Jiang, L. (2017). Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin: its emulsifying property and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 727-734. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.024
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016...
). To determine the emulsion stability index, the emulsion was left at 25 °C for 10 min, and then 50 µL of the emulsion was diluted with 5 mL of 0.1% (w/v) SDS solution and the absorbance at 500 nm was measured (Jongjareonrak et al., 2015Jongjareonrak, A., Srikok, K., Leksawasdi, N., & Andreotti, C. (2015). Extraction and fundamental properties of protein from de-oiled rice bran of rice bran oil production industry. Chiang Mai University Journal of Natural Sciences, 14(2), 163-174. http://dx.doi.org/10.12982/CMUJNS.2015.0079
http://dx.doi.org/10.12982/CMUJNS.2015.0...
). Emulsion activity and stability index were calculated according to the following Equations 2 and 3:
Where T equals to 2.303; A0 is the absorbance at 0 min; N is the dilution factor; is the proportion of the oil phase (0.25); L is the thickness of the cuvette (1 cm); C is the concentration of gluten protein (g/mL); A10 is the absorbance at 10 min; T0 represents 0 min; and T10 represents 10 min (Sui et al., 2017Sui, X., Bi, S., Qi, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Li, Y., & Jiang, L. (2017). Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin: its emulsifying property and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 727-734. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.024
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016...
).
2.2.6 Foaming capacity and foaming stability
The foaming capacity -FC and foaming stability - FS were determined according to the method of Cano-Medina et al. (2011)Cano-Medina, A., Jiménez-Islas, H., Dendooven, L., Herrera, R. P., González-Alatorre, G., & Escamilla-Silva, E. M. (2011). Emulsifying and foaming capacity and emulsion and foam stability of sesame protein concentrates. Food Research International, 44(3), 684-692. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.015
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010...
and Yilmaz & Emir (2016)Yilmaz, E., & Emir, D. D. (2016). Extraction and functional properties of proteins from pre-roasted and enzyme treated poppyseed (Papaver somniferum L.) press cakes. Journal of Oleo Science, 65(4), 319-329. PMid:26972462. http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228
http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228...
with slight modification. The FC and FS were examined for a supernatant sample of various concentrations (0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, and 2%) by dissolving them in distilled water and they were whipped at high speed with a hand blender and poured into 100 mL volumetric cylinder.
The FC was reported by the Formula 4 below,
The samples were allowed to stand for 30 min at room temperature to estimate the FS given by the Formula 5 below,
2.2.7 Solubility
Solubility was determined by the method outlined by Chang & Zhang (2017)Chang, S. K. C., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Protein analysis (pp. 315-331). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-5.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-...
. A 5-mL biuret reagent was mixed with a 1-mL portion of protein solution (1 to 10 mg protein/mL). The reagent includes copper sulfate, NaOH, and potassium sodium tartrate, which was used to stabilize the cupric ion in the alkaline solution. After the reaction, mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature for 15 or 30 min, the absorbance was read at 540 nm against a reagent blank. A standard curve of concentration versus absorbance was developed using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA).
2.2.8 SDS PAGE
Determination of molecular weight changes was performed by (Babiker et al., 1996Babiker, E. F. E., Fujisawa, N., Matsudomi, N., & Kato, A. (1996). Improvement in the functional properties of gluten by protease digestion or acid hydrolysis followed by microbial transglutaminase treatment. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 44(12), 3746-3750. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf960302d
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf960302d...
) method with slight modification. method with slight modification. SDS-poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of freeze-dried samples was done using 12% acrylamide separating gel and 5% acrylamide stacking gel containing 0.1% SDS. 7 mL of 12% resolving gel was poured in the gel unit and allowed to polymerize. After 45 min, 3 mL of 5% stacking gel was poured, and the comb was inserted, and then tris glycine buffer was loaded into the upper and lower chambers and kept for 1h. After that, 35 µL of the sample was prepared in a Tris-glycine buffer at pH 6.8 containing 2% SDS was loaded into wells of gel unit. Electrophoresis was done at a current of 60 mA for 1 h, and after that at 80 mA for 2 h. After electrophoresis, the gel sheets were stained with 0.2% Coomassie brilliant blue-R250 and destained with 10% acetic acid containing 30% methanol for 18 h to remove any traces of the staining solution.
