ABSTRACT
This study was to develop, characterize, and evaluate the physical-chemical stability, in vitro antioxidant activity and in vitro safety profile of liquid crystalline systems (LCS) and microemulsions (MEs) with and without organic cocoa (OC) extract. LCS stabilized by surfactant polyoxyethylene 20 cetyl ether, containing water and oleic acid were studied. LCS and MEs were characterized using polarized light microscopy, small angle X-ray scattering, rheology and in vitro bioadhesion, and were evaluated for a period of 30 days by visual aspects, centrifuge test, pH value and relative density. PLM and SAXS assays showed the presence of domains of MEs, cubic and hexagonal mesophasephases, varying the proportions of the components of the formulations; where in the addition of the extract did not change rheological behavior of the formulations. All of the formulations were stable in the period analyzed and presented higher bioadhesive strength. In vitro antioxidant activity suggests that LCS and MEs presented a high capacity to maintain the antioxidant activity of OC extract. The results showed that the incorporation of OC in LCS improved the safety profile, according to cytotoxicity assays of systems may be a promising platform to OC extract for topical application for the potential treatment of skin disorders.
Keywords:
Liquid crystals/evaluation/physical-chemical stability; Microemulsions/evaluation; Surfactant-based system; Organic cocoa extract; Skin bioadhesion
INTRODUCTION
Skin is routinely exposed to stressful environmental factors such as pollutants and UV radiation. These factors produce a large number of aggressive oxidants that damage all of the biological skin cell membranes (Silva et al., 2010Silva AR, Menezes PFC, Martinello T, Novakovich GFL, Praes CEO, Feferman IHS. Antioxidant kinetics of plant-derived substances and extracts. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010;32(1):73-80.; Binic et al., 2013Binic I, Lazarevic V, Ljubenovic M, Mojsa J, Sokolovic D. Skin ageing: natural weapons and strategies. J Evid-Based Complem Altern Med. 2013;2013:ID827248.; Datta et al., 2011Datta HS, Mitra SK, Paramesh R, Patwardhan B. Theories and management of aging: modern and ayurveda perspectives. J Evid-Based Complem Altern Med. 2011;2011:ID528527.; Dupont, Gomez, Bilodeau, 2013Dupont E, Gomez J, Bilodeau D. Beyond UV radiation: a skin under challenge. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013;35(3):224-32.). Accordingly, the use of skin care products and cosmetics has been utilized to mitigate the cutaneous photoaging process (Visscher, Pan, Kitzmiller, 2013Visscher MO, Pan BS, Kitzmiller WJ. Photodamage: treatments and topicals for facial skin. Facial Plastic Surg Clin of North Am. 2013;21(1):61-75.) and these products are commonly composed of plant extracts (Binic et al., 2013).
A great number of plants and plant extracts are studied for their antioxidative action arising from their phenolic substructures. Phenolic compounds are composed of an aromatic ring that is linked to a hydroxyl group, which donates electrons and hydrogen atoms. As a result, these compounds are exceptional antioxidants (Silva et al., 2010Silva AR, Menezes PFC, Martinello T, Novakovich GFL, Praes CEO, Feferman IHS. Antioxidant kinetics of plant-derived substances and extracts. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010;32(1):73-80.; Binic et al., 2013Binic I, Lazarevic V, Ljubenovic M, Mojsa J, Sokolovic D. Skin ageing: natural weapons and strategies. J Evid-Based Complem Altern Med. 2013;2013:ID827248.; Reuter, Merfort, Schempp, 2010Reuter J, Merfort I, Schempp C. Botanicals in dermatology. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11(4):247-67.).
Cocoa, the dried and fermented seeds derived from Theobroma cacao, has been consumed since 1100 B.C. by ancient civilizations such as the Mayans and Aztecs (Hurst et al., 2002Hurst WJ, Tarka SM, Powis TG, Valdez F, Hester TR. Archaeology: Cacao usage by the earliest Maya civilization. Nature. 2002;418(6895):289-90.). Cocoa contains high amounts of the flavonoids (−)-epicatechin (EC) and (+)-catechin, and procyanidins B2 and B1. Additionally, other polyphenols such as quercetin, isoquercitrin (quercetin 3-O-glucoside), quercetin 3-O-arabinose, hyperoside (quercetin 3-O-galactoside), naringenin, luteolin, and apigenin have also been found in cocoa in minor quantities (Sánchez-Rabaneda et al., 2003Sánchez-Rabaneda F, Jáuregui O, Casals I, Andrés-Lacueva C, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Lamuela-Raventós RM. Liquid chromatographic/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric study of the phenolic composition of cocoa (Theobroma cacao). J Mass Spectrom. 2003;38(1):35-42.). While the natural amount of polyphenols may be high in cocoa, the manufacturing process often decreases the amount of polyphenols in the final product (as in chocolate). Accordingly, much research has focused on the health effects of polyphenol contained in cocoa extracts (Andújar et al., 2011Andu´jar I, Recio MC, Giner RM, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Laghi S, Muguerza Ba, et al. Inhibition of ulcerative colitis in mice after oral administration of a polyphenol-enriched cocoa extract is mediated by the inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation in colon cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(12):6474-83.; Tomas-Barberán et al., 2007Tomas-Barberán FA, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Marín A, Muguerza B, Gil-Izquierdo A, Cerdá B, et al. A new process to develop a cocoa powder with higher flavonoid monomer content and enhanced bioavailability in healthy humans. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(10):3926-35.; Calatayud et al., 2013Calatayud M, López-de-Dicastillo C, López-Carballo G, Vélez D, Hernández Muñoz P, Gavara R. Active films based on cocoa extract with antioxidant, antimicrobial and biological applications. Food Chem. 2013;139(1-4):51-8.; Mellor et al., 2010Mellor DD, Sathyapalan T, Kilpatrick ES, Beckett S, Atkin SL. High-cocoa polyphenol-rich chocolate improves HDL cholesterol in Type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetic Med. 2010;27(11):1318-21.; Monagas et al., 2009Monagas M, Khan N, Andres-Lacueva C, Casas R, Urpí-Sardà M, Llorach R, et al. Effect of cocoa powder on the modulation of inflammatory biomarkers in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(5):1144-50.).
Cocoa polyphenols have a positive effect on skin structure when applied for at least 5 days. This study observed that cocoa polyphenols, at doses of 0.75% and 0.50%, improve skin tone and elasticity through the glycosaminoglycans and collagens I, III, and IV (Gasser et al., 2008Gasser P, Lati E, Peno-Mazzarino L, Bouzoud D, Allegaert L, Bernaert H. Cocoa polyphenols and their influence on parameters involved in ex vivo skin restructuring. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2008;30(5):339-45.). In addition to demonstrating antioxidant activity higher than that of black tea and of red wine, the polyphenols also demonstrated in vitro inhibition of lipid peroxidation (Schinella et al., 2010Schinella G, Mosca S, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Pasamar MÁ, Muguerza B, Ramón D, et al. Antioxidant properties of polyphenol-rich cocoa products industrially processed. Food Res Int. 2010;43(6):1614-23.; Hatano et al., 2002Hatano T, Miyatake H, Natsume M, Osakabe N, Takizawa T, Ito H, et al. Proanthocyanidin glycosides and related polyphenols from cacao liquor and their antioxidant effects. Phytochemistry. 2002;59(7):749-58.). Therefore, it can be used in topical formulations in order to prevent premature skin aging (Katz, Doughty, Ali, 2011Katz DL, Doughty K, Ali A. Cocoa and chocolate in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signaling. 2011;15(10):2779-811.; Williams, Tamburic, Lally, 2009Williams S, Tamburic S, Lally C. Eating chocolate can significantly protect the skin from UV light. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(3):169-73.) and the use of cocoa to inhibit skin aging processes is encouraging.
