Abstract
Despite being a bird with a broad and extensive distribution in Chile, the black-chinned siskin, Spinus barbatus Molina, 1782 is not well studied in relation to its parasites. This paper aims to describe the ectoparasite fauna of S. barbatus in central and southern Chile. A total of 125 individuals caught with mist nets were examined alive; a total of 22 parasites were found dead and were exposed to parasit autopsy. The extracted parasites were preserved in 70% alcohol for subsequent mounting and identification. Ectoparasites were found in 56 black-chinned siskins (38%); 48 of them (33%) had 870 mites – 680 feather mites (Astigmata: Analgoidea) were identified as Proctophyllodes spini, 167 as Knemidokoptes jamaicensis, 19 as Strelkoviacarus critesi, and one as Analges passerinus. Moreover, three mites were chiggers belonging to the tribe Schoengastiini (Prostigmata: Trombiculidae). In 21 birds (14%), 54 lice were found, 21 of which were identified as Philopterus roehreri, 18 as Myrsidea serini, and 15 as Ricinus carolynae. Endoparasites were not found in the necropsied individuals. All of the parasites that were found represent new records for Chile, and they also serve as new records of host–parasite associations for S. barbatus.
Keywords:
Ectoparasites; mites; lice; Fringillidae
Resumo
Spinus barbatus (Molina, 1782), apesar de ser uma ave de distribuição rica e extensa no Chile, não existem estudos relacionados com os seus parasitas. Este trabalho tem como objetivo classificar taxonomicamente os parasitas de S. barbatus no Chile central e do sul. Para isso, foram analisados 125 indivíduos capturados com redes de neblina e 22 que foram submetidos a autópsia parasitária. Os parasitas extraídos foram conservados em álcool 70% para um posterior montagem e identificação. Em 56 indivíduos de S. barbatus (38%) foram encontrados ectoparasitas, 48 deles (33%) tinham 870 ácaros, 680 identificados como Proctophyllodes spini, 167 como Knemidokoptes jamaicensis, 19 como Strelkoviacarus critesi, três ácaros pertencentes à tribo Schoengastiini e um Analges passerinus. Em 21 aves (14%) 54 piolhos foram encontrados, 21 dos quais foram identificados como Philopterus roehreri; 18 como Myrsidea serini e 15 como Ricinus carolynae. Não foram encontradas endoparasitas em indivíduos necropsiados. Todos os parasitas encontrados são novos registros para o Chile e, por sua vez novos recordes parasitológicos para a espécie S. barbatus, por isso são novas associações hospedeiro-parasita.
Palavras-chave:
Ectoparasitas; ácaros; piolhos; Fringillidae
Introduction
A bird can be seen as a resource that provides various habitats for parasites, offering benefits to the parasite while the host is harmed or suffers in some way (ATKINSON et al., 2008Atkinson CT, Thomas NJ, Hunter DB. Parasitic diseases of wild birds. Ames: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.). Parasites account for more than half of all animal diversity, which is largely due to the specificity of each parasite in relation to each host (TOMPKINS & CLAYTON, 1999Tompkins DM, Clayton DH. Host resources govern the specificity of swiftlet lice: size matters. J Anim Ecol 1999; 68(3): 489-500. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00297.x.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2656.19...
). Wild birds serve as hosts for many parasites; however, there are few studies on the specific species affecting these animals (FREITAS et al., 2002Freitas MFL, Oliveira JB, Cavalcanti MDB, Leite AS, Magalhaes VS, Oliveira RA, et al. Parásitos gastrointestinales de aves silvestres en cautiverio en el Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Parasitol Latinoam 2002; 57(1-2): 50-54.).
In Chile, there are five species of the genus Spinus, of which the black-chinned siskin Spinus barbatus Molina, 1782 is the most widely distributed in this country (JARAMILLO, 2005Jaramillo A. Aves de Chile. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions; 2005.), spanning from the Valle del Huasco to the Cabo de Hornos archipelago, and from sea level to 2,600 meters (COUVE & VIDAL-OJEDA, 2000Couve E, Vidal-Ojeda C. Aves del Canal Beagle y Cabo de Hornos. Punta Arenas: Fantástico Sur; 2000.; MARTINEZ & GONZALEZ, 2004Martínez D, González G. Las aves de Chile: nueva guía de campo. Santiago: Ediciones del Naturalista; 2004.). Despite being an abundant and widespread bird, there is no information about its parasitic fauna. Therefore, the aim of this study is to contribute to the knowledge of the parasitic fauna of S. barbatus in the central and southern areas of Chile.