3 Result and discussion
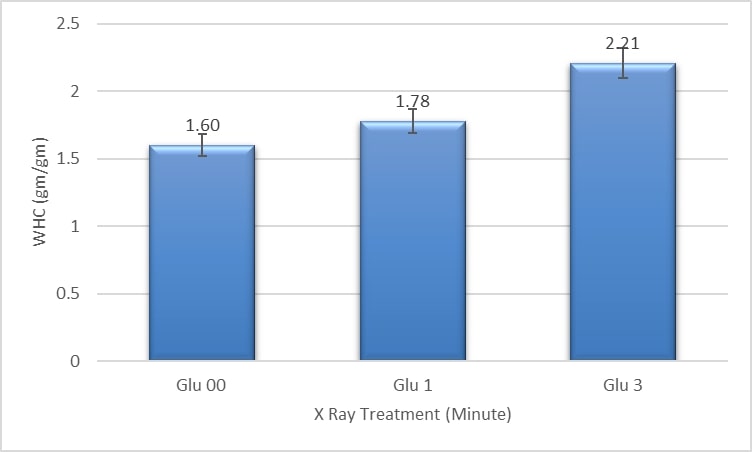
3.1 Water holding capacity
The water absorption capacity of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 was 1.60 gm/gm, 1.78 gm/gm, and 2.21 gm/gm, respectively. Approximately 11.25% and 38.12% of water holding capacity could be increased (Figure 1). This indicates that the water holding capacity could increase by increasing the exposure time of X-ray. All three samples were found to be significantly different (p < 0.05) from each other. This gradual increase may be owing to an irradiation that leads to protein denaturation (Pollard, 1960Pollard, E. C. (1960). Effects of ionizing radiation on nucleoproteins. Cancer, 13(S6), 38-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(196011/12)13:6+<38::AID-CNCR2820130709>3.0.CO;2-W
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(1960...
). Protein denaturation leads to unfolding and exposure of hydrophilic groups Or due to an increase in charge of amino acid profiling (Margesin & Schinner, 1999Margesin, R., & Schinner, F. (1999). Cold-adapted organisms: Ecology, physiology, enzymology and molecular biology. Berlin: Springer. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06285-2.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-0628...
). Consistent with our study, WHC of KPS20 and KPM20 was influenced by irradiation treatment (Lee et al., 2017Lee, N.-Y., Kang, C.-S., & Kim, H.-S. (2017). Effects of γ-irradiation on the quality changes of fresh noodles prepared from wheat cultivated with N-fertilization treatments. Food Science and Biotechnology, 26(1), 135-142. PMid:30263520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0018-1
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-001...
). The water holding capacity of dough is considered an essential factor in the food processing of various bakery products (Kaushik et al., 2015Kaushik, R., Kumar, N., Sihag, M. K., & Ray, A. (2015). Isolation, characterization of wheat gluten and its regeneration properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(9), 5930-5937. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1690-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-169...
).
3.2 Oil holding capacity
The obtained values of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 were 0.96/gm, 1.29/gm, and 1.74/gm, respectively (Figure 2). A significant increase in oil holding capacity was observed as the exposure time of radiation was increased. 34.37% and 81% of oil absorption enhancement could be found in the x-ray treatment consisting of 1 and 3-minute samples. This increase should be observed due to the exposure of more hydrophobic regions associated with crosslinking reactions (Hmed & Osman, 2009Hmed, S. E. A., & Osman, G. A. M. (2009). Effect of gamma irradiation on the physico-chemical characterstics of groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea). Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(3), 2856-2860.). The oil absorption capacity is a vital parameter during frying and cooking of noodles and pasta (Kaushik et al., 2015Kaushik, R., Kumar, N., Sihag, M. K., & Ray, A. (2015). Isolation, characterization of wheat gluten and its regeneration properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(9), 5930-5937. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1690-2
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-169...