Organic cocoa can further enhance antioxidant activity when associated with surfactant-based systems such as liquid crystalline systems (LCS) and microemulsions (MEs). Liquid crystalline systems (LCS) are mesomorphic phases of matter in an intermediate state in the thermal transformation from a solid to a liquid. LCS have the characteristic properties of solids and liquids: they have the structural order, rigidity, and defined links as in solids, and they also have the mobility, fluidity, and disordered regions as in liquids (Chorilli et al., 2011Chorilli M, Prestes PS, Rigon RB, Leonardi GR, Chiavacci LA, Sarmento VHV, et al. Structural characterization and in vivo evaluation of retinyl palmitate in non-ionic lamellar liquid crystalline system. Colloids Surf B. 2011;85(2):182-8.; Prestes et al., 2009Prestes PS, Chorilli M, Chiavacci LA, Scarpa MV, Leonardi GR. Physicochemical characterization and rheological behavior evaluation of the liquid crystalline mesophases developed with different silicones. J Dispersion Sci Technol. 2009;31(1):117-23.; Mezzenga, 2012Mezzenga R. Physics of self-assembly of lyotropic liquid crystals. In: Garti N, Somasundaran P, Mezzenga R, editors. Self-assembled supramolecular architectures: lyotropic liquid crystals. Hoboken: Wiley; 2012. p. 1-20.). MEs are defined as dispersion made of water, oil, and surfactants that is an isotropic and thermodynamically stable system with dispersed in globular or interconnected size diameter varying approximately from 1 to 100 nm, usually 10 to 50 nm (Slomkowski et al., 2011Slomkowski S, Aleman JV, Gilbert RG, Hess M, Horie K, Jones RG, et al. Terminology of polymers and polymerization processes in dispersed systems (IUPAC Recommendations 2011). Pure Appl Chem. 2011;83(12):2229-59.; McClements, 2012McClements DJ. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter. 2012;8(6):1719-29.). LCS and MEs can increase the physical stability, solubilization, and efficacy of a series of active principles and they can explored to drug or active compounds delivery (Chorilli et al., 2011; Chen, Ma, Gui, 2014Chen Y, Ma P, Gui S. Cubic and hexagonal liquid crystals as drug delivery systems. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:ID815981.; Guo et al., 2010Guo C, Wang J, Cao F, Lee RJ, Zhai G. Lyotropic liquid crystal systems in drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15(23-24):1032-40.; Lawrence, Rees, 2000Lawrence MJ, Rees GD. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000;45(1):89-121.). They can be formed by the association of varying concentrations of water, oil, and surfactant and changing the concentrations of surfactant can self-assembly at forms different such as microemulsions or lamellar, hexagonal, and cubic mesophase (Malmsten, 2002Malmsten M. Surfactants and polymers in drug delivery. New York: Infoma Healthcare; 2002. 348 p.; Romsted, 2012Romsted LS. Introduction to self-assembly. In: Steed JW, Gale PA, editors. Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. p. 181-204.).
As such, the objectives of this study were to develop, characterize, and evaluate the physical-chemical stability, in vitro antioxidant activity and in vitro safety profile of liquid crystalline systems (LCS) with and without organic cocoa (OC) extracts.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Material
Oleic acid, OA (Synth, Brazil); ethanol (Synth, Brazil); hexane (Synth, Brazil); Folin-Ciocalteau reagent (Sigma Aldrich, USA); polyoxyethylene 20 cetyl ether, PCE (Sigma, USA); 2,2-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical (Buchs, Switzerland); and organic cocoa seed powder - OCSP (Via Farma, Brazil) were all obtained from their specified vendors and used without further purification unless otherwise stated.
Methods
Botanical tissue characterization
A sample of OCSP was previously intumesced and discolored and it was then colored with Toluidin Blue (BT). The prepared sample was analysed with an optical microscopic, searching for lipid globules, pectic compounds, phenolics cells, starch grains and mucilage as described in the literature (Martini et al., 2008aMartini MH, Figueira A, Lenci CG, Tavares DdQ. Polyphenolic cells and their interrelation with cotyledon cells in seven species of Theobroma (Sterculiaceae). Braz J Bot. 2008a;31(3):425-31.; Martini et al., 2008b).
OCSP extract preparation
OCSP (1.0 g) was previously defatted with 5 mL of hexane by 20 minutes into a sonication bath. The extraction was prepared separately with hydroalcoholic solutions composed of 80 % methanol (v/v) and 70 % ethanol (v/v). Then, 10 mL of each solvent was added to the sample, and the sample was left for 20 minutes into a sonication bath. This extraction procedure was performed three times resulting a final volume of 30 mL, and it was performed in triplicate. The extracts were dried under air and in a desiccator with silica gel.
· Determination of the phenolic content of the extracts
The phenolic content of the extracts was determined according to the method described (Singleton, Rossi, 1965Singleton VL, Rossi JA. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic. 1965;16(3):144-58.). Using the Folin-Ciocalteau reagent, the polyphenols were expressed as galic acid and quercetin. Aliquots containing 20 µg of dried sample extracts and the standard (0.25 µg/mL, 0.50 µg/mL, 0.75 µg/mL, 1.00 µg/mL e 1.25 µg/mL) were added to 100 µL of Folin-Ciocalteau reagent with 1.58 mL of water. After 8 min, 300 µL of 20% (w/v) sodium carbonate solution were added and the mixtures were stirred. After 2 hours at room temperature, the absorbance was measured in a UV/Vis spectrophotometer (U-2001 Hitachi, Japan) at a wavelength of 765 nm. The analytical curve was constructed with the absorbance values obtained for the different concentrations of galic acid and quercetin.
· Determination of antioxidant potential of SPOC extracts
The free radical scavenging activity was evaluated by a modified DPPH test. One hundred microliters of extract solutions (containing 10 - 60 µg/mL of dry mass) were added to 3.9 mL of DPPH (60 µM) in ethanol. After 30 minutes in the dark, the absorbance at 517 nm was measured. All measurements were taken in triplicate. The free radical scavenging activity was calculated using equation 1, where AC is absorbance of the control and AS is absorbance of the sample. The IC50 value was determined by plotting the concentration of cocoa extracts versus the percentage of remaining DPPH at a steady state.
Preparation of the formulations
The samples were produced by heating the mixture of the oleic acid and PCE to 45 °C. Distilled water at 40 °C (W) was then added under constant stirring, and the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature. Binary mixtures were obtained similarly, but each mixture contained a different proportion of OA and PCE. Systems obtained with different proportions of the OA and PCE were described by pseudo-ternary phase diagrams to characterize the LCS studied. During the titration process, the formed systems and their viscosities were analyzed visually. The concentrations of each component in the formulation were calculated, and these points were used in the delimitation of different regions in the phase diagram. The transitions from the semisolid phase to the transparent liquid system (microemulsion), transparent viscous system (hexagonal, lamellar and cubic phases), cloudy system (emulsion) and separation of phases (S) were delimited. The OC extract was added to the aqueous phase of the system to prepare loaded-formulations.