Materials and Methods
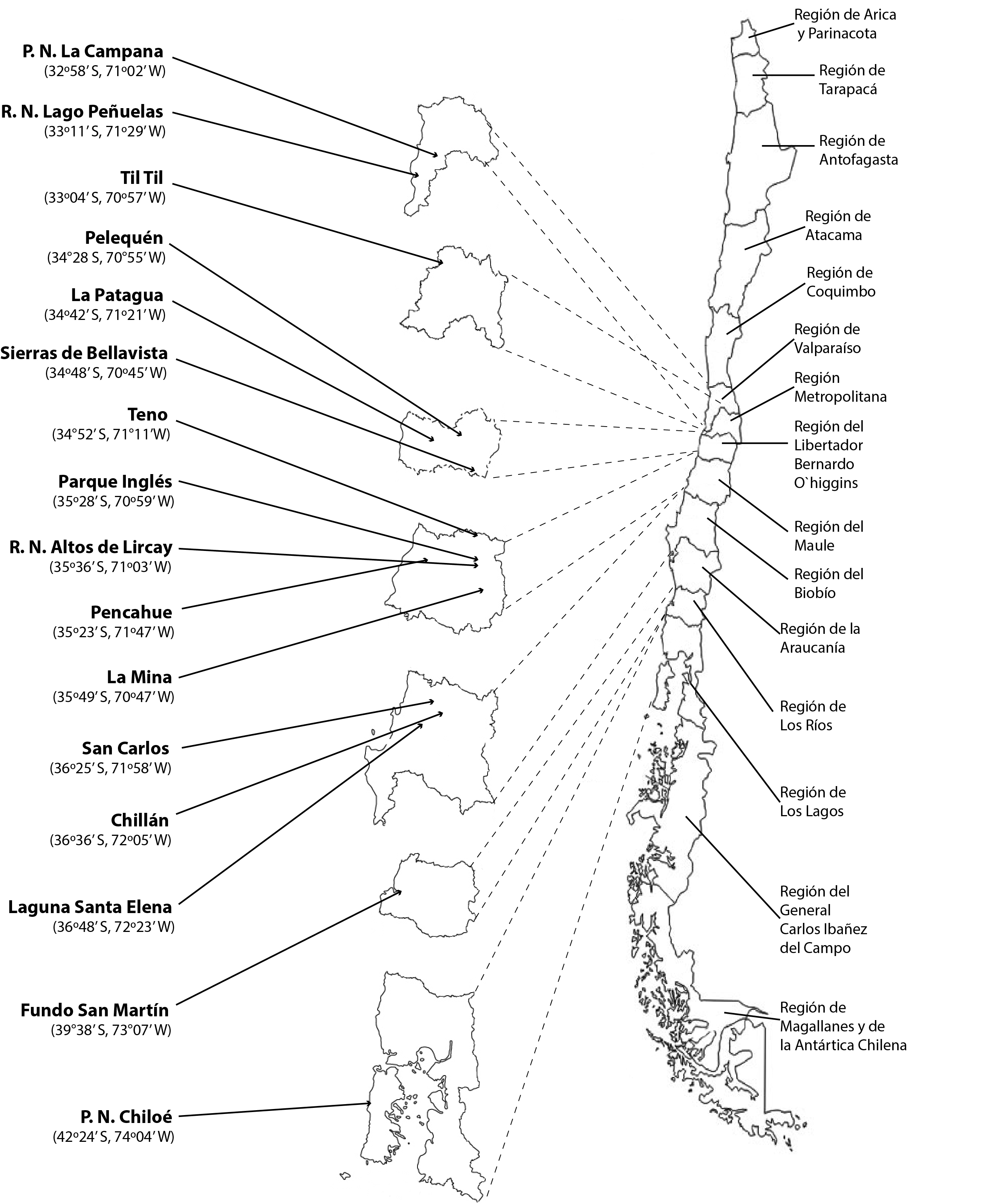
A total of 147 black-chinned siskins from 16 locations in central and southern Chile (Figure 1) were analyzed. Samplings were taken from 125 live individuals captured using mist nets. These birds were examined for no longer than five minutes to avoid excessive stress. The parasites were removed from feathers via anatomic tweezers and the parasites were preserved in 70% alcohol for subsequent identification. In addition, 22 birds were found dead (being trampled or poached, and death by cats were among the most common causes), at which point we performed necropsies that included a search for gastrointestinal parasites and ectoparasites. Each of these individuals was stored in plastic bags and frozen to ensure that the least amount of feathers and ectoparasites was lost. Subsequently, the search for gastrointestinal parasites was performed using the technique described by Kinsella & Forrester (1972)Kinsella JM, Forrester DJ. Helminths of the Florida duck, Anas platyrhynchos fulvigula.Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 1972; 39(2): 173-176..
With respect to black-chinned siskins that had crusted lesions on their legs, deep scraping was performed to remove the crusts; these samples were preserved in the same manner as for the other ectoparasites.
In the laboratory setting, the lice that were found were cleaned in 20% KOH and carried by ascending alcohol solutions (40%, 80%, and 100%); they were then rinsed for 24 hours in clove oil, and were finally mounted in Canada Balsam (PALMA, 1978Palma RL. Slide-mounting of lice: a detalied description of the Canada balsam tecnique. NZ Entomol 1978; 6(4): 432-436. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00779962.1978.9722313.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00779962.1978....
; PRICE et al., 2003Price RD, Hellenthal RA, Palma RL, Johnson KP, Clayton DH. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey; 2003. no. 24. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication.). The obtained mites were rinsed in Nesbitt solution (40 g of chloral hydrate, 25 mL of distilled water, and 2.5 mL of concentrated HCl) for 72 h and mounted in permanent preparation with Berlese solution (Hoyer medium) (KRANTZ & WALTER, 2009Krantz GW, Walter DE. A manual of acarology. 3rd ed. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press; 2009.).
Identification of lice was based on the keys and descriptions proposed by Klockenhoff (1984)Klockenhoff HF. A redescription of (Mallophaga: Menoponidae), a parasite from passerine birds. Myrsidea seriniNZ J Zool 1984; 11(1): 17-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03014223.1984.10428223.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03014223.1984....
and Price et al. (2003)Price RD, Hellenthal RA, Palma RL, Johnson KP, Clayton DH. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey; 2003. no. 24. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication. were used; for mites, the keys and descriptions of Turk (1950)Turk FA. A new species of parasitic mite, Cnemidocoptes jamaicensis, a causative agent of scaly leg in Turdus aurantiacus.Parasitology 1950; 40(1-2): 60-62. PMid:15401172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118200001787X.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000017...
, Hill et al. (1967)Hill DS, Wilson N, Corbet GB. Mites associated with British species of (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). OrnithomyaJ Med Entomol 1967; 4(2): 102-122. PMid:6052122. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.102.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.10...
, Atyeo & Braasch (1966)Atyeo WT, Braasch NL. The feather mite genus (Sarcoptiformes: Proctophyllodidae). ProctophyllodesBull Univ Nebr State Mus 1966; 5: 1-354., Fain & Elsen (1967)Fain A, Elsen P. Les acariens de la famille Knemidokoptidae producteurs de gale chez les oiseaux (Sarcoptiformes). Acta Zool Pathol Antverp 1967; 47: 3-145., and Kolarova & Mitov (2008)Kolarova NT, Mitov PG. Feather mites of the superfamily Analgoidea (Acari: Astigmata) from Passerines (Aves: Passeriformes) in South Dobrudzha, Bulgaria. Acta Zool Bulg 2008;(Suppl. 2): 91-102. were used.
For the isolated parasites, their basic population parameters were calculated; the prevalence is represented by the percentage of hosts infected with a particular parasite species, the average intensity is an average of collected parasites in infected hosts, abundance is the number of individuals of a particular parasite on a single host (BUSH et al., 1997Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 1997; 83(4): 575-583. PMid:9267395. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3284227.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3284227...