).
3.3 Emulsion activity index and emulsification stability index
The Emulsion Activity Index (EAI) values of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 were 0.54 m2/g, 0.27 m2/g, and 0.25 m2/g, respectively. The Emulsification Stability Index (ESI) values of GLU 00, GLU 01, and GLU 3 were 70 min, 52 min, and 63 min, respectively (Figure 3). Significantly decrease in EAI and ESI might have occurred since irradiation leads to denaturation and aggregation of the protein molecule, particularly at high dosage. Therefore it can be noted that emulsifying properties changed significantly after irradiation. Consistent with our study, the EAI and ESI decreased the interfacial tension of sorghum grains after irradiation (Ahmed et al., 2018Ahmed, M. M., Abdalla, I. G., Salih, A. M., & Hassan, A. B. (2018). Effect of gamma radiation on storability and functional properties of sorghum grains (Sorghum bicolor L.). Food Science & Nutrition, 6(7), 1933-1939. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752...
).
3.4 Foaming capacity of gluten protein
The effects of X-ray irradiation on the foaming properties are shown in Figure 4. The FC of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 showed a significant decrease in FC (p < 0.05). This change in decrease might be associated with the ionizing radiation that would have change the solubility and protein nature. Ionizing irradiation promotes change in proteins and may lead to a change in foaming properties (Ahmed et al., 2018Ahmed, M. M., Abdalla, I. G., Salih, A. M., & Hassan, A. B. (2018). Effect of gamma radiation on storability and functional properties of sorghum grains (Sorghum bicolor L.). Food Science & Nutrition, 6(7), 1933-1939. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752...
). Furthermore, the FS was unchanged. The FS of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 was 77%, 74%, 70%, respectively. The FS of all the three samples, such as GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3, were significantly different from each other.
3.5 Protein content
Figure 5 shows the protein content present in gluten protein. It was estimated by the Kjeldahl method, in which the crude protein content of the food could be evaluated since nitrogen is also referred to non-protein components(Chang & Zhang, 2017Chang, S. K. C., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Protein analysis (pp. 315-331). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-5.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-...
).
The protein contents in GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 were 870.05%, 85.83%, and 85.22%, respectively. A significant decrease (p < 0.05) in protein percentage was observed in X-ray treated samples. Irradiation leads to denaturation in which proteins can be unfolded, and structure might have destabilized (Pollard, 1960Pollard, E. C. (1960). Effects of ionizing radiation on nucleoproteins. Cancer, 13(S6), 38-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(196011/12)13:6+<38::AID-CNCR2820130709>3.0.CO;2-W
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(1960...
).
3.6 Moisture content
Figure 6 shows the moisture content of gluten protein. The moisture contents of GLU 00, GLU 1, GLU 3 were 0.3, 0.7, 0.9%, respectively. All three samples were significantly different (p < 0.05) from each other. The same moisture effect was mentioned by Molins (2001)Molins, R. A. (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications. New York: Wiley..