Characterization of the formulations
· Polarized light microscopy (PLM)
A drop of each formulation was placed on a glass slide covered with a cover slip, and then the sample was examined under polarized light. A Motic Type 102 M Optical Microscope equipped with a digital camera was used to analyze several fields of each sample at room temperature. Photomicrographs were taken at a magnification of 200x.
· Small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
The nanometric structure of the phases was investigated using SAXS. The results were collected at the Synchrotron SAXS beam line of the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (Campinas, Brazil), equipped with an asymmetrically cut and bent Si (1 1 1) monochromator (λ = 1.608 Å) that yields a horizontally focused beam. A vertical position-sensitive X-ray detector and a multichannel analyzer were used to record the SAXS intensity, I(q), as a function of the modulus of the scattering vector q (q = (4π/λ)sin(ε/2), and ε is the scattering angle). The parasitic scattering produced by the slits was subtracted from the total scattering intensity.
· Determination of rheological behavior
The rheological analysis of the formulations were performed with a controlled-stress Carri Med CSL 100 rheometer (TA instruments, UK) with plate-plate geometry using assays of flow-dynamics. This geometry consists of two stainless steel plates that are 2 cm in diameter with a gap of 200 µm between the plates. Samples were carefully applied to the lower plate, ensuring that formulation shearing was minimized, and the samples were allowed to equilibrate for at least 3 min prior to analysis. The experiments were performed with shear rates () in the range of 0.001 s-1 to 100 s-1. The shear rate region used was selected based on the strength of resistance to the applied stresses. The rheological measurements were performed on both the up and down curves. The data from the shear cycle were fitted to a power-law model using Rheology Solutions Software (version Data V1.1.7, TA Instruments).
· In vitro bioadhesion assays
In this study, pig ear skin was obtained from a local slaughterhouse. The cutaneous bioadhesive strength was evaluated in terms of the force required to separate the formulations of pig ear skin. The maximum force of detachment was analyzed using a Stable Micro Systems TA-XTplus texturometer (Surrey, England). The formulations were warmed in a thermostatic bath at 32 ºC for the bioadhesive analyses. These assays were performed under the following conditions: a strength (trigger force) of 0.002 N for viscous samples, a strength of 0.01 N semi-solid samples, and a strength of 0N for liquid samples. All assays used a contact time of 60 s.
· Preliminary stability studies
The formulations were evaluated for a period of 24 hours by visual inspection, centrifuge testing, pH values and relative densities and 1 month to visual aspect of formulations. For visual evaluation, the samples were visually observed for changes such as color, phase separation, and homogeneity. The evaluation of the stability to centrifugation was performed using 5 grams of each test sample. The samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min. The pH measurement was performed using a pH meter, using 5% (p/v) samples diluted in distilled water. The relative density (RD) was determined using a pycnometer. The relative density was calculated by the methodology described by Brazilian Pharmacopea (Anvisa, 2010). All formulations were kept at room temperature (25ºC ± 2ºC) and without exposure to light.
· Determination of the antioxidant potential of the LCS
To determine the antioxidant activity of the formulations, one gram of the extract formulations was solubilized in 1 mL of 70% ethanol. One hundred microliters of each solution was used in the DPPH assay. A formulation without extract was used as the blank solution.
Cell culture
In vitro testing for the cytotoxicity analysis of the formulations was performed using J-774 mouse macrophages as a template. Cells were seeded in the bottom of the microplates (Nucleon, 96 wells, 2.5-10.0×105 cells/well) with different doses of the formulations and free OC extract (18.6, 10, 5 and 1 μM) or control for 48 hours. The cells were washed with PBS after removing the compounds, and the cell viability was assessed by a colorimetry formazan assay (MTT). The method of 3 [4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) is a simple, reliable, and reproducible colorimetric method for measuring mitochondrial metabolic reduction of yellow tetrazolium salt to insoluble formazan crystals in an aqueous solution of viable cells. Cells and MTT (0.4 mg/mL) were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. Subsequently, the supernatant was removed and formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO (180 µL). The plates were agitated for 10 min, and the optical density was measured using a multiwall spectrophotometer operating at 560 nm. Concentrations were measured in triplicate using six additional controls (cells in medium). Cell viability was calculated using the following equation 2:
where ODs and ODc are the samples and control optical density, respectively.
Statistical analysis
The data were analysed using the mean and standard deviation and were compared by analysis of variance (ANOVA). The Tukey post-hoc test was used to obtain a unidirectional comparison and to evaluate significant differences between samples, where values of p <0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Origin® 7.0 SRO (OriginLab, Northampton, MA) was used for data analysis.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Botanical tissue characterization
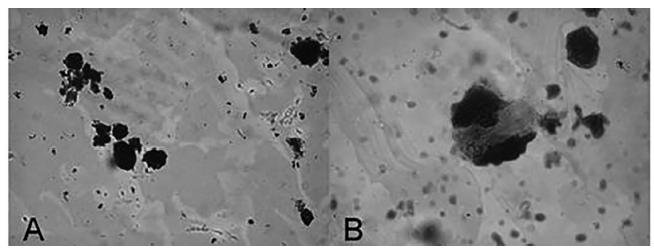
Because the seeds were composed of a fine powder, certain structural features present in OC seeds described by the literature could not be observed (Elwers et al., 2010Elwers S, Zambrano A, Rohsius C, Lieberei R. Histological features of phenolic compounds in fine and bulk cocoa seed (Theobroma cacao L.). J Appl Bot Food Qual. 2010;83(2):182-8.). Phenolic compounds were observed in the OCSP sample, taking the forms of grains of starch and mucilage (Figure 1). This finding suggests that the sample is composed of OC and corroborate with supplier report analysis.
A sample of powder of divided seeds viewed using an optical microscope at 400x. Phenolic compounds (A) and mucilages (B) are present.
Extract characterization
Determination of total phenolic
Least-squares linear regression of the analytical data obtained for gallic acid (y = 61.2x + 0,0457; R 2=0.9982) and quercetin (y = 118.0x + 0.0825; R 2=0.9980) was used to determine the total phenolic content. The total gallic acid content obtained from the 80% methanol and 70% ethanol extractions was 1.40 mg/g and 1.96 mg/g, respectively. The total quercetin content obtained from the 80% methanol and 70% ethanol extractions was 480 µg/g and 870 µg/g, respectively. According to these results, the ethanol extractions yielded greater amounts of polyphenols were expressed as gallic acid and quercetin. This outcome is important, as the toxicity of methanol restricts methanol-based botanical extractions in pharmaceutical processes.
Determination of antioxidant potential of OC extract
The IC50 values for the 80 % methanol and 70 % ethanol extractions were 43.5 and 29.2 µg/mL, respectively. Therefore, the ethanol extract exhibits a higher antioxidant activity than does the methanol extract. These results are in agreement with that obtained in the determination of total phenolics content, in which higher concentrations of phenolics result in a higher antioxidant activity. Then, the 70% ethanol extraction was used to prepare the subsequent formulations.
