ABSTRACT
Background:
The pyogenic liver abscess has an incidence of 1.1/1,000 habitants. Mortality can reach 100%. The use of less invasive procedures diminish morbidity and hospital stay.
Aim:
Identify risk factors in patients who underwent percutaneous drainage guided by ultrasound as treatment.
Method:
Were analyzed 10 patients submitted to the method. Epidemiological characteristics, laboratory markers and imaging exams (ultrasound and CT) were evaluated.
Results:
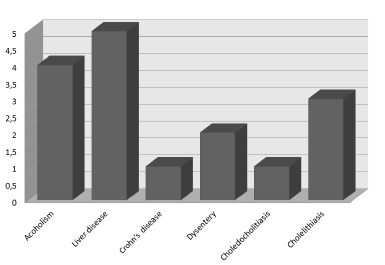
The majority of the patients were men with mean age of 50 years old. Liver disease, alcoholism and biliary tract disease were the most common prodromes. Abdominal pain (90%), fever (70%) and jaundice (40%) were the most common clinical manifestations. Mortality of 20% was observed in this series. Hypoalbuminemia and days of hospitalization had a statistically significant positive association with death.
Conclusion:
The pyogenic liver abscess has subacute evolution which makes the diagnosis difficult. Image exams have high sensitivity in diagnosis, particularly computed tomography. Percutaneous drainage associated with antibiotic therapy is safe and effective therapeutic resource.
HEADINGS:
Pyogenic liver abscess. Drainage. Ultrasonography; interventional. Hypoalbuminemia.