), and the range indicates the lowest and highest number of parasites isolated in infected hosts. Analyses were performed using the Quantitative Parasitology 3.0 program (RÓZSA et al., 2000Rózsa L, Reiczigel J, Majoros G. Quantifying parasites in samples of hosts. J Parasitol 2000; 86(2): 228-232. PMid:10780537. http://dx.doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0228:QPISOH]2.0.CO;2.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2000...
).
Results and Discussion
In the 147 black-chinned siskins analyzed for the presence of ectoparasites (125 captured and 22 necropsied), the following groups of parasites were found: four mite species belonging to the suborder Astigmata, one mite species of the suborder Prostigmata, and three species of lice (Phthiraptera). In the 22 necropsied birds that were investigated, endoparasites were not registered. Ectoparasites were found in 56 black-chinned siskins (38% of birds analyzed). Table 1 and 2 summarize the population parameters of the collected mites and lice respectively from the 147 black-chinned siskins that were analyzed. Table 3 show the sex and age of all collected lice.
Population parameters of mites collected from the 147 black-chinned siskins that were analyzed.
Population parameters of lice collected from the 147 black-chinned siskins that were analyzed.
Astigmata
Of the birds that were analyzed, 48 (33%) hosted 870 mites, which included 680 Proctophyllodes spini Atyeo and Braasch, 1966 (Proctophyllodidae); 167 Knemidokoptes jamaicensis Turk, 1950 (Knemidokoptidae); 19 Strelkoviacarus critesi Spory, 1965 (Analgidae); and one Analges passerinus Linnaeus, 1758 (Analgidae).
Proctophyllodes spini Atyeo & Braasch, 1966
In the 41 specimens of black-chinned siskins (34 live and 7 dead), 680 specimens of Proctophyllodes spini (216 males, 315 females, and 149 preimaginal instars) (Figure 2) were collected from the primaries and tail feathers. These mites were found on birds captured in Laguna Santa Elena, Pencahue, Til Til, La Campana National Park, La Patagua, Parque Inglés, La Mina, Altos de Lircay Natural Reserve, Sierras de Bellavista, Lago Peñuelas National Reserve, San Carlos, Chillan, Fundo San Martin, and Chiloé National Park.
P. spini occurs only on birds of the family Fringillidae. It has been found on Spinus tristis in the United States and Canada, on S. psaltria and S. pinus in the United States, on S. notatus in Mexico (ATYEO & BRAASCH, 1966Atyeo WT, Braasch NL. The feather mite genus (Sarcoptiformes: Proctophyllodidae). ProctophyllodesBull Univ Nebr State Mus 1966; 5: 1-354.; KNOWLES & KLIMOV, 2011Knowles LL, Klimov PB. Estimating phylogenetic relationships despite discordant gene trees across loci: the species tree of a diverse species group of feather mites (Acari: Proctophyllodidae). Parasitology 2011; 138(13): 1750-1759. PMid:21554840. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118201100031X.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0031182011000...
; GALLOWAY et al., 2014Galloway TD, Proctor HC, Mironov SV. Chewing lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Amblycera, Ischnocera) and feather mites (Acari: Astigmatina: Analgoidea, Pterolichoidea): ectosymbionts of grassland birds in Canada. In: Cárcamo HA, Giberson DJ. Arthropods of Canadian grasslands. Ottawa: Entomological Society of Canada; 2014. p. 139-188. vol. 3. Biodiversity and systematics. Part 1. Biological Survey of Canada.), and on S. spinus in Russia (MIRONOV, 1996Mironov SV. Feather mites from passerines on the North-West of Russia. Parazitologiya 1996; 30(6): 521-539.). Therefore, this study represents the first record of P. spini in fringillid birds in the Neotropics.
The genus Proctophyllodes Robin, 1868 (Astigmata: Analgoidea: Proctophyllodidae: Proctophyllodinae) currently includes about 170 species. These mites are usually found on the flight feathers (primaries, secondaries, and tertialis) and greater coverts of the wings and on the rectrices (MIRONOV et al., 2012Mironov SV, Dabert J, Dabert M. A new feather mite species of the genus Robin, 1877 (Astigmata: Proctophyllodidae) from the long-tailed tit . ProctophyllodesAegithalos caudatus (Passeriformes: Aegithalidae)-morphological description with DNA barcode dataZootaxa 2012; 3253: 54-61.).
Knemidokoptes jamaicensis Turk, 1950
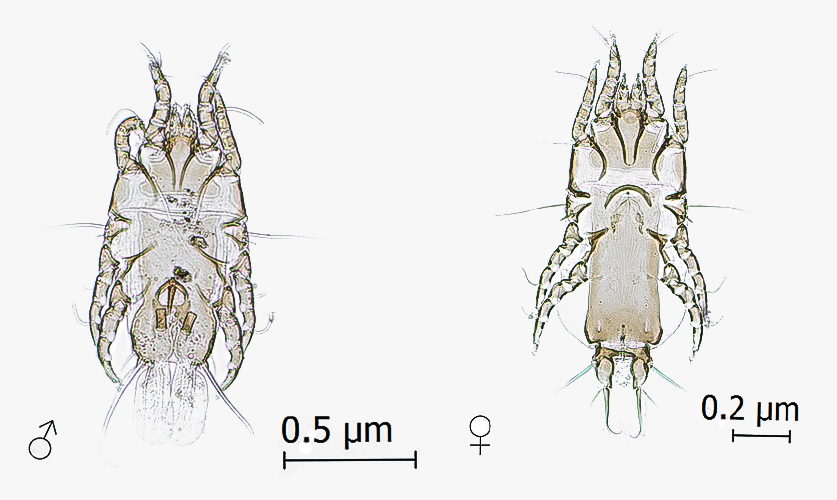
On the legs of five live black-chinned siskins, the scaly lesions characteristic of scabies were observed. These black-chinned siskins came from Pencahue, Altos de Lircay Natural Reserve, Sierras de Bellavista, and La Patagua. A total of 127 females and 40 larvae of Knemidokoptes jamaicensis (Figure 3) were collected; no males were found.
A Knemidokoptes jamaicensis female; to its left, a larva of the same species (400X magnification).