Preparation of the formulations
Figure 2 presents the ternay phase diagram of the system with different proportions and type of components resulted in distinct systems. The phase diagram shows the characteristics of points classified as phase-separated (SF), microemulsions (ME), as a cloudy system (EM), or as a liquid crystalline system (LCS). The regions known as EM, like emulsions, were observed in the upper vertex of diagram, where there was low water concentration (0-25%) and high surfactant concentration (100-70%); in the bottom vortex of diagram, there are found system like EM, where the water concentrations was higher (70-100%) and oily phase was used in different range of concentrations (10-80%). LCS was found in the left region and center of the diagram with a oil concentration (0-50%) and surfactant concentration (30-70%). PS occurred with a low water concentration (10-40%) and surfactant concentration (~20%) and water concentration (~10%) and surfactant concentration (50-70%).
Phase diagram of W, OA, and PCE indicating areas where the formulation will exist as fully phase-separated (SF), as a microemulsion (ME), as a cloudy system (EM), or as a liquid crystalline system (LCS).
In this diagram is possible to evaluate the regions of ME can generate liquid crystalline systems where the water in the system is increased. This phenomena, known as transition mesophase, is also possible to be noted within regions of LCS, where the increase of water in the system, leaded a formation of more complex structures (hexagonal to cubic mesophases). This change from a less viscous phase into a hexagonal phase or cubic structure can be explained by the critical packing parameter (cpp) (Mezzenga, 2012Mezzenga R. Physics of self-assembly of lyotropic liquid crystals. In: Garti N, Somasundaran P, Mezzenga R, editors. Self-assembled supramolecular architectures: lyotropic liquid crystals. Hoboken: Wiley; 2012. p. 1-20.; Malmsten, 2002Malmsten M. Surfactants and polymers in drug delivery. New York: Infoma Healthcare; 2002. 348 p.). The cpp relates the shape of the molecule to properties that influence the curvature of the polar-nonpolar interface and consequently the type of aggregate formed. Therefore, the cpp is a useful parameter for predicting the mesophase that is preferably formed by an amphiphile and can be calculated via Equation 3 (Israelachvili, 1994Israelachvili J. The science and applications of emulsions: an overview. Colloids Surf. A. 1994;91:1-8.).
where cpp represents the critical packing parameter, vs is the hydrophobic chain volume, a0 is the polar head group area, and lc is the chain length. The increase in the water system leads to an increase in hydration of the polar head of the surfactant, increasing its curvature and consequently increase the value of vs. Lamellar mesophase the angle of curvature is zero and increased surfactant curvature angle and it tends to generate self-assembly systems, such as hexagonal and cubic liquid crystals (Garti, Libster, Aserin, 2014Garti N, Libster D, Aserin A. Solubilization and delivery of drugs from gmo-based lyotropic liquid crystals. In: Li Q, editor. Nanoscience with liquid crystals: from self-organized nanostructures to applications. London: Springer; 2014. p. 355-414.).
Characterization of the formulations
PLM
The formulations were analyzed using MLP, in which structures such were identified as lamellar mesophase and hexagonal arrays (Figure 3). The system cubic and microemulsions are showed as dark field in PLM, because these systems are anisotropic. MEs are transparent and fluid systems whereas cubic phases are transparent and a rigid system, like a gel (Shah, Sadhale, Chilukuri, 2001Shah JC, Sadhale Y, Chilukuri DM. Cubic phase gels as drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(2-3):229-50.).
Polarized light micrography of LCS: lamellar phase (left) and hexagonal phase (right). Magnification of 400 x.
Six points from the phase diagram were selected to incorporate the OC. Namely, these points consisted of three cubic phases (C1, C2, C3), two hexagonal phases (H1, H2) and one microemulsion (M1). Table I shows the percentages of formulation components for each selected point.
The concentration of OC to be incorporated in the formulation was determined according the IC50 of the extract analyzed. Ultimately, 0.6% of the OC extract was incorporated in the aqueous phase of the system. The formulations containing the extract are named as C1E, C2E, C3E, H1E, H2E and M1E.
Small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
The values of the scattering vector q, shown in Table II, correspond to peaks q1, q2, q3, q4, which are equal to 1:1,73:2:2,64. This result indicates that the sample has a liquid crystal hexagonal structure. The liquid crystal cubic phase correlated values are 1,41:1,73:2,82:3 (Beaucage et al., 1995Beaucage G, Ulibarri TA, Black EP, Schaefer DW. Multiple size scale structures in silica-siloxane composites studied by small-angle scattering. hybrid organic-inorganic composites. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society; 1995. p. 97-111. (ACS Symposium Series. 585).). The cubic phase is an isotropic, thermodynamically stable, and highly viscous formulation with a bicontinuous structure (Hyde et al., 1984Hyde ST, Andersson S, Ericsson B, Larsson K. A cubic structure consisting of a lipid bilayer forming an infinite periodic minimum surface of the gyroid type in the glycerolmonooleat-water system. Zeitschrift für Kristallogr. 1984;164(1):213-9.). Because of its amphiphilic character, the cubic phase is suitable for accommodating both hydrophilic, hydrophobic, and amphiphilic substances. In systems of microemulsions, SAXS curves exhibit a broad band or peak, associated with low 3D spatial correlation (Yariv et al., 2010Yariv D, Efrat R, Libster D, Aserin A, Garti N. In vitro permeation of diclofenac salts from lyotropic liquid crystalline systems. Colloids Surf B 2010;78(2):185-92.).
Ratio of the interplanar distances and lattice parameter d (nm) for the formulations obtained by SAXS
The results confirm the information of the analysis of PLM. It was also observed that the incorporation of extract in the formulations did not alter the type of structure observed.
Determination of rheological behavior
Due to the high viscosity of the formulations C1, C1E, C2, C2E, C3 and C3E, it was not possible to analyze the rheological behavior of these formulations. Figure 4 shows the variation in shear stress as a function of shear rate for formulations H1 and H2. The curves indicate that the formulations behave as non-Newtonian systems because the curves exhibit a linear relationship between tension and shear rates.
The formulation H1 exhibited pseudoplastic and thixotropic fluid characteristics because of the decrease in viscosity. Such behavior can be attributed to the disorganization of the internal system with the applied shear. These results reveal the presence of a structured network formed by the interaction between the components of the formulation. This network is gradually broken with increasing shear rate, resulting in a reduction of the internal resistance of the system, and ultimately decreasing the viscosity. This rheological parameter indicates that sample H1 can show good spreadability during application in the skin (Alam, Aramaki, 2009Alam MM, Aramaki K. Effect of molecular weight of triglycerides on the formation and rheological behavior of cubic and hexagonal phase based gel emulsions. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2009;336(1):329-34.; Ribeiro, Morais, Eccleston, 2004Ribeiro HM, Morais JA, Eccleston GM. Structure and rheology of semisolid o/w creams containing cetyl alcohol/non-ionic surfactant mixed emulsifier and different polymers. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2004;26(2):47-59.; Zhang, Liu, 2013Zhang W, Liu L. Study on the formation and properties of liquid crystal emulsion in cosmetic. J Cosmet Dermatol Sci Appl. 2013;3(2):139-144.; Isaac et al., 2012Isaac VLB, Cefali LC, Chiari BG, Almeida MGJ, Ribeiro HM, Corrêa MA. Effect of various thickening agents on the rheological properties of oil-in-water emulsions containing nonionic emulsifier. J Dispersion Sci Technol. 2012;34(6):880-5.). It can be correlated with the spreadability and with how easy formulation flow from package (Niraula et al., 2004Niraula B, King TC, Misran M. Evaluation of rheology property of dodecyl maltoside, sucrose dodecanoate, Brij 35p and SDS stabilized O/W emulsion: effect of head group structure on rheology property and emulsion stability. Colloids Surf A. 2004;251(1-3):59-74.).