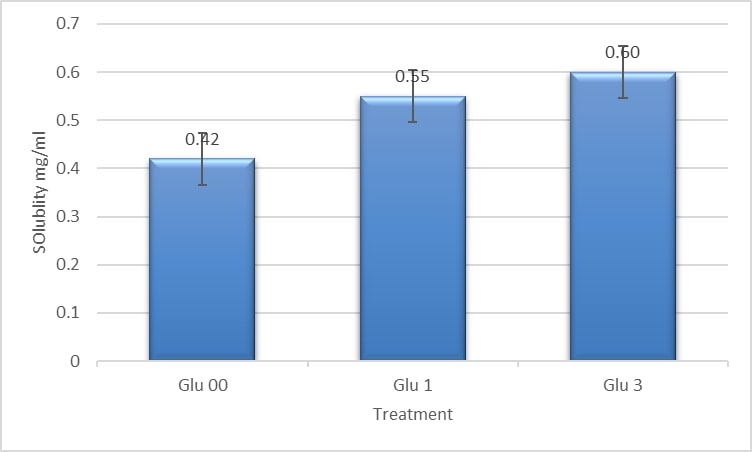
3.7 Solubility
The water solubilities of GLU 00, GLU 1, and GLU 3 were 0.4267, 0.3767, and 0.4333 mg/mL, respectively (Figure 7). The increase in water solubility was observed between control and treated samples (p < 0.05). This increase might be related to irradiation since it breaks down covalent linkages and might be associated with depolymerization and exposure of hydrophobic groups as explained in Molins (2001)Molins, R. A. (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications. New York: Wiley..
3.8 Molecular weight
The glutenin and gliadin fractions in GPP were determined through the SDS page. It was evident from the electropherograms that more significant numbers of polypeptides were present in the region falling within the high molecular weight glutenin subunits. The High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GS) were ranging between 90kDa to 200kDa, and Low-Molecular-Weight (LMW) gliadin was ranging between 20kDa to 50kDa. The X-ray treatment did not show any noticeable effects on the gluten protein in electrophotography (Figure 8). A similar effect was observed in whey protein, where molecular weight should remain unchanged, however, a significant changehas been shown in other protein properties (Segat et al., 2014Segat, A., Biasutti, M., Iacumin, L., Comi, G., Baruzzi, F., Carboni, C., & Innocente, N. (2014). Use of ozone in production chain of high moisture Mozzarella cheese. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft + Technologie, 55(2), 513-520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.029
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10....
).
3.9 The net charge on emulsion
Zeta potential is an essential physicochemical parameter that represents the native charges on a solvent system with the solute. Ionization may generate various amino acid residues are formed by partial ionization (Zhao et al., 2017Zhao, Y., Sun, N., Li, Y., Cheng, S., Jiang, C., & Lin, S. (2017). Effects of electron beam irradiation (EBI) on structure characteristics and thermal properties of walnut protein flour. Food Research International, 100(Pt 1), 850. PMid:28873758. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.08.004
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017...
). The hydrolysis led to the exposure of negatively charged ions, such as carboxyl groups. Therefore, the amino acids possessed many surfaces negative in Glu 00, however, the Glu 03 showed the increase in the charge towards the positive side (Figure 9). The same effect was described in the Molins (2001)Molins, R. A. (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications. New York: Wiley. where ionization generates free electrons from macromolecules like protein. The release of the free electron creates positive charges, and the same effect has been proved with zeta potential analysis.
3.10 Secondary structure of protein and functional groups
The FTIR spectra did not reflect any changes in Beta sheets and random coils and no noticeable changes were found in the region 1700 to 1600 cm-1. This indicates that the X-ray treatment does not affect intramolecular hydrogen bonds of beta-sheet proteins (Figure 10).
In Glu-00, absorption associated with 2258.8cm-1 band leads to N=C=O stretching, which shows the presence of isocyanate functional group. Isocyanate group has numerous functions in mechanical and thermal properties. It tends to react with an amino group and the hydroxyl group of the protein molecule. However, since the sample was treated with irradiation, the N=C=O stretching band have disappeared. Mechanical and thermal properties might have been affected due to the absence of this band in the treated sample (Hemsri et al., 2009Hemsri, S., Simpson, C., Parnas, R., & Asandei, A. D. (2009). Isocyanate, thiol, epoxide and hydroxy functionalized silane coated alumina/wheat gluten blends. Polymer Preprints, 50(1), 171-172.).