The mite K. jamaicensis was described by Turk (1950)Turk FA. A new species of parasitic mite, Cnemidocoptes jamaicensis, a causative agent of scaly leg in Turdus aurantiacus.Parasitology 1950; 40(1-2): 60-62. PMid:15401172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118200001787X.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000017...
in a golden thrush Turdus aurantiacus in Jamaica. Subsequently, it was found to parasitize birds of the Alaudidae, Corvidae, Drepanidae, Emberizidae, Fringillidae, Icteridae, Motacillidae, Mimidae, Paridae, Parulidae, Sittidae, Sylviidae, Turdidae, Tyranidae, and Thraupidae families (Passeriformes) (FAIN & ELSEN, 1967Fain A, Elsen P. Les acariens de la famille Knemidokoptidae producteurs de gale chez les oiseaux (Sarcoptiformes). Acta Zool Pathol Antverp 1967; 47: 3-145.; DABERT et al., 2013Dabert J, Dabert M, Gal AF, Miclăuş V, Mihalca AD, Sándor AD. Multidisciplinary analysis of Knemidocoptes jamaicensis parasitising the common chaffinch, : proofs for a multispecies complex? Fringilla coelebsParasitol Res 2013; 112(6): 2373-2380. PMid:23563901. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3402-7.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-340...
). Mete et al. (2014)Mete A, Stephenson N, Rogers K, Hawkins MG, Sadar M, Sanchez-Migallón D, et al. Knemidocoptic mange in wild golden eagles, California, USA. Emerg Infect Dis 2014; 20(10): 1716-1718. PMid:25271842. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2010.140504.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2010.140504...
described K. jamaicensis parasitizing Golden Eagles Aquila chrysaetos (Aves: Accipitridae) in the United States. These numerous and geographically diverse records serve as evidence of the nearly ubiquitous distribution of K. jamaicensis in passerines (PENCE et al., 1999Pence DB, Cole RA, Brugger KE, Fischer JR. Epizootic podoknemidokoptiasis in American robins. J Wildl Dis 1999; 35(1): 1-7. PMid:10073340. http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-35.1.1.
http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-35.1...
); however, in Chile, there had been no previous records of this parasite.
Species of the genus Knemidokoptes Furstenberg, 1870 cause knemidokoptic scabies in birds, and they are more commonly referred to as the Scaly Face and/or Scaly Leg mites (GAUDIOSO et al., 2009Gaudioso JM, LaPointe DA, Hart PJ. Knemidokoptic mange in Hawai‘i’ Amakihi (Hemignathus virens) on the island of Hawai’i. J Wildl Dis 2009; 45(2): 497-501. PMid:19395759. http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-45.2.497.
http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-45.2...
). They can be found in various regions of the body. Knemidocoptes jamaicensis is usually found under the scales of the feet and legs of domestic and wild birds (LANGENSCHEIDT, 1958Langenscheidt M. Embryologische, morphologische und histologische Untersuchungen an Knemidocoptes mutans (Robin et Lanquetin). Z Parasitenkd 1958; 18(4): 349-385. PMid:13604749. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00259664.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00259664...
; KIRMSE, 1966Kirmse P. Cnemidocoptic mite infestations in wild birds. J Wildl Dis 1966; 2(4): 86-99.).
Strelkoviacarus critesi Spory, 1965
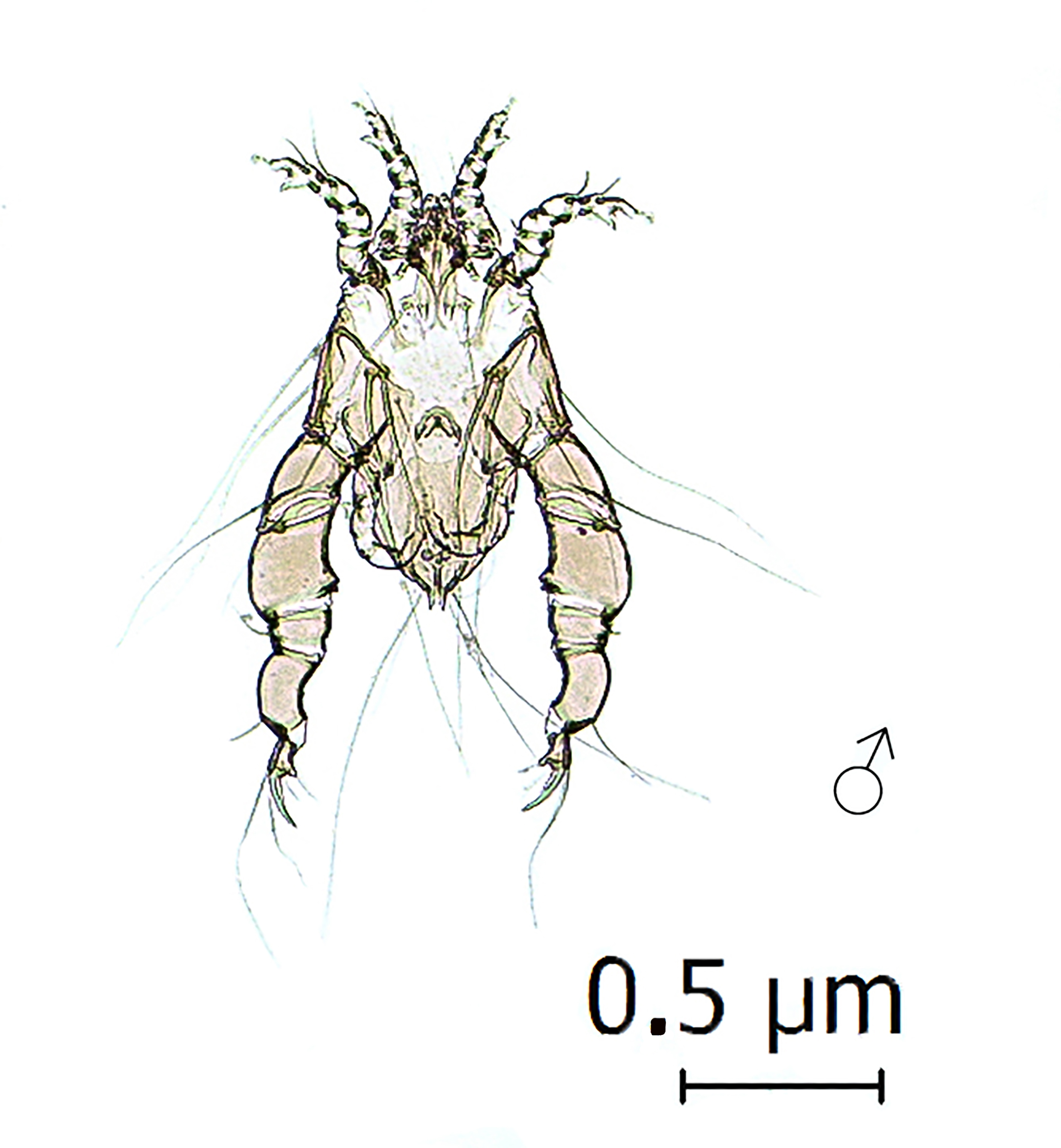
In five black-chinned siskins (three live and two dead), the mite Strelkoviacarus critesi (Figure 4) was found. Infected birds originated from Pencahue, La Mina, Altos de Lircay National Reserve, and Chillan. Twelve males and seven females were collected from the rachis of the primary wing feathers.