For the H2, the opposite phenomenon was observed. This formulation exhibited characteristics of dilatant and reopetics fluids because of the increase in viscosity with increasing shear stress. This behaviour can be explained by filling the space between the particles with increasing shear stress: the sorting of particles promotes an increase in volume, causing an increase in melt strength, i.e., the viscosity (Carvalho et al., 2010aCarvalho FC, Bruschi ML, Evangelista RC, Gremião MPD. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2010a;46(1):1-17.).
After the extracts were added to formulations H1E and H2E, no alteration was observed in the rheological behaviour of formulations. Thus, the addition of the extract did not influence the rheological behaviour of the formulations.
In vitro bioadhesion assays
Bioadhesion is used to describe the adhesion of synthetic or biological macromolecules to biological tissues. Table III shows the results from the bioadhesion tests. The force obtained by the graph represents the maximum force observed for the detachment of the skin sample of the formulation, while the area is the work of bioadhesion. From these results, it can be determined that between all formulations, the formulation of the cubic phase had greater bioadhesive strength than that of the hexagonal phase, which in turn had greater strength than did the microemulsion. The addition of the extract did not significantly alter bioadhesiveness of the formulations.
Nielsen, Schubert and Hansen (1998Nielsen LS, Schubert L, Hansen J. Bioadhesive drug delivery systems: I. Characterisation of mucoadhesive properties of systems based on glyceryl mono-oleate and glyceryl monolinoleate. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1998;6(3):231-9.) has studied bioadhesion by tensiometric measurements, and the results showed that LCS phases have the greatest mucoadhesion, followed by lamellar phases and cubic phases. The mechanism of bioadhesion is unspecific and most likely involves dehydration of the mucosa (Nielsen, Schubert, Hansen, 1998).
Gonçalez, Correa and Chorilli (2013Gonçalez ML, Correa MA, Chorilli M. Skin delivery of kojic acid-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. Biomed Res Int. 2013;(2013):1-9.) developed an LCS and studied the bioadhesion of hexagonal phases on porcine skin, and the results showed that bioadhesion depended on the water phase in the systems. Carvalho et al. (2013Carvalho FC, Campos ML, Peccinini RG, Gremião MPD. Nasal administration of liquid crystal precursor mucoadhesive vehicle as an alternative antiretroviral therapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;84(1):219-27.) developed an LC precursors system, and the mucoadhesion was evaluated. The results suggest that the adhesive force is not influenced by the mesophase type (Carvalho et al., 2010b). However, the adhesive forces presented by lamellar phases (0.304-0.262 N) are similar to well-known mucoadhesive polymers to skin (Carvalho et al., 2012) such as carbomers and polycabophyls, which exhibit great bio/mucoadhesive properties (Carvalho et al., 2012; Bruschi et al., 2007Bruschi ML, Jones DS, Panzeri H, Gremião MPD, de Freitas O, Lara EHG. Semisolid systems containing propolis for the treatment of periodontal disease: in vitro release kinetics, syringeability, rheological, textural, and mucoadhesive properties. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(8):2074-89.; Peppas, Sahlin, 1996Peppas NA, Sahlin JJ. Hydrogels as mucoadhesive and bioadhesive materials: a review. Biomaterials. 1996;17(16):1553-61.).
Studies explained that the force of bioadhesion is correlated with a rank order of resistance measurements, such as the index of viscosity (k) of semisolids matrixes (Carvalho et al., 2012Carvalho FC, Calixto G, Hatakeyama IN, Luz GM, Gremião MPD, Chorilli M. Rheological, mechanical, and bioadhesive behavior of hydrogels to optimize skin delivery systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2012;39(11):1750-7.; Carvalho et al., 2013). Another study studied by Tamburic and Craig found a correlation between rheological and textural results, that is, an increase in the interaction between a highly viscous sample and mucus (Tamburic, Craig, 1997).
Various theories exist to explain at least some of the experimental observations made during the bioadhesion process. LCS are biodhesive systems, because they leads a dehydration of skin. These findings show that the water present in the mucus layer can interact with liquid crystal system to adhesion process (Souza et al., 2014Souza C, Watanabe E, Borgheti-Cardoso LN, De Fantini MCA, Lara MG. Mucoadhesive system formed by liquid crystals for buccal administration of poly(hexamethylene biguanide) hydrochloride. J Pharm Sci. 2014;103(12):3914-23.; Ganem-Quintanar, Qintanar-Guerrero, Buri, 2000Ganem-Quintanar A, Quintanar-Guerrero D, Buri P. Monoolein: a review of the pharmaceutical applications. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26(8):809-20.). Mesophase formed in LCS can influence this process, where lamellar systems exhibit mucoadhesive properties higher than hexagonal mesophase (Lee, Young, Kellaway, 2001Lee J, Young SA, Kellaway IW. Water quantitatively induces the mucoadhesion of liquid crystalline phases of glyceryl monooleate. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001;53(5):629-36.).
Preliminary stability studies
No phase separation or color changes were observed over a period of one month. The formulations were evaluated 24 hours after their preparation. Stability evaluation to centrifugation test found that the formulations kept the same visual appearance and phase separation was not observed. The determination of pH was performed 24 h after preparation and the results are shown in Table III. The pH values were 3.95 to 4.97 to the formulations and the addition of cocoa extract led to little change in the pH of the formulations. The skin surface pH is on average 4.7 (Lambers et al., 2006Lambers H, Piessens S, Bloem A, Pronk H, Finkel P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2006;28(5):359-70.) and the use of these formulations under the skin should not influence or change the pH of the skin. The maintenance of the correct pH of the skin plays a role in controlling the presence of resident skin microflora as well as supporting important physiological processes like the formation of an optimal structure of the lipid barrier and stratum corneum homeostasis. (Parra, Paye, 2003Parra JL, Paye M. EEMCO guidance for the in vivo assessment of skin surface pH. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2003;16(3):188-202.)
All formulations had densities near to density of water (d = 1.0 g/cm³). The cubic phase formulations had a higher density than did the other formulations, and the microemulsion had the lowest density. The incorporation of OC extracts lead an increase of density the formulations.
In vitro antioxidant activity of the formulations.
The formulations with or without the addition of OC extract were evaluated for antioxidant activity during a period of 21 days. The results obtained are shown in Figure 5.
Percentage inhibition of DPPH radical of formulations for a period of 21 days to the formulations.
It can be see that in the period of 21 days, there was a decrease in antioxidant power. The samples C1, C2, C3, H1, H2 and M1 with cocoa were not significantly different in relation to the extract (p>0.05).