In Glu-3, absorption associated with 1740 cm-1 bands has been corresponded to C=O. The carbonyl groups are chemically relevant. It is vital in the interpretation of infrared spectra. The carbonyl group present was consisted of aldehyde due to wavelength as well as the carbonyl group pointed toward a terminal group and had only one substituent group and one being a single hydrogen atom. Carbonyl group acts as a hydrogen acceptor and leads to hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is of considerable significance seeing that it leads to the formation of secondary and tertiary structures and thereby leads to the stabilization of protein molecules (Cole, 2000Cole, B. B. (2000). Managed futures: out of favor or outta here? Polar Investment Counsel). X-ray irradiated protein can cause specific permanent changes such as decarboxylation, deamination, reduction of disulfide linkages, oxidation of sulfhydryl groups, modification of amino acid moieties, valence change of coordinated metal ions, peptide chain cleavage and aggregation (Kuan et al., 2013Kuan, Y.-H., Bhat, R., Patras, A., & Karim, A. A. (2013). Radiation processing of food proteins: A review on the recent developments. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 30(2), 105-120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.12.002
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.12...
). The proteins are composed of many NH and OH functional groups that can donate hydrogen bonds, and CO, and other groups accept them. Hydrogen bonds determine the secondary and tertiary structure of protein molecules (Kostal, 2016Kostal, J. (2016). Computational chemistry in predictive toxicology: status quo et quo vadis? Advances in Molecular Toxicology, 10, 139-186. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804700-2.00004-0
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-8047...
). Hydrogen bonds are not often the primary driving force determining the conformation and aggregation of globular proteins, but they do play a crucial role in stabilizing the structures once formed (Cole, 2000Cole, B. B. (2000). Managed futures: out of favor or outta here? Polar Investment Counsel). The FTIR spectra showed that the OH group have been eliminated when the dose of irradiation has been increased. It might affect the secondary and tertiary structure of the protein, and thereby denaturation of protein might have occurred. Denaturation leads to unfolding, and exposure of hydrophilic and hydrophobic group took place, and water and oil holding capacities might have been increased (Margesin & Schinner, 1999Margesin, R., & Schinner, F. (1999). Cold-adapted organisms: Ecology, physiology, enzymology and molecular biology. Berlin: Springer. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06285-2.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-0628...
). The reaction between cysteine and cystine disulfide bonds exerts a strong influence on the functional properties of the protein (Gelita, 2018Gelita. (2018). Functional properties. Gelita Service.). The FTIR study revealed that as the irradiation dose increased, the thiol groups were eliminated. Disulfide bonds in intermolecular glutenin influence the viscoelastic property of wheat gluten protein (Hammann & Schmid, 2014Hammann, F., & Schmid, M. (2014). Determination and quantification of molecular interactions in protein films: A review. Materials, 7(12), 7975-7996. PMid:28788285. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975
http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975...
). So the disappearance of thiol group may affect the viscoelastic property of wheat gluten.
4 Conclusion
Gluten protein powder was treated with X-ray irradiation at 108 kV for 1 sec and 3-second and was also exposured to X-ray radiation. Functional and physiological properties of these treated gluten protein powder were studied and compared with untreated gluten protein powder. X-ray treatment resulted in improved water and oil holding capacities. These “tailor-made proteins” consisting of Good water holding capacity can be used in the preparation of bakery applications, soups, gravies, and due to their influence of oil holding capacity, they can also be used for cooking noodles and pasta. The X-ray treatment resulted in negative impacts on EAI and ESI. However, it was suspected that the excess of energy after increasing X-ray irradiation of prolonged dose may form too many hydrophobic regions within the GPP to be exposed to the exterior aqueous environment. This process, in turn, led to the aggregation of the proteins and finally the emulsion stability of GPP can be reduced. On the other hand, it has also influenced the FS as irradiation leads to protein unfolding and changes the protein nature. Owing to the influence of FS, it can be used to prepare ice-cream, cake, cream etc. Thus, the X-ray on gluten protein can alter the functional and physiological properties which can be used in food industry.