The S. critesi was described to parasitize Agelaius phoeniceus (Icteridae) in the United States (SPORY, 1965Spory GR. Some internal and external parasites of the redwinged blackbird, L., from central Ohio, including descriptions of three new feather mites. Agelaius phoeniceus phoeniceusOhio J Sci 1965; 65(2): 49-59.). Subsequently, it has also been found on A. phoeniceus and Quicalus quiscula (Icteridae) in Canada (GALLOWAY et al., 2014Galloway TD, Proctor HC, Mironov SV. Chewing lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Amblycera, Ischnocera) and feather mites (Acari: Astigmatina: Analgoidea, Pterolichoidea): ectosymbionts of grassland birds in Canada. In: Cárcamo HA, Giberson DJ. Arthropods of Canadian grasslands. Ottawa: Entomological Society of Canada; 2014. p. 139-188. vol. 3. Biodiversity and systematics. Part 1. Biological Survey of Canada.). This study represents the first known record of S. critesi on birds of the family Fringillidae, as well as the first record of this parasite on Neotropical birds.
Species of the genus Strelkoviacarus are normally found on the skin of their hosts (most commonly on the skin of the wings), but they can also be found on the rachis of the basal part of the primary flight feathers and on the tubes of growing contour feathers (during molting) (MIRONOV et al., 2010Mironov SV, Skirnisson K, Thorarinsdottir ST, Nielsen OK. Feather mites (Astigmata: Psoroptidia) parasitising the rock ptarmigan Lagopus muta (Montin) (Aves: Galliformes) in Iceland. Syst Parasitol 2010; 75(3): 187-206. PMid:20157794. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9219-1.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-921...
). The representatives of this genus are regularly associated with louse flies of the genus Ornithomya, as well as with related genera (Diptera: Hippoboscidae), which are specialized parasites of birds (HILL et al., 1967Hill DS, Wilson N, Corbet GB. Mites associated with British species of (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). OrnithomyaJ Med Entomol 1967; 4(2): 102-122. PMid:6052122. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.102.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.10...
; PHILIPS & FAIN, 1991Philips JR, Fain A. Acarine symbionts louseflies (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). Acarologia 1991; 32(4): 377-384.). Phoresy of Strelkoviacarus mites by these flies represents an additional way that these mites disperse among individual birds. This is why the Strelkoviacarus species can be found on birds of various genera, families, and even orders, which is in contrast to most other feather mites that disperse only through direct contact between individual birds (MIRONOV et al., 2010Mironov SV, Skirnisson K, Thorarinsdottir ST, Nielsen OK. Feather mites (Astigmata: Psoroptidia) parasitising the rock ptarmigan Lagopus muta (Montin) (Aves: Galliformes) in Iceland. Syst Parasitol 2010; 75(3): 187-206. PMid:20157794. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9219-1.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-921...
). However, in Chile, there are no studies demonstrating the association between these hippoboscids flies and black-chinned siskins.
Analges passerinus Linnaeus, 1758
Only one male Analges passerinus was collected (Figure 5) on the back body feathers of a necropsied black-chinned siskin; data on its origin are unknown.
A. passerinus mites are usually located on the feathers of various body parts of bird hosts, as is the case for most representatives of the family Analgidae. This species is widely distributed in Eurasia, mainly in birds of the family Fringillidae (MIRONOV, 1985Mironov SV. Feather mites of the genera and. Analges Pteronyssoides from the European part of the USSR Sarcoptiformes, AnalgoideaParazitol Sb 1985; 33: 159-208.; RODRIGUES et al., 2015Rodrigues P, Mironov S, Sychra O, Resendes R, Literak I. Feather mites (Acari, Astigmata) from Azorean passerines (Aves, Passeriformes): lower species richness compared to European mainland. Parasite 2015; 22: 8. PMid:25665827. http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2015009.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/parasite/20150...
).
Representatives of the genus Analges live exclusively on passerines and are located primarily on the down feathers and coverts of the body. Given their location in the plumage of their hosts, the analgids are a group of mites that are quite difficult to collect from live birds and even from museum specimens. For this reason, the intensity of these parasites could not be well evaluated. The genus Analges currently includes about 50 species and it is the most speciose in the family Analgidae (MIRONOV, 1985Mironov SV. Feather mites of the genera and. Analges Pteronyssoides from the European part of the USSR Sarcoptiformes, AnalgoideaParazitol Sb 1985; 33: 159-208.).
Prostigmata
Three chigger mites belonging to the tribe Schoengastiini (Trombiculoidea: Trombiculidae) were found on one bird that originated from Altos de Lircay.
Mites of the tribe Shoengastiini
Three mites belonging to the tribe Schoengastiini (Prostigmata: Trombiculidae) (Figure 6) were found on the head of a black-chinned siskin captured in Altos de Lircay National Reserve. These mites could not be precisely identified to species given that they were fully engorged and their shields were poorly visible.
The Schoengastiini tribe was created by Vercammen-Grandjean to accommodate family Trombiculidae members who had expanded sensilla (BROWN, 2006Brown WA. An African chigger, n. sp. (Acari: Trombiculidae, shoengastiini), from primate monkey hosts, Chlorocebus sabaeus (L.) from Gambia. Schoengastia pitheciagambiae (L.) and Papio papioInt J Acarol 2006; 32(3): 283-286. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01647950608684469.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01647950608684...