Regarding the formulations, the initial antioxidant activity was lower when compared to the extract, but by day 7, inhibition of DPPH of the formulations C2 and C3 with the extract was observed. This result is most likely due to a greater stabilization of the formulation. The same outcome was not observed for C1, and the difference between these formulations is the concentration of the surfactant. C1 has a higher concentration of surfactant than does C2 and C3. In the cubic phase formulations, it can be observed that the formulation prevented the extract from being oxidized, maintaining the antioxidant activity similar to the extract, and in some cases the antioxidant activity was slightly higher when compared to that of the extract.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the high capacity of several plant polyphenolic antioxidants to protect living organisms from alterations produced by reactive oxygen species (ROS), including skin damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation (Reuter, Merfort, Schempp, 2010Reuter J, Merfort I, Schempp C. Botanicals in dermatology. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11(4):247-67.; González et al., 2013González N, Ribeiro D, Fernandes E, Nogueira DR, Conde E, Moure A, et al. Potential use of Cytisus scoparius extracts in topical applications for skin protection against oxidative damage. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013;125(0):83-9.; Adhami et al., 2008Adhami VM, Syed DN, Khan N, Afaq F. Phytochemicals for prevention of solar ultraviolet radiation-induced damages. Photochem Photobiol. 2008;84(2):489-500.; Saija et al., 1998Saija A, Tomaino A, Trombetta D, Giacchi M, De Pasquale A, Bonina F. Influence of different penetration enhancers on in vitro skin permeation and in vivo photoprotective effect of flavonoids. Int J Pharm. 1998;175(1):85-94.). ROS load has been implicated in several pathological states including photoaging of the skin, leading to abnormal matrix degradation and accumulation of non-functional matrix componentes (Pillai, Oresajo, Hayward, 2005Pillai S, Oresajo C, Hayward J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation- a review. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2005;27(1):17-34.).
For formulations H1, H2 and M1, inhibition by DPPH was not higher than that observed in the extract. These formulations exhibit an oily phase, unlike C1, C2 and C3, which have only components of the aqueous phase and surfactant. The presence of an oil phase, which was composed of oleic acid, may have interfered with antioxidant activity because unsaturated oils tend to oxidize. In this case, the OC extract added may have oxidized to protect the formulation from oxidation.
In vitro safety profile
An in vitro cytotoxicity study of the formulations using J-774 mouse macrophages as the cellular model was performed. The data are expressed in percentage of cellular viability, according to Figure 6.
The assay results of cellular viability indicated that the OCE free and the formulations were unable to kill normal cell macrophages: all of them exhibited cellular viability greater than 94%. The use of higher concentration of fatty acids, such as OA, induce apoptosis and necrosis using J-774 mouse macrophages (Martins de Lima et al., 2006). None of the formulations without the drug showed toxic activity (C1, C2, C3, H1, H2 and M1), nor did they show toxic activity when the extract was incorporated in the formulations (C1E, C2E, C3E, H1E, H2E and M1E). No have differences between mean of groups (p < 0.05).
The same study was performed by others authors using J-774 mouse macrophages as the cellular model. The results of cellular viability for formulations of liquid crystals and nanostructured lipid carriers were greater than 92% (Gonçalez, Correa, Chorilli, 2013Gonçalez ML, Correa MA, Chorilli M. Skin delivery of kojic acid-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. Biomed Res Int. 2013;(2013):1-9.; Oliveira et al., 2014Oliveira MB, Prado AH, Bernegossi J, Sato CS, Lourenço-Brunetti I, Scarpa MV, et al. Topical application of retinyl palmitate-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:ID63257.; Kolenyak-Santos et al., 2015Kolenyak-Santos F, Garnero C, De Oliveira RN, de Souza ALR, Chorilli M, Allegretti SM, et al. Nanostructured lipid carriers as a strategy to improve the in vitro schistosomiasis activity of praziquantel. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(1):761-72.; Oyafuso et al., 2015Oyafuso MH, Carvalho FC, Chiavacci LA, Gremião MPD, Chorilli M. Design and characterization of silicone and surfactant based systems for topical drug delivery. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(1):817-26.).
CONCLUSION
The results of bioadhesion studies showed a bioadhesive potential of cubic phase than hexagonal mesophases. For drug delivery purposes, the term bioadhesion implies attachment of a drug carrier system to a specific biological location (Smart, 2005Smart JD. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57(11):1556-68.). Topical drug delivery has become a very attractive alternative to subcutaneous delivery as the skin has the largest area. It provides good compliance of patients and controls release characteristics of drugs, and avoids drug degradation from the gastric intestinal tract or first-pass liver effect. The skin can also provide a painless interface for systemic administration (Prausnitz, Mitragotri, Langer, 2004Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S, Langer R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(2):115-24.; Thomas, Finnin, 2004Thomas BJ, Finnin BC. The transdermal revolution. Drug Discov Today. 2004;9(16):697-703.), besides the new methods of bioadhesive system applied in skin delivery system, which can prolong the contact time greatly by adhesion effect and doesn’t produce discomfort (Zhu et al., 2013Zhu Z, Zhai Y, Zhang N, Leng D, Ding P. The development of polycarbophil as a bioadhesive material in pharmacy. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2013;8(4):218-27.). However, the advantages of using bioadhesive systems as drug carriers are the prolongation of drug residence time at the absorption site (Smart, 2005; Carvalho et al., 2010bCarvalho FC, Barbi MS, Sarmento VHV, Chiavacci LA, Netto FM, Gremião MPD. Surfactant systems for nasal zidovudine delivery: structural, rheological and mucoadhesive properties. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010b;62(4):430-9.).
In vitro safety profile showed that this formulation is not cytotoxic and in vitro antioxidant activity suggested that LCS presented a higher capacity to maintain the antioxidant activity of OC extracts. Novel drug delivery systems, such as nanotechnological, provide several advantages over traditional forms including the enhancement of solubility, bioavailability, protection from toxicity, enhancement of pharmacological activity, enhancement of stability (Ajazuddin, 2010Ajazuddin, Saraf S. Applications of novel drug delivery system for herbal formulations. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(7):680-9.) and controlled release of biomarkers (Devi, Jain, Valli, 2010Devi VK, Jain N, Valli KS. Importance of novel drug delivery systems in herbal medicines. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010;4(7):27-31.; Summerlin et al., 2015Summerlin N, Soo E, Thakur S, Qu Z, Jambhrunkar S, Popat A. Resveratrol nanoformulations: Challenges and opportunities. Int J Pharma. 2015;479(2):282-90.). Antioxidant capacity can provide protection from endogenous and exogenous oxidative stresses by scavenging free radicals. Topical antioxidants are available in multivariate combinations through over-the-counter skin care products that are aimed at preventing the clinical signs of photoaging (Bogdan Allemann, Baumann, 2008Bogdan Allemann I, Baumann L. Antioxidants used in skin care formulations. Skin Ther Lett. 2008;13(7):5-9.). The incorporation these antioxidant agents into different types of nanomaterials used in cosmetic formulations to obtain the best effect of antioxidants applied onto the skin has been reported in many studies (Vinardell, Mitjans, 2015Vinardell MP, Mitjans M. Nanocarriers for delivery of antioxidants on the skin. Cosmetics. 2015;2(4):342-254.)