Acknowledgements
A special thanks to Diya Lab (Scientific & Reference Laboratories) for obtaining FTIR and Particle Size Analysis results.
-
Cite as: Chandra, D., Dabade, A., Damgude, G., & Malhotra, C. (2021). Effect of X-rays on structural, physicochemical and functional properties of gluten protein. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology, 24, e2020074. https://doi.org/10.1590/1981-6723.07420
-
Funding: None.
References
- Ahmed, M. M., Abdalla, I. G., Salih, A. M., & Hassan, A. B. (2018). Effect of gamma radiation on storability and functional properties of sorghum grains (Sorghum bicolor L.). Food Science & Nutrition, 6(7), 1933-1939. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.752 - Babiker, E. F. E., Fujisawa, N., Matsudomi, N., & Kato, A. (1996). Improvement in the functional properties of gluten by protease digestion or acid hydrolysis followed by microbial transglutaminase treatment. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 44(12), 3746-3750. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf960302d
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf960302d - Ballesteros, L. F., Teixeira, J. A., & Mussatto, S. I. (2014). Chemical, functional, and structural properties of spent coffee grounds and coffee silverskin. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(12), 3493-3503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1349-z
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1349-z - Barron, E. S. G., & Finkelstein, P. (1952). Studies on the mechanism of action of ionizing radiations. X. Effect of x-rays on some physicochemical properties of proteins. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 41(1), 212-232. PMid:12997265. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(52)90521-3
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(52)90521-3 - Cano-Medina, A., Jiménez-Islas, H., Dendooven, L., Herrera, R. P., González-Alatorre, G., & Escamilla-Silva, E. M. (2011). Emulsifying and foaming capacity and emulsion and foam stability of sesame protein concentrates. Food Research International, 44(3), 684-692. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.015
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.015 - Chang, S. K. C., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Protein analysis (pp. 315-331). Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-5
» https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45776-5 - Chau, C.-F., Cheung, P. C. K., & Wong, Y.-S. (1997). Functional properties of protein concentrates from three Chinese indigenous legume seeds. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(7), 2500-2503. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf970047c
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jf970047c - Cole, B. B. (2000). Managed futures: out of favor or outta here? Polar Investment Counsel
- Farkas, J. (2006). Irradiation for better foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 17(4), 148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.003
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.003 - Gelita. (2018). Functional properties. Gelita Service.
- Hammann, F., & Schmid, M. (2014). Determination and quantification of molecular interactions in protein films: A review. Materials, 7(12), 7975-7996. PMid:28788285. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975
» http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ma7127975 - Harder, M. N. C., Arthur, V., & Arthur, P. B. (2015). Irradiation of foods: processing technology and effects on nutrients: effect of ionizing radiation on food components. In B. Caballero, P. M. Finglas & F. Toldrá (Eds.), Encyclopedia of food and health (pp. 476-471). Amsterdam: Academic Press.
- Hemsri, S., Simpson, C., Parnas, R., & Asandei, A. D. (2009). Isocyanate, thiol, epoxide and hydroxy functionalized silane coated alumina/wheat gluten blends. Polymer Preprints, 50(1), 171-172.
- Hmed, S. E. A., & Osman, G. A. M. (2009). Effect of gamma irradiation on the physico-chemical characterstics of groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea). Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3(3), 2856-2860.