). Trombiculid mites do not highly host specific, and they can infect a wide range of vertebrates; they are mainly located on the head (WALL & SHEARER, 2001Wall R, Shearer D. Veterinary ectoparasites: biology, pathology & control. 2nd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 2001.).
Phthiraptera
In 21 black-chinned siskins (14%), 54 lice were found; 21 were identified as Philopterus roehreri Eichler, 1956; 18 were identified as Myrsidea serini Seguy, 1944; and 15 were found to be Ricinus carolynae Nelson, 1972.
Philopterus roehreri Eichler, 1956
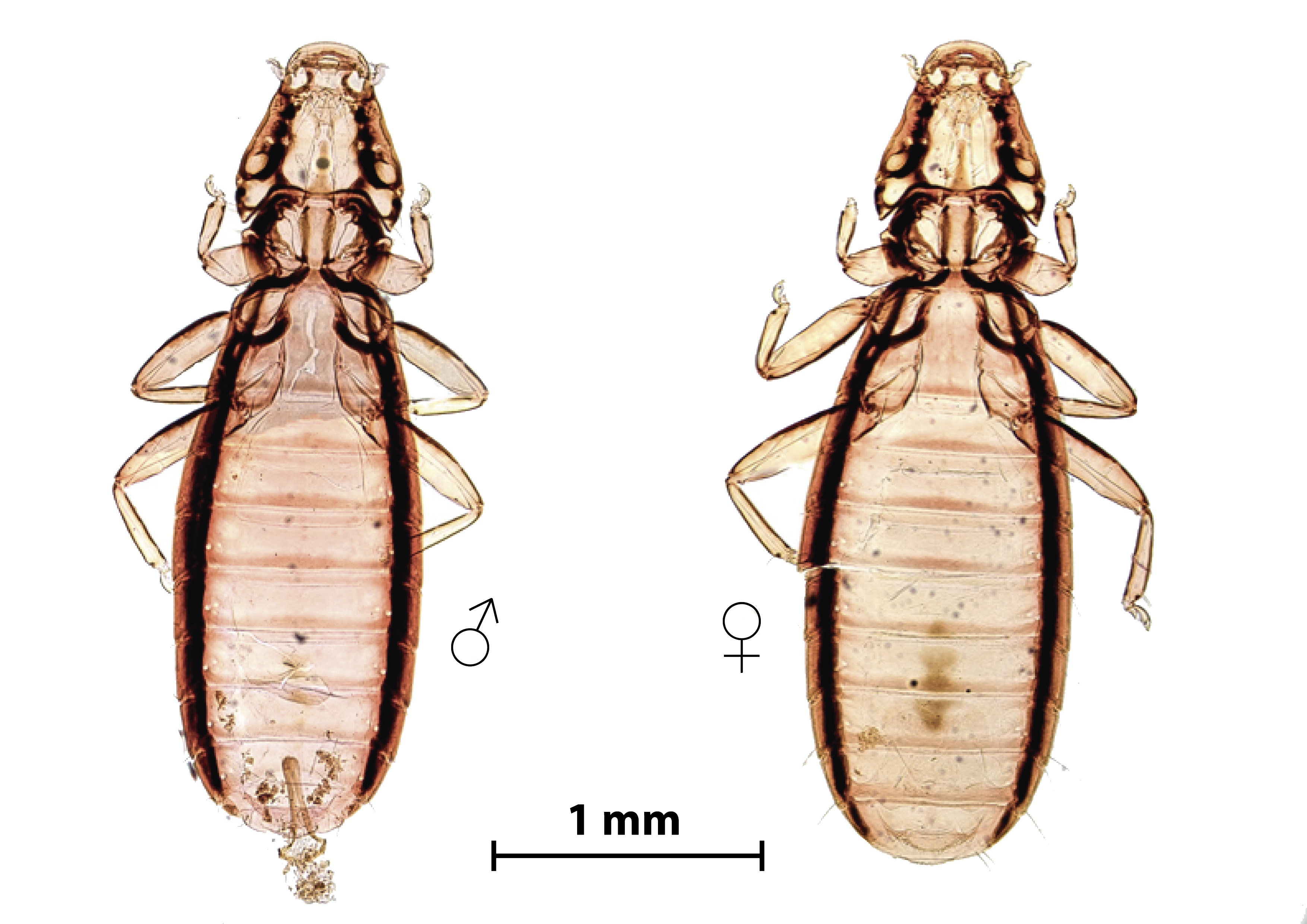
Philopterus roehreri (Figure 7) lice were collected in nine black-chinned siskins from La Campana National Park, La Patagua, La Mina, Penuelas Lake, Altos de Lircay National Reserve, and Cato. The sex ratio was 0.28. The ratio of adult to young P. roehreri was 0.5.
Lice P. roehreri were previously described in Spinus atrata (PRICE et al., 2003Price RD, Hellenthal RA, Palma RL, Johnson KP, Clayton DH. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey; 2003. no. 24. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication.). This is the first record of P. roehreri in black-chinned siskins and the first record of this louse in Chile.
The genus Philopterus belongs to the family Philopteridae, which is the only one in the suborder Ischnocera (these mites are known to parasitize birds) (SAAVEDRA-ORJUELA et al., 2014Saavedra-Orjuela A, Arévalo-Barreto S, Soler-Tovar D. Ectoparásitos del orden Phthiraptera en aves silvestres. Mem Conf Interna Med Aprovech Fauna Sil Exót Conv 2014; 10(2): 5-27.). Philopterus is a very speciose genus of Ischnocera and, to date, no reviews have considered the entire genus (SYCHRA et al., 2011Sychra O, Palma RL, Saxena AK, Ahmad A, Bansal N, Adam C. Chewing lice of the genus (Phthiraptera: Philopteridae) from drongos (Passeriformes: Dicruridae). PhilopterusZootaxa 2011; 2868: 51-61.).
Myrsidea serini Seguy, 1944
Myrsidea serini lice (Figure 8) were recorded in four necropsied black-chinned siskins from Altos de Lircay National Reserve and Chillan, and it was also found in a specimen without exact collection data. The sex ratio was 0.13. The ratio of adult versus young M. serini was 5.