In summary, it was possible to develop a system with adhesive properties, besides maintaining the antioxidant properties of the extract incorporated in them, with good biocompatibility. Therefore, it is feasible to conclude that these systems can be used for optimization of drug delivery systems on the skin for the treatment of skin aging.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP (grant number 10/17723-7), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico - CNPq, and Programa de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico da Faculdade de Ciências Farmacêuticas da UNESP - PADC. The authors are grateful to Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS) for SAXS facilities.
REFERENCES
- Adhami VM, Syed DN, Khan N, Afaq F. Phytochemicals for prevention of solar ultraviolet radiation-induced damages. Photochem Photobiol. 2008;84(2):489-500.
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. ANVISA. Farmacopeia Brasileira. Brasília: Anvisa; 2010. 546 p.
- Ajazuddin, Saraf S. Applications of novel drug delivery system for herbal formulations. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(7):680-9.
- Alam MM, Aramaki K. Effect of molecular weight of triglycerides on the formation and rheological behavior of cubic and hexagonal phase based gel emulsions. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2009;336(1):329-34.
- Andu´jar I, Recio MC, Giner RM, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Laghi S, Muguerza Ba, et al. Inhibition of ulcerative colitis in mice after oral administration of a polyphenol-enriched cocoa extract is mediated by the inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation in colon cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59(12):6474-83.
- Beaucage G, Ulibarri TA, Black EP, Schaefer DW. Multiple size scale structures in silica-siloxane composites studied by small-angle scattering. hybrid organic-inorganic composites. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society; 1995. p. 97-111. (ACS Symposium Series. 585).
- Binic I, Lazarevic V, Ljubenovic M, Mojsa J, Sokolovic D. Skin ageing: natural weapons and strategies. J Evid-Based Complem Altern Med. 2013;2013:ID827248.
- Bogdan Allemann I, Baumann L. Antioxidants used in skin care formulations. Skin Ther Lett. 2008;13(7):5-9.
- Bruschi ML, Jones DS, Panzeri H, Gremião MPD, de Freitas O, Lara EHG. Semisolid systems containing propolis for the treatment of periodontal disease: in vitro release kinetics, syringeability, rheological, textural, and mucoadhesive properties. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(8):2074-89.
- Calatayud M, López-de-Dicastillo C, López-Carballo G, Vélez D, Hernández Muñoz P, Gavara R. Active films based on cocoa extract with antioxidant, antimicrobial and biological applications. Food Chem. 2013;139(1-4):51-8.
- Carvalho FC, Barbi MS, Sarmento VHV, Chiavacci LA, Netto FM, Gremião MPD. Surfactant systems for nasal zidovudine delivery: structural, rheological and mucoadhesive properties. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010b;62(4):430-9.
- Carvalho FC, Bruschi ML, Evangelista RC, Gremião MPD. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2010a;46(1):1-17.
- Carvalho FC, Calixto G, Hatakeyama IN, Luz GM, Gremião MPD, Chorilli M. Rheological, mechanical, and bioadhesive behavior of hydrogels to optimize skin delivery systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2012;39(11):1750-7.
- Carvalho FC, Campos ML, Peccinini RG, Gremião MPD. Nasal administration of liquid crystal precursor mucoadhesive vehicle as an alternative antiretroviral therapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;84(1):219-27.
- Chen Y, Ma P, Gui S. Cubic and hexagonal liquid crystals as drug delivery systems. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:ID815981.
- Chorilli M, Prestes PS, Rigon RB, Leonardi GR, Chiavacci LA, Sarmento VHV, et al. Structural characterization and in vivo evaluation of retinyl palmitate in non-ionic lamellar liquid crystalline system. Colloids Surf B. 2011;85(2):182-8.
- Datta HS, Mitra SK, Paramesh R, Patwardhan B. Theories and management of aging: modern and ayurveda perspectives. J Evid-Based Complem Altern Med. 2011;2011:ID528527.
- Devi VK, Jain N, Valli KS. Importance of novel drug delivery systems in herbal medicines. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010;4(7):27-31.
- Dupont E, Gomez J, Bilodeau D. Beyond UV radiation: a skin under challenge. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013;35(3):224-32.
- Elwers S, Zambrano A, Rohsius C, Lieberei R. Histological features of phenolic compounds in fine and bulk cocoa seed (Theobroma cacao L.). J Appl Bot Food Qual. 2010;83(2):182-8.
- Ganem-Quintanar A, Quintanar-Guerrero D, Buri P. Monoolein: a review of the pharmaceutical applications. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26(8):809-20.
- Garti N, Libster D, Aserin A. Solubilization and delivery of drugs from gmo-based lyotropic liquid crystals. In: Li Q, editor. Nanoscience with liquid crystals: from self-organized nanostructures to applications. London: Springer; 2014. p. 355-414.
- Gasser P, Lati E, Peno-Mazzarino L, Bouzoud D, Allegaert L, Bernaert H. Cocoa polyphenols and their influence on parameters involved in ex vivo skin restructuring. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2008;30(5):339-45.
- González N, Ribeiro D, Fernandes E, Nogueira DR, Conde E, Moure A, et al. Potential use of Cytisus scoparius extracts in topical applications for skin protection against oxidative damage. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013;125(0):83-9.
- Gonçalez ML, Correa MA, Chorilli M. Skin delivery of kojic acid-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. Biomed Res Int. 2013;(2013):1-9.
- Guo C, Wang J, Cao F, Lee RJ, Zhai G. Lyotropic liquid crystal systems in drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15(23-24):1032-40.
- Hatano T, Miyatake H, Natsume M, Osakabe N, Takizawa T, Ito H, et al. Proanthocyanidin glycosides and related polyphenols from cacao liquor and their antioxidant effects. Phytochemistry. 2002;59(7):749-58.
- Hurst WJ, Tarka SM, Powis TG, Valdez F, Hester TR. Archaeology: Cacao usage by the earliest Maya civilization. Nature. 2002;418(6895):289-90.
- Hyde ST, Andersson S, Ericsson B, Larsson K. A cubic structure consisting of a lipid bilayer forming an infinite periodic minimum surface of the gyroid type in the glycerolmonooleat-water system. Zeitschrift für Kristallogr. 1984;164(1):213-9.
- Isaac VLB, Cefali LC, Chiari BG, Almeida MGJ, Ribeiro HM, Corrêa MA. Effect of various thickening agents on the rheological properties of oil-in-water emulsions containing nonionic emulsifier. J Dispersion Sci Technol. 2012;34(6):880-5.
- Israelachvili J. The science and applications of emulsions: an overview. Colloids Surf. A. 1994;91:1-8.
- Katz DL, Doughty K, Ali A. Cocoa and chocolate in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signaling. 2011;15(10):2779-811.
- Kolenyak-Santos F, Garnero C, De Oliveira RN, de Souza ALR, Chorilli M, Allegretti SM, et al. Nanostructured lipid carriers as a strategy to improve the in vitro schistosomiasis activity of praziquantel. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(1):761-72.
- Lambers H, Piessens S, Bloem A, Pronk H, Finkel P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2006;28(5):359-70.
- Lawrence MJ, Rees GD. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000;45(1):89-121.
- Lee J, Young SA, Kellaway IW. Water quantitatively induces the mucoadhesion of liquid crystalline phases of glyceryl monooleate. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001;53(5):629-36.