- Jongjareonrak, A., Srikok, K., Leksawasdi, N., & Andreotti, C. (2015). Extraction and fundamental properties of protein from de-oiled rice bran of rice bran oil production industry. Chiang Mai University Journal of Natural Sciences, 14(2), 163-174. http://dx.doi.org/10.12982/CMUJNS.2015.0079
» http://dx.doi.org/10.12982/CMUJNS.2015.0079 - Kaushik, R., Kumar, N., Sihag, M. K., & Ray, A. (2015). Isolation, characterization of wheat gluten and its regeneration properties. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(9), 5930-5937. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1690-2
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1690-2 - Kostal, J. (2016). Computational chemistry in predictive toxicology: status quo et quo vadis? Advances in Molecular Toxicology, 10, 139-186. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804700-2.00004-0
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804700-2.00004-0 - Kovacs, M. I. P., Fu, B. X., Woods, S. M., & Khan, K. (2004). Thermal stability of wheat gluten protein: its effect on dough properties and noodle texture. Journal of Cereal Science, 39(1), 9-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(03)00058-4
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0733-5210(03)00058-4 - Kuan, Y.-H., Bhat, R., Patras, A., & Karim, A. A. (2013). Radiation processing of food proteins: A review on the recent developments. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 30(2), 105-120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.12.002
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2012.12.002 - Lee, N.-Y., Kang, C.-S., & Kim, H.-S. (2017). Effects of γ-irradiation on the quality changes of fresh noodles prepared from wheat cultivated with N-fertilization treatments. Food Science and Biotechnology, 26(1), 135-142. PMid:30263520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0018-1
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0018-1 - Li, C., Huang, X., Peng, Q., Shan, Y., & Xue, F. (2014). Physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-glucomannan conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21(5), 1722-1727. PMid:24703823. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.03.018
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.03.018 - Margesin, R., & Schinner, F. (1999). Cold-adapted organisms: Ecology, physiology, enzymology and molecular biology Berlin: Springer. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06285-2
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06285-2 - Molins, R. A. (2001). Food irradiation: principles and applications. New York: Wiley.
- Pollard, E. C. (1960). Effects of ionizing radiation on nucleoproteins. Cancer, 13(S6), 38-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(196011/12)13:6+<38::AID-CNCR2820130709>3.0.CO;2-W
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(196011/12)13:6+<38::AID-CNCR2820130709>3.0.CO;2-W - Roger, D. D., Jean-Justin, E. N., & François-Xavier, E. (2007). Nutritive value, toxicological and hygienic quality of some cassava based products consumed in Cameroon. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 6(4), 404-408. http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2007.404.408
» http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2007.404.408 - Segat, A., Biasutti, M., Iacumin, L., Comi, G., Baruzzi, F., Carboni, C., & Innocente, N. (2014). Use of ozone in production chain of high moisture Mozzarella cheese. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft + Technologie, 55(2), 513-520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.029
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.029 - Sui, X., Bi, S., Qi, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Li, Y., & Jiang, L. (2017). Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin: its emulsifying property and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 727-734. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.024
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.024 - Yalcin, E., Sakiyan, O., Sumnu, G., Celik, S., & Koksel, H. (2008). Functional properties of microwave-treated wheat gluten. European Food Research and Technology, 227(5), 1411-1417. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0860-8
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0860-8 - Yilmaz, E., & Emir, D. D. (2016). Extraction and functional properties of proteins from pre-roasted and enzyme treated poppyseed (Papaver somniferum L.) press cakes. Journal of Oleo Science, 65(4), 319-329. PMid:26972462. http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228
» http://dx.doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15228 - Yu, J., Ahmedna, M., & Goktepe, I. (2007). Peanut protein concentrate: production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chemistry, 103(1), 121-129. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.08.012
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.08.012 - Zhao, Y., Sun, N., Li, Y., Cheng, S., Jiang, C., & Lin, S. (2017). Effects of electron beam irradiation (EBI) on structure characteristics and thermal properties of walnut protein flour. Food Research International, 100(Pt 1), 850. PMid:28873758. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.08.004
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.08.004
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
09 Apr 2021 -
Date of issue
2021
History
-
Received
17 Apr 2020 -
Accepted
01 Sept 2020