This louse was previously registered in birds of the families Fringillidae and Emberizidae (Passeriformes) in Europe (MEY, 2003Mey E. Verzeichnis der Tierläuse (Phthiraptera) Deutschlands. Entomofauna Germanica 2003; 6: 72-129.; GALLOWAY, 2005Galloway TD. Ectoparasites from native and introduced birds from Christchurch and surrounding areas, New Zealand. Tuhinga 2005; 16: 13-20.; VAS et al., 2012Vas Z, Rékási J, Rózsa L. A checklist of lice of Hungary (Insecta: Phthiraptera). Ann Hist-Nat Mus Natl Hung 2012; 104: 5-109.).
This study represents the first record of M. serini in the Neotropics.
Lice of the genus Myrsidea Waterston, 1915 mainly parasitize birds of the order Passeriformes. With more than 350 species described thus far, this genus is the most specious of all genera in the order Phthiraptera; descriptions of other new species are still lacking (VALIM & WECKSTEIN, 2013Valim MP, Weckstein JD. A drop in the bucket of the megadiverse chewing louse genus Myrsidea (Phthiraptera, Amblycera, Menoponidae): ten new species from Amazonian Brazil. Folia Parasitol 2013; 60(5): 377-400. PMid:24471279. http://dx.doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.040.
http://dx.doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.040...
).
Ricinus carolynae Nelson, 1972
R. carolynae lice (Figure 9) were collected on six black-chinned siskins from Altos de Lircay National Reserve, Sierras de Bellavista, and Chillan. The sex ratio was 0.13. No juveniles were found.
Lice R. carolynae Nelson, 1972 have been described in the Carduelis notata, C. pinus, and C. psaltria species (PRICE et al., 2003Price RD, Hellenthal RA, Palma RL, Johnson KP, Clayton DH. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey; 2003. no. 24. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication.). This study is the first record of R. carolynae in Chile.
The genus Ricinus De Geer, 1778 is composed of 72 species, which are characterized by their relatively large size (3.1-5.3 mm), and they feed on the blood of birds, although some of them can supplement their diet with feathers. They infest avian hosts belonging to at least 30 families of Passeriformes (CICCHINO & CASTRO, 1998Cicchino AC, Castro D. Ischnocera. In: Morrone JJ, Coscarón S. Biodiversidad de artrópodos argentinos: una perspectiva biotaxonómica. La Plata: Ediciones Sur; 1998. p. 104-124.).
All parasites collected in this study serve as new parasitological records for the black-chinned siskin, which represent new parasite–host associations. In addition, they also mark new arthropod species (Acari and Phthiraptera) for the entomological biodiversity of Chile.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support given by the National Forest Corporation, CONAF, as well as by the Agricultural and Livestock Service, SAG, of Chile. We thank Daniela Castro, Carolina Silva, Pedro Alvarez, Sebastián Muñoz, Braulio Muñoz, Ivan Torres, Nicolás Fernández, Pablo Olmedo, Gonzalo Torres, and Camilo Fuentes for their support in the field. This research was funded by FONDECYT Project 1130948.
References
- Atkinson CT, Thomas NJ, Hunter DB. Parasitic diseases of wild birds. Ames: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Atyeo WT, Braasch NL. The feather mite genus (Sarcoptiformes: Proctophyllodidae). ProctophyllodesBull Univ Nebr State Mus 1966; 5: 1-354.
- Brown WA. An African chigger, n. sp. (Acari: Trombiculidae, shoengastiini), from primate monkey hosts, Chlorocebus sabaeus (L.) from Gambia. Schoengastia pitheciagambiae (L.) and Papio papioInt J Acarol 2006; 32(3): 283-286. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01647950608684469
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01647950608684469 - Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 1997; 83(4): 575-583. PMid:9267395. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3284227
» http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3284227 - Cicchino AC, Castro D. Ischnocera. In: Morrone JJ, Coscarón S. Biodiversidad de artrópodos argentinos: una perspectiva biotaxonómica. La Plata: Ediciones Sur; 1998. p. 104-124.
- Couve E, Vidal-Ojeda C. Aves del Canal Beagle y Cabo de Hornos. Punta Arenas: Fantástico Sur; 2000.
- Dabert J, Dabert M, Gal AF, Miclăuş V, Mihalca AD, Sándor AD. Multidisciplinary analysis of Knemidocoptes jamaicensis parasitising the common chaffinch, : proofs for a multispecies complex? Fringilla coelebsParasitol Res 2013; 112(6): 2373-2380. PMid:23563901. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3402-7
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3402-7 - Fain A, Elsen P. Les acariens de la famille Knemidokoptidae producteurs de gale chez les oiseaux (Sarcoptiformes). Acta Zool Pathol Antverp 1967; 47: 3-145.
- Freitas MFL, Oliveira JB, Cavalcanti MDB, Leite AS, Magalhaes VS, Oliveira RA, et al. Parásitos gastrointestinales de aves silvestres en cautiverio en el Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Parasitol Latinoam 2002; 57(1-2): 50-54.
- Galloway TD, Proctor HC, Mironov SV. Chewing lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Amblycera, Ischnocera) and feather mites (Acari: Astigmatina: Analgoidea, Pterolichoidea): ectosymbionts of grassland birds in Canada. In: Cárcamo HA, Giberson DJ. Arthropods of Canadian grasslands. Ottawa: Entomological Society of Canada; 2014. p. 139-188. vol. 3. Biodiversity and systematics. Part 1. Biological Survey of Canada.
- Galloway TD. Ectoparasites from native and introduced birds from Christchurch and surrounding areas, New Zealand. Tuhinga 2005; 16: 13-20.
- Gaudioso JM, LaPointe DA, Hart PJ. Knemidokoptic mange in Hawai‘i’ Amakihi (Hemignathus virens) on the island of Hawai’i. J Wildl Dis 2009; 45(2): 497-501. PMid:19395759. http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-45.2.497
» http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-45.2.497 - Hill DS, Wilson N, Corbet GB. Mites associated with British species of (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). OrnithomyaJ Med Entomol 1967; 4(2): 102-122. PMid:6052122. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.102
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/4.2.102 - Jaramillo A. Aves de Chile. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions; 2005.
- Kinsella JM, Forrester DJ. Helminths of the Florida duck, Anas platyrhynchos fulvigula.Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 1972; 39(2): 173-176.