- Malmsten M. Surfactants and polymers in drug delivery. New York: Infoma Healthcare; 2002. 348 p.
- Martini MH, Figueira A, Lenci CG, Tavares DdQ. Polyphenolic cells and their interrelation with cotyledon cells in seven species of Theobroma (Sterculiaceae). Braz J Bot. 2008a;31(3):425-31.
- Martini MH, Lenci CG, Figueira A, Tavares DdQ. Localization of the cotyledon reserves of Theobroma grandiflorum (Willd. ex Spreng.) K. Schum., T. subincanum Mart., T. bicolor Bonpl. and their analogies with T. cacao L. Braz J Bot. 2008b;31(1):147-54.
- Martins De Lima T, Cury-Boaventura MF, Giannocco G, Nunes MT, Curi R. Comparative toxicity of fatty acids on a macrophage cell line (J774). Clin Sci. 2006;111(5):307-17.
- McClements DJ. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter. 2012;8(6):1719-29.
- Mellor DD, Sathyapalan T, Kilpatrick ES, Beckett S, Atkin SL. High-cocoa polyphenol-rich chocolate improves HDL cholesterol in Type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetic Med. 2010;27(11):1318-21.
- Mezzenga R. Physics of self-assembly of lyotropic liquid crystals. In: Garti N, Somasundaran P, Mezzenga R, editors. Self-assembled supramolecular architectures: lyotropic liquid crystals. Hoboken: Wiley; 2012. p. 1-20.
- Monagas M, Khan N, Andres-Lacueva C, Casas R, Urpí-Sardà M, Llorach R, et al. Effect of cocoa powder on the modulation of inflammatory biomarkers in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(5):1144-50.
- Nielsen LS, Schubert L, Hansen J. Bioadhesive drug delivery systems: I. Characterisation of mucoadhesive properties of systems based on glyceryl mono-oleate and glyceryl monolinoleate. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1998;6(3):231-9.
- Niraula B, King TC, Misran M. Evaluation of rheology property of dodecyl maltoside, sucrose dodecanoate, Brij 35p and SDS stabilized O/W emulsion: effect of head group structure on rheology property and emulsion stability. Colloids Surf A. 2004;251(1-3):59-74.
- Oliveira MB, Prado AH, Bernegossi J, Sato CS, Lourenço-Brunetti I, Scarpa MV, et al. Topical application of retinyl palmitate-loaded nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of skin aging. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:ID63257.
- Oyafuso MH, Carvalho FC, Chiavacci LA, Gremião MPD, Chorilli M. Design and characterization of silicone and surfactant based systems for topical drug delivery. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(1):817-26.
- Parra JL, Paye M. EEMCO guidance for the in vivo assessment of skin surface pH. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2003;16(3):188-202.
- Peppas NA, Sahlin JJ. Hydrogels as mucoadhesive and bioadhesive materials: a review. Biomaterials. 1996;17(16):1553-61.
- Pillai S, Oresajo C, Hayward J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation- a review. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2005;27(1):17-34.
- Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S, Langer R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(2):115-24.
- Prestes PS, Chorilli M, Chiavacci LA, Scarpa MV, Leonardi GR. Physicochemical characterization and rheological behavior evaluation of the liquid crystalline mesophases developed with different silicones. J Dispersion Sci Technol. 2009;31(1):117-23.
- Reuter J, Merfort I, Schempp C. Botanicals in dermatology. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11(4):247-67.
- Ribeiro HM, Morais JA, Eccleston GM. Structure and rheology of semisolid o/w creams containing cetyl alcohol/non-ionic surfactant mixed emulsifier and different polymers. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2004;26(2):47-59.
- Romsted LS. Introduction to self-assembly. In: Steed JW, Gale PA, editors. Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. p. 181-204.
- Saija A, Tomaino A, Trombetta D, Giacchi M, De Pasquale A, Bonina F. Influence of different penetration enhancers on in vitro skin permeation and in vivo photoprotective effect of flavonoids. Int J Pharm. 1998;175(1):85-94.
- Sánchez-Rabaneda F, Jáuregui O, Casals I, Andrés-Lacueva C, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Lamuela-Raventós RM. Liquid chromatographic/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric study of the phenolic composition of cocoa (Theobroma cacao). J Mass Spectrom. 2003;38(1):35-42.
- Schinella G, Mosca S, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Pasamar MÁ, Muguerza B, Ramón D, et al. Antioxidant properties of polyphenol-rich cocoa products industrially processed. Food Res Int. 2010;43(6):1614-23.
- Shah JC, Sadhale Y, Chilukuri DM. Cubic phase gels as drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(2-3):229-50.
- Silva AR, Menezes PFC, Martinello T, Novakovich GFL, Praes CEO, Feferman IHS. Antioxidant kinetics of plant-derived substances and extracts. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2010;32(1):73-80.
- Singleton VL, Rossi JA. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic. 1965;16(3):144-58.
- Slomkowski S, Aleman JV, Gilbert RG, Hess M, Horie K, Jones RG, et al. Terminology of polymers and polymerization processes in dispersed systems (IUPAC Recommendations 2011). Pure Appl Chem. 2011;83(12):2229-59.
- Smart JD. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57(11):1556-68.
- Souza C, Watanabe E, Borgheti-Cardoso LN, De Fantini MCA, Lara MG. Mucoadhesive system formed by liquid crystals for buccal administration of poly(hexamethylene biguanide) hydrochloride. J Pharm Sci. 2014;103(12):3914-23.
- Summerlin N, Soo E, Thakur S, Qu Z, Jambhrunkar S, Popat A. Resveratrol nanoformulations: Challenges and opportunities. Int J Pharma. 2015;479(2):282-90.
- Tamburic S, Craig DQM. A comparison of different in vitro methods for measuring mucoadhesive performance. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1997;44(2):159-67.
- Thomas BJ, Finnin BC. The transdermal revolution. Drug Discov Today. 2004;9(16):697-703.
- Tomas-Barberán FA, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, Marín A, Muguerza B, Gil-Izquierdo A, Cerdá B, et al. A new process to develop a cocoa powder with higher flavonoid monomer content and enhanced bioavailability in healthy humans. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(10):3926-35.
- Vinardell MP, Mitjans M. Nanocarriers for delivery of antioxidants on the skin. Cosmetics. 2015;2(4):342-254.
- Visscher MO, Pan BS, Kitzmiller WJ. Photodamage: treatments and topicals for facial skin. Facial Plastic Surg Clin of North Am. 2013;21(1):61-75.
- Williams S, Tamburic S, Lally C. Eating chocolate can significantly protect the skin from UV light. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(3):169-73.
- Yariv D, Efrat R, Libster D, Aserin A, Garti N. In vitro permeation of diclofenac salts from lyotropic liquid crystalline systems. Colloids Surf B 2010;78(2):185-92.
- Zhang W, Liu L. Study on the formation and properties of liquid crystal emulsion in cosmetic. J Cosmet Dermatol Sci Appl. 2013;3(2):139-144.
- Zhu Z, Zhai Y, Zhang N, Leng D, Ding P. The development of polycarbophil as a bioadhesive material in pharmacy. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2013;8(4):218-27.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
2017
History
-
Received
05 Nov 2015 -
Accepted
10 Oct 2016