- Kirmse P. Cnemidocoptic mite infestations in wild birds. J Wildl Dis 1966; 2(4): 86-99.
- Klockenhoff HF. A redescription of (Mallophaga: Menoponidae), a parasite from passerine birds. Myrsidea seriniNZ J Zool 1984; 11(1): 17-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03014223.1984.10428223
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/03014223.1984.10428223 - Knowles LL, Klimov PB. Estimating phylogenetic relationships despite discordant gene trees across loci: the species tree of a diverse species group of feather mites (Acari: Proctophyllodidae). Parasitology 2011; 138(13): 1750-1759. PMid:21554840. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118201100031X
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118201100031X - Kolarova NT, Mitov PG. Feather mites of the superfamily Analgoidea (Acari: Astigmata) from Passerines (Aves: Passeriformes) in South Dobrudzha, Bulgaria. Acta Zool Bulg 2008;(Suppl. 2): 91-102.
- Krantz GW, Walter DE. A manual of acarology. 3rd ed. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press; 2009.
- Langenscheidt M. Embryologische, morphologische und histologische Untersuchungen an Knemidocoptes mutans (Robin et Lanquetin). Z Parasitenkd 1958; 18(4): 349-385. PMid:13604749. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00259664
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00259664 - Martínez D, González G. Las aves de Chile: nueva guía de campo. Santiago: Ediciones del Naturalista; 2004.
- Mete A, Stephenson N, Rogers K, Hawkins MG, Sadar M, Sanchez-Migallón D, et al. Knemidocoptic mange in wild golden eagles, California, USA. Emerg Infect Dis 2014; 20(10): 1716-1718. PMid:25271842. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2010.140504
» http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2010.140504 - Mey E. Verzeichnis der Tierläuse (Phthiraptera) Deutschlands. Entomofauna Germanica 2003; 6: 72-129.
- Mironov SV, Dabert J, Dabert M. A new feather mite species of the genus Robin, 1877 (Astigmata: Proctophyllodidae) from the long-tailed tit . ProctophyllodesAegithalos caudatus (Passeriformes: Aegithalidae)-morphological description with DNA barcode dataZootaxa 2012; 3253: 54-61.
- Mironov SV, Skirnisson K, Thorarinsdottir ST, Nielsen OK. Feather mites (Astigmata: Psoroptidia) parasitising the rock ptarmigan Lagopus muta (Montin) (Aves: Galliformes) in Iceland. Syst Parasitol 2010; 75(3): 187-206. PMid:20157794. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9219-1
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11230-009-9219-1 - Mironov SV. Feather mites from passerines on the North-West of Russia. Parazitologiya 1996; 30(6): 521-539.
- Mironov SV. Feather mites of the genera and. Analges Pteronyssoides from the European part of the USSR Sarcoptiformes, AnalgoideaParazitol Sb 1985; 33: 159-208.
- Palma RL. Slide-mounting of lice: a detalied description of the Canada balsam tecnique. NZ Entomol 1978; 6(4): 432-436. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00779962.1978.9722313
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00779962.1978.9722313 - Pence DB, Cole RA, Brugger KE, Fischer JR. Epizootic podoknemidokoptiasis in American robins. J Wildl Dis 1999; 35(1): 1-7. PMid:10073340. http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-35.1.1
» http://dx.doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-35.1.1 - Philips JR, Fain A. Acarine symbionts louseflies (Diptera: Hippoboscidae). Acarologia 1991; 32(4): 377-384.
- Price RD, Hellenthal RA, Palma RL, Johnson KP, Clayton DH. The chewing lice: world checklist and biological overview. Champaign: Illinois Natural History Survey; 2003. no. 24. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication.
- Rodrigues P, Mironov S, Sychra O, Resendes R, Literak I. Feather mites (Acari, Astigmata) from Azorean passerines (Aves, Passeriformes): lower species richness compared to European mainland. Parasite 2015; 22: 8. PMid:25665827. http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2015009
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2015009 - Rózsa L, Reiczigel J, Majoros G. Quantifying parasites in samples of hosts. J Parasitol 2000; 86(2): 228-232. PMid:10780537. http://dx.doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0228:QPISOH]2.0.CO;2
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0228:QPISOH]2.0.CO;2 - Saavedra-Orjuela A, Arévalo-Barreto S, Soler-Tovar D. Ectoparásitos del orden Phthiraptera en aves silvestres. Mem Conf Interna Med Aprovech Fauna Sil Exót Conv 2014; 10(2): 5-27.
- Spory GR. Some internal and external parasites of the redwinged blackbird, L., from central Ohio, including descriptions of three new feather mites. Agelaius phoeniceus phoeniceusOhio J Sci 1965; 65(2): 49-59.
- Sychra O, Palma RL, Saxena AK, Ahmad A, Bansal N, Adam C. Chewing lice of the genus (Phthiraptera: Philopteridae) from drongos (Passeriformes: Dicruridae). PhilopterusZootaxa 2011; 2868: 51-61.
- Tompkins DM, Clayton DH. Host resources govern the specificity of swiftlet lice: size matters. J Anim Ecol 1999; 68(3): 489-500. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00297.x
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2656.1999.00297.x - Turk FA. A new species of parasitic mite, Cnemidocoptes jamaicensis, a causative agent of scaly leg in Turdus aurantiacus.Parasitology 1950; 40(1-2): 60-62. PMid:15401172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118200001787X
» http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S003118200001787X - Valim MP, Weckstein JD. A drop in the bucket of the megadiverse chewing louse genus Myrsidea (Phthiraptera, Amblycera, Menoponidae): ten new species from Amazonian Brazil. Folia Parasitol 2013; 60(5): 377-400. PMid:24471279. http://dx.doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.040
» http://dx.doi.org/10.14411/fp.2013.040 - Vas Z, Rékási J, Rózsa L. A checklist of lice of Hungary (Insecta: Phthiraptera). Ann Hist-Nat Mus Natl Hung 2012; 104: 5-109.
- Wall R, Shearer D. Veterinary ectoparasites: biology, pathology & control. 2nd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 2001.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
12 Dec 2016 -
Date of issue
Oct-Dec 2016
History
-
Received
22 Sept 2016 -
Accepted
27 Oct